Related Research Articles

The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) was a voluntary government work relief program that ran from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men ages 18–25 and eventually expanded to ages 17–28. The CCC was a major part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal that supplied manual labor jobs related to the conservation and development of natural resources in rural lands owned by federal, state, and local governments. The CCC was designed to supply jobs for young men and to relieve families who had difficulty finding jobs during the Great Depression in the United States

The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States launched by Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964–65. The term was first coined during a 1964 commencement address by President Lyndon B. Johnson at the University of Michigan and came to represent his domestic agenda. The main goal was the total elimination of poverty and racial injustice.

The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the Secretary of Agriculture, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Tom Vilsack, who has served since February 24, 2021.

Richard Norman Hastings is an American politician and member of the Republican Party who served as the U.S. representative for Washington's 4th congressional district from 1995 until his retirement in 2015. The district includes much of central Washington including the Tri-Cities, Yakima, and Moses Lake. The most conservative Republican in Washington's Congressional delegation, he chaired the House Committee on Ethics from 2005 to 2007 and chaired the House Committee on Natural Resources from 2011 to his leaving office.
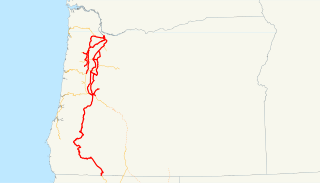
The Oregon and California Railroad was formed from the Oregon Central Railroad when it was the first to operate a 20-mile (32 km) stretch south of Portland in 1869. This qualified the railroad for land grants in California, whereupon the name of the railroad soon changed to Oregon & California Rail Road Company. In 1887, the line was completed over Siskiyou Summit, and the Southern Pacific Railroad assumed control of the railroad, although it was not officially sold to Southern Pacific until January 3, 1927. This route was eventually spun off from the Southern Pacific as the Central Oregon and Pacific Railroad.

Douglas Carmichael "Mike" McIntyre II is an American attorney and politician who was first elected to represent North Carolina's 7th congressional district in the U.S. House of Representatives in 1996. He served for 18 years from 1997 to 2015. McIntyre is a Democrat and, during his tenure in the House of Representatives, was a member of the Blue Dog Coalition.

The Indian Health Service (IHS) is an operating division (OPDIV) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). IHS is responsible for providing direct medical and public health services to members of federally-recognized Native American Tribes and Alaska Native people. IHS is the principal federal health care provider and health advocate for Indian people.

Packwood is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) located in easternmost Lewis County, Washington, in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the CDP had a population of 319, while the town and surrounding Packwood community had a total population of 1,277.

The Lower Brulé Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation that belongs to the Lower Brulé Lakota Tribe. It is located on the west bank of the Missouri River in Lyman and Stanley counties in central South Dakota in the United States. It is adjacent to the Crow Creek Indian Reservation on the east bank of the river. The Kul Wicasa Oyate, the Lower Brulé Sioux, are members of the Sicangu, one of the bands of the Lakota Tribe. Tribal headquarters is in Lower Brule.

The Food, Conservation, and Energy Act of 2008 was a $288 billion, five-year agricultural policy bill that was passed into law by the United States Congress on June 18, 2008. The bill was a continuation of the 2002 Farm Bill. It continues the United States' long history of agricultural subsidies as well as pursuing areas such as energy, conservation, nutrition, and rural development. Some specific initiatives in the bill include increases in Food Stamp benefits, increased support for the production of cellulosic ethanol, and money for the research of pests, diseases and other agricultural problems.

Land use in Oregon concerns the evolving set of laws affecting land ownership and its restrictions in the U.S. state of Oregon.
Native American self-determination refers to the social movements, legislation and beliefs by which the Native American tribes in the United States exercise self-governance and decision making on issues that affect their own people.
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is a staff division of the Office of the Secretary, within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. ONC leads national health IT efforts, charged as the principal federal entity to coordinate nationwide efforts to implement and use the most advanced health information technology and the electronic exchange of health information.
The Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act of 2000 was a bill passed into law by the United States Congress on October 30, 2000. The law amended the United States Forest Service's county payments program for FY2001-FY2006 to allow states or counties to choose to receive the average of the three highest payments for FY1986-FY1999 in lieu of the regular 25% payment, but requiring that 15–20% of those payments be used by the counties for specified purposes, in accordance with recommendations of resource advisory committees for projects on federal lands, or returned to the Treasury.
The Coos Bay Wagon Road Lands is land managed by the United States Bureau of Land Management. The land was originally granted to the Oregon & California Railroad to create a road between Coos Bay, Oregon and Roseburg, Oregon. The land was reconveyed to the United States in 1937.
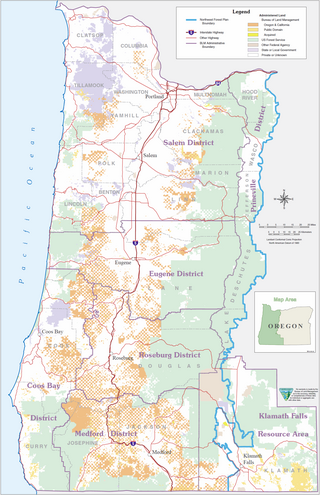
The Oregon and California Railroad Revested Lands, are approximately 2,600,000 acres (1,100,000 ha) of land located in eighteen counties of western Oregon. Originally granted to the Oregon & California Railroad to build a railroad between Portland, Oregon and San Francisco, California, the land was reconveyed to the United States government by act of Congress in 1916 and is currently managed by the United States Bureau of Land Management.
Salazar v. Ramah Navajo Chapter, 567 U.S. 182 (2012), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that the United States government, when it enters into a contract with a Native American Indian tribe for services, must pay contracts in full, even if Congress has not appropriated enough money to pay all tribal contractors. The case was litigated over a period of 22 years, beginning in 1990, until it was decided in 2012.

The Restoring Healthy Forests for Healthy Communities Act is a bill that was introduced in the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. The Restoring Healthy Forests for Healthy Communities Act would direct the United States Department of Agriculture to establish at least one Forest Reserve Revenue Area within each unit of the National Forest System designated for sustainable forest management for the production of national forest materials and forest reserve revenues. The bill then states that the purpose of an Area is to provide a dependable source of 25% payments and economic activity for each beneficiary county containing System land that was eligible to receive payments through its state under the Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act of 2000.
African-American self-determination refers to efforts to secure self-determination for African-Americans and related peoples in North America. It often intersects with the historic Back-to-Africa movement and general Black separatism, but also manifests in present and historic demands for self-determination on North American soil, ranging from autonomy to independence. The freedom to make whatever choices as a free American, and willfulness to do for self are often a key demand for advocates of African-American self-determination.
References
- ↑ "Secure Rural Schools - Payments". US Forest Service. 2016-12-01. Retrieved 2016-12-01.
- ↑ "County Payments" . Retrieved 2016-12-01.
- ↑ "The Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination". crsreports.congress.gov.
 This article incorporates public domain material from Jasper Womach. Report for Congress: Agriculture: A Glossary of Terms, Programs, and Laws, 2005 Edition (PDF). Congressional Research Service.
This article incorporates public domain material from Jasper Womach. Report for Congress: Agriculture: A Glossary of Terms, Programs, and Laws, 2005 Edition (PDF). Congressional Research Service.