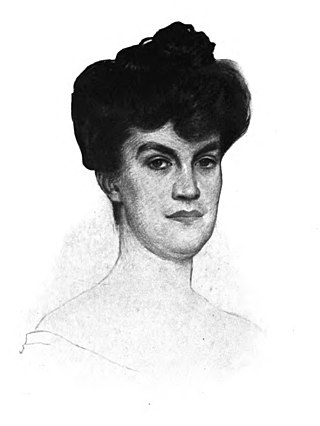Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe was an American author and abolitionist. She came from the religious Beecher family and wrote the popular novel Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852), which depicts the harsh conditions experienced by enslaved African Americans. The book reached an audience of millions as a novel and play, and became influential in the United States and in Great Britain, energizing anti-slavery forces in the American North, while provoking widespread anger in the South. Stowe wrote 30 books, including novels, three travel memoirs, and collections of articles and letters. She was influential both for her writings as well as for her public stances and debates on social issues of the day.

Ray Stannard Baker was an American journalist, historian, biographer, and writer.
Physical Review is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, Physical Review Letters, which publishes shorter articles of broader interest.

Thomas Joseph Mooney was an American political activist and labor leader, who was convicted with Warren K. Billings of the San Francisco Preparedness Day Bombing of 1916. It quickly became apparent that Mooney and Billings had been convicted based on falsified evidence and perjured testimony; and the Mooney case and campaigns to free him became an international cause célèbre for two decades, with a substantial number of publications demonstrating the falsity of the conviction. These publications and the facts of the case are surveyed in Richard H. Frost, The Mooney Case. Mooney served 22 years in prison before finally being pardoned in 1939.

The London Magazine is the title of six different publications that have appeared in succession since 1732. All six have focused on the arts, literature and poetry. A number of Nobel Laureates, including Annie Ernaux, Albert Camus, Doris Lessing, and Nadine Gordimer have been published in its pages. It is England's oldest literary journal.
The Mother of Fraternities usually refers to Union College or Miami University, both of which founded many early collegiate fraternities.

Charles Edward Russell was an American journalist, opinion columnist, newspaper editor, and political activist. The author of a number of books of biography and social commentary, he won the 1928 Pulitzer Prize for Biography or Autobiography for The American Orchestra and Theodore Thomas.

Art in America is an illustrated quarterly, international magazine concentrating on the contemporary art world in the United States, including profiles of artists and genres, updates about art movements, show reviews and event schedules. It is designed for collectors, artists, art dealers, art professionals and other readers interested in the art world. It has an active website, ArtinAmericaMagazine.com.

Stephen Smith was a New York City surgeon and civic leader who made important contributions to medical education, nursing education, public health, housing improvement, mental health reform, charity oversight, and urban environmentalism. Smith maintained an active medical practice, was an attending physician at Bellevue Hospital for thirty-seven years, and authored three surgical texts, but he was best known for his public service. Three mayors, seven governors, and two U.S. presidents appointed Smith to almost fifty years of public responsibilities. Shortly before Smith’s death in 1922, Columbia University President and future Nobel Peace Prize winner Nicholas Murray Butler awarded him the school’s highest honor and pronounced Smith, “the most interesting figure in American medicine and in American public service today.” The New York Academy of Medicine initiated the annual Stephen Smith Medal for lifetime achievement in public health in 2005.

William Stanley Beaumont Braithwaite was an African-American writer, poet, literary critic, anthologist, and publisher in the United States. His work as a critic and anthologist was widely praised and important in the development of East Coast poetry styles in the early 20th century. He was awarded the Spingarn Medal in 1918.

John Lawson Stoddard was an American lecturer, author and photographer. He was a pioneer in the use of the stereopticon or magic lantern, adding photographs to his popular lectures about his travels around the world. Because he published books related to his travels, he is credited with developing the genre of travelogues.

Scribner's Monthly: An Illustrated Magazine for the People was an illustrated American literary periodical published from 1870 until 1881. Following a change in ownership in 1881 of the company that had produced it, the magazine was relaunched as The Century Magazine.
The Magazine of American History was established in January 1877 by Martha Joanna Lamb, Nathan Gillett Pond and John Austin Stevens with the long title The Magazine of American History with Notes and Queries. It was issued monthly. The first seven volumes were published by the A. S. Barnes Company of New York and Chicago, volumes 8 through 28 by the Historical Publication Co., and, after Mrs. Lamb's death, the final two volumes of the initial series by the Magazine of American History Company. It lasted into its 30th volume; the last of the three numbers in that volume was issued in September 1893. In addition to scholarly articles, and answers to readers' queries it also included original documents such as the letters of George Washington, and diary extracts from various Revolutionary War figures.
Francis Hallett Johnson was an American career diplomat and ambassador to Costa Rica. He served in the United States Foreign Service for 36 years.

Charles Howard Shinn (1852–1924) was a horticulturalist, author, inspector of California Experiment Stations, and forest ranger in California.

Marjorie Benton Cooke was an American monologist, playwright, and novelist. A specialist in comic dramatic sketches and light romantic fiction, she also wrote and performed monologues on suffragist issues.
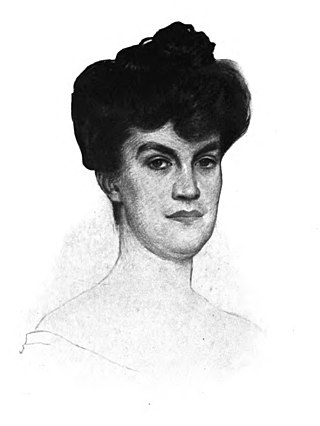
Bessie Van Vorst, also known as Mrs. John Van Vorst, was an American author and journalist. She is best known as a co-author of the magazine series and the book The Woman Who Toils: Being the Experiences of Two Ladies as Factory Girls (1903) with a preface by US President Theodore Roosevelt, an influential example of social investigation. Her study of women and child labor in the mills of Alabama and New Hampshire helped stir reform sentiment.
Francis Griswold Landon was an American soldier and politician from New York.

Henry Middlebrook Crane was an American engineer and pioneer in the automobile industry. He was the president of Crane Motor Car Company, vice president of engineering for the Simplex Automobile Company, and designed the Pontiac Six motor for General Motors.
Jessie Gillespie Willing was an American illustrator during the Golden Age of illustration. She was considered the foremost silhouette illustrator of her time, although she did traditional illustration as well. Willing illustrated for books and magazines including Life, The Ladies' Home Journal, Woman's Home Companion, Mother and Child, McClure's Magazine, Childhood Education, the Sunday Magazine, Association Men, Farm and Fireside, Every Week, Children: The Magazine for Parents, and the American Magazine. She is perhaps most well known for her work for the Girl Scouts.