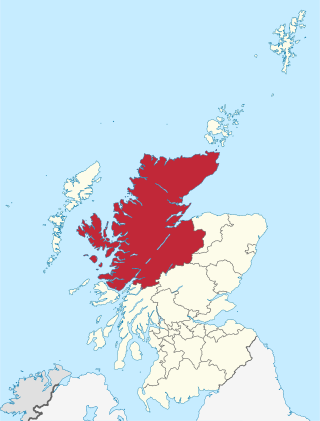
Highland is a council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the 2011 census. It shares borders with the council areas of Aberdeenshire, Argyll and Bute, Moray and Perth and Kinross. Their councils, and those of Angus and Stirling, also have areas of the Scottish Highlands within their administrative boundaries.

Cromarty is a town, civil parish and former royal burgh in Ross and Cromarty, in the Highland area of Scotland. Situated at the tip of the Black Isle on the southern shore of the mouth of Cromarty Firth, it is 5 miles (8 km) seaward from Invergordon on the opposite coast. In the 2001 census, it had a population of 719.

Dingwall is a town and a royal burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,491. It was an east-coast harbour that now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest castle north of Stirling. On the town's present-day outskirts lies Tulloch Castle, parts of which may date back to the 12th century. In 1411 the Battle of Dingwall is said to have taken place between the Clan Mackay and the Clan Donald.
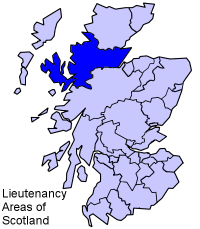
Ross and Cromarty, also referred to as Ross-shire and Cromartyshire, is a variously defined area in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. There is a registration county and a lieutenancy area in current use, the latter of which is 8,019 square kilometres in extent. Historically there has also been a constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, a local government county, a district of the Highland local government region and a management area of the Highland Council. The local government county is now divided between two local government areas: the Highland area and Na h-Eileanan Siar. Ross and Cromarty border Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south.

Greenlaw Town Hall is a municipal building in The Square, Greenlaw, Scottish Borders, Scotland. The structure, which served as the county headquarters of Berwickshire in the 19th century, is a Category A listed building.

Perth Sheriff Court is an historic building on Tay Street in Perth, Perth and Kinross, Scotland. The structure, which is used as the main courthouse for the area, is a Category A listed building.

Dingwall Town Hall is a municipal structure in the High Street, Dingwall, Highland, Scotland. The structure, which is now used as a museum, is a Category B listed building.

County Buildings is a municipal structure in the High Street in Kinross, Perth and Kinross, Scotland. The structure, which accommodates the local area offices for Perth and Kinross Council, is a Category B listed building.

Tain Tolbooth is a municipal building in the High Street, Tain, Highland, Scotland. The structure, which is used as a courthouse, is a Category A listed building.

Newburgh Town House is a municipal building in the High Street in Newburgh, Fife, Scotland. The structure, which is used as a series of artists' studios, is a Category B listed building.

Invergordon Town Hall is a municipal building in the High Street in Invergordon in the Highland area of Scotland. The structure, which is used as a community events venue, is a Category B listed building.

Cromarty Courthouse, formerly Cromarty Town House, is a municipal building in Church Street, Cromarty, in the Highland area of Scotland. The structure, which is used as a museum, is a Category A listed building.

Banff Sheriff Court is a judicial structure in Low Street, Banff, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The structure, which was the headquarters of Banffshire County Council and was also used as a courthouse, is a Category B listed building.

Elgin Sheriff Court is a municipal structure in the High Street, Elgin, Moray, Scotland. The structure, which was the headquarters of Morayshire County Council and remains in use as a courthouse, is a Category B listed building.

Kirkwall Sheriff Court is a judicial structure in Watergate, Kirkwall, Orkney, Scotland. The structure, which was the headquarters of Orkney County Council and is currently used as a courthouse, is a Category C listed building.

Dingwall Sheriff Court is a former judicial structure in the High Street, Dingwall, Highland, Scotland. The complex, which was used as the headquarters of Ross and Cromarty County Council as well as the local courthouse before being converted for residential use in 2015, is a Category B listed building.

County Buildings is a municipal structure in Newtown Street, Duns, Scottish Borders, Scotland. The complex, which was the headquarters of Berwickshire County Council and was also used as a courthouse, is a Category C listed building.

The Highland Council Headquarters, formerly County Buildings, is a municipal structure in Glenurquhart Road, Inverness, Highland, Scotland. The oldest part of the complex, which currently serves as the headquarters of The Highland Council, is a Category C listed building.

Wick Sheriff Court is a judicial structure in Bridge Street, Wick, Caithness, Scotland. The structure, which remains in use as a courthouse, is a Category B listed building.

Stonehaven Sheriff Court, formerly known as County Buildings, is a judicial structure in Dunnottar Avenue, Stonehaven, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The structure, which was used as the headquarters of Kincardineshire County Council as well as a courthouse, is a Category B listed building.





















