The Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children is a protocol to the United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime. It is one of the three Palermo protocols, the others being the Protocol Against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air and the Protocol Against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms.

Sex trafficking is human trafficking for the purpose of sexual exploitation. Perpetrators of the crime are called sex traffickers or pimps—people who manipulate victims to engage in various forms of commercial sex with paying customers. Sex traffickers use force, fraud, and coercion as they recruit, transport, and provide their victims as prostitutes. Sometimes victims are brought into a situation of dependency on their trafficker(s), financially or emotionally. Every aspect of sex trafficking is considered a crime, from acquisition to transportation and exploitation of victims. This includes any sexual exploitation of adults or minors, including child sex tourism (CST) and domestic minor sex trafficking (DMST). It has been called a form of modern slavery because of the way victims are forced into sexual acts non-consensually, in a form of sexual slavery.
Human rights in Romania are generally respected by the government. However, there have been concerns regarding allegations of police brutality, mistreatment of the Romani minority, government corruption, poor prison conditions, and compromised judicial independence. Romania was ranked 59th out of 167 countries in the 2015 Democracy Index and is described as a "flawed democracy", similar to other countries in Central or Eastern Europe.

Human rights are largely respected in Switzerland, one of Europe's oldest democracies. Switzerland is often at or near the top in international rankings of civil liberties and political rights observance. Switzerland places human rights at the core of the nation's value system, as represented in its Federal Constitution. As described in its FDFA's Foreign Policy Strategy 2016-2019, the promotion of peace, mutual respect, equality and non-discrimination are central to the country's foreign relations.

Human trafficking is the act of recruiting, transporting, transferring, harboring, or receiving individuals through force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of exploitation. This exploitation may include forced labor, sexual slavery, or other forms of commercial sexual exploitation. It is considered a serious violation of human rights and a form of modern slavery. Efforts to combat human trafficking involve international laws, national policies, and non-governmental organizations.
Latvia ratified the 2000 UN TIP Protocol in May 2004.
In 2008 Luxembourg was a destination country for women trafficked transnationally for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation. During the reporting period, women were trafficked from Bulgaria and Ukraine. According to the Luxembourg Red Cross, an increasing number of women from Africa and Latin America were engaged in prostitution in the country, and could be victims of trafficking.
Human trafficking in Canada is prohibited by law, and is considered a criminal offence whether it occurs entirely within Canada or involves the "transporting of persons across Canadian borders. Public Safety Canada (PSC) defines human trafficking as "the recruitment, transportation, harbouring and/or exercising control, direction or influence over the movements of a person in order to exploit that person, typically through sexual exploitation or forced labour. It is often described as a modern form of slavery."
The United Nations Global Initiative to Fight Human Trafficking (UN.GIFT) is a multi-stakeholder initiative providing global access to expertise, knowledge and innovative partnerships to combat human trafficking.
The Netherlands ratified the 2000 UN TIP Protocol in July 2005.
Egypt ratified the 2000 UN TIP Protocol in March 2004.

Finland is a transit, destination, and a limited source country for women, men and girls subjected to forced marriage, forced labor and sex trafficking. Finnish legislation condemns trafficking as a crime and has met the standards of the EU Protocol even before the convention came into effect. NGOs and the government cooperate in providing help for the victims of trafficking in Finland. Although the Finnish Police investigated and referred more people to care in 2013, prosecution and conviction numbers of suspected offenders remain low relative to the number of potential victims. The government is currently working on improving the anti-trafficking laws and practices to improve the situation.
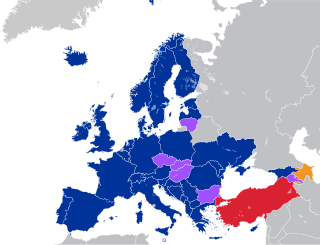
The Council of Europe Convention on Preventing and Combating Violence Against Women and Domestic Violence, better known as the Istanbul Convention, is a human rights treaty of the Council of Europe opposing violence against women and domestic violence which was opened for signature on 11 May 2011, in Istanbul, Turkey. The convention aims at prevention of violence, victim protection and to end the impunity of perpetrators.

The Blue Heart Campaign is an international anti-trafficking program started by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). Established in 1997, the UNODC supported countries in implementing three UN drug protocols. In 2000, after the UN General Assembly adopted the Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, the UNODC became the “guardian” of that protocol and assumed the functions of fighting against human trafficking. The Blue Heart Campaign was launched in March 2009 by the Executive Director of the UNODC, Antonio Maria Costa, during his address to the World's Women's Conference meeting in Vienna. The campaign's symbol is a blue heart. The Blue Heart Campaign uses its website, as well as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Flickr to communicate goals, objectives, and news with the public.

Maria Grazia Giammarinaro is an Italian judge and policy-maker.
Violence against women is an entrenched social problem in Ukrainian culture engendered by traditional male and female stereotypes. It was not recognized during Soviet era, but in recent decades the issue became an important topic of discussion in Ukrainian society and among academic scholars.

The Group of Experts on Action against Trafficking in Human Beings, more commonly known as GRETA, is the monitoring mechanism on human trafficking established by the Council of Europe Convention on Action against Trafficking in Human Beings in Article 36. It stipulates that GRETA can have from 10 to 15 members of independent and impartial experts from a variety of backgrounds. They have been chosen from amongst nationals of the States Parties to the Convention and are known for their competence and professional experience in the areas covered by the Convention; the term of office is four years, renewable once. The current composition of GRETA reflects a gender and geographical balance.

The Inter-American Convention on the Prevention, Punishment, and Eradication of Violence against Women, better known as the Belém do Pará Convention, is an international human rights instrument adopted by the Inter-American Commission of Women (CIM) of the Organization of American States (OAS) at a conference held in Belém do Pará, Brazil, on 9 June 1994. It is the first legally binding international treaty that criminalises all forms of violence against women, especially sexual violence. On 26 October 2004, the Follow-Up Mechanism (MESECVI) agency was established to ensure the State parties' compliance with the Convention.

Violence against women in Belarus is a significant issue in Belarusian society. Belarus is ranked 29th on the Gender Inequality Index and 36th on the Global Gender Gap Index. Despite this, the government of Belarus has been criticised by the United Nations and human rights activists for its active role in suppressing women's rights and perpetuating violence against women.









