
The Batavian Republic was the successor state to the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 and ended on 5 June 1806, with the accession of Louis Bonaparte to the Dutch throne. From October 1801 onward, it was known as the Batavian Commonwealth. Both names refer to the Germanic tribe of the Batavi, representing both the Dutch ancestry and their ancient quest for liberty in their nationalistic lore.

The United Provinces of the Netherlands, officially the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands, and commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands, and the first independent Dutch state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against Spanish rule, forming a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 and declaring their independence in 1581. It comprised Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland and Zeeland.
The Union of Utrecht was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain.

The coat of arms of the Kingdom of the Netherlands was originally adopted in 1815 and later modified in 1907. The arms are a composite of the arms of the former Dutch Republic and the arms of the House of Nassau, it features a checkered shield with a lion grasping a sword in one hand and a bundle of arrows in the other and is the heraldic symbol of the monarch and the country. The monarch uses a version of the arms with a mantle while the government of the Netherlands uses a smaller version without the mantle (cloak) or the pavilion, sometimes only the shield and crown are used. The components of the coats of arms were regulated by Queen Wilhelmina in a royal decree of 10 July 1907, affirmed by Queen Juliana in a royal decree of 23 April 1980.

The States of Holland and West Frisia were the representation of the two Estates (standen) to the court of the Count of Holland. After the United Provinces were formed — and there no longer was a count, but only his "lieutenant" — they continued to function as the government of the County of Holland.
The grand pensionary was the most important Dutch official during the time of the Dutch Republic. In theory, a grand pensionary was merely a civil servant of the Estates of the dominant province, the County of Holland, among the Seven United Provinces. In practice, the grand pensionary of Holland was the political leader of the entire Dutch Republic when there was no stadtholder at the centre of power.

Rutger Jan, Count Schimmelpenninck, Lord of Nyenhuis, Peckedam and Gellicum, was a Dutch jurist, ambassador and politician who served as Grand Pensionary of the Batavian Republic from 1805 to 1806. Historian Niek Sas called him the first Dutch liberal politician.
Landdrost was the title of various officials with local jurisdiction in the Netherlands and a number of former territories in the Dutch Empire. The term is a Dutch compound, with land meaning "region" and drost, from Middle Dutch drossāte which originally referred to a lord’s chief retainer, equivalent to:

The Batavian Revolution was a time of political, social and cultural turmoil at the end of the 18th century that marked the end of the Dutch Republic and saw the proclamation of the Batavian Republic.

In the Vlieter incident on 30 August 1799, a squadron of the Batavian Navy, commanded by Rear-Admiral Samuel Story, surrendered to the British navy. The incident occurred during the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland. It occurred in the tidal trench between Texel and the mainland that was known as De Vlieter, near Wieringen.
A referendum on the constitution of the Batavian Republic was held on August 8, 1797. The draft constitution was rejected, eventually culminating in a coup d'état.

Pieter Philips Jurriaan Quint Ondaatje was an illustrious Dutch patriot and influential revolutionary politician at the end of the 18th century. Ondaatje is regarded as a pioneer of Dutch democracy. When Utrecht was besieged by States army troops he allied himself with Rhinegrave von Salm, entrusted with the defence Holland and Utrecht. At the end of 1787 he lived as refugee in Brussels and French Flanders. From 1795 he served the Batavian Republic and in 1806 the Kingdom of Holland. Up to the Hundred Days he worked in Paris.

Jacob Abraham Uitenhage de Mist was a Dutch statesman. He was the Head of State of the National Assembly of the Batavian Republic from 17 April 1797 – 1 May 1797, and Commissioner-General of the Cape Colony during the Interregnum from 21 February 1803 – 25 September 1804, in accordance with the short-lived Treaty of Amiens. The Cape Colony had been under Dutch control from 1652.
Nassau-Orange-Fulda was a short-lived principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1803 to 1806. It was created for William Frederick, the son and heir of William V, Prince of Orange, the ousted stadtholder of the abolished Dutch Republic after the Batavian Revolution of 1795.

Pieter baron Melvill van Carnbee was a Dutch naval officer from a military family of Scottish descent, who rose to the rank of vice admiral. His name was sometimes spelled Melville van Carnbée. His grandson Pieter Melvill van Carnbee (1816-1856) was a notable geographer.

The Dutch Republic Lion was the badge of the Union of Utrecht, the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands, and a precursor of the current coat of arms of the Kingdom the Netherlands.
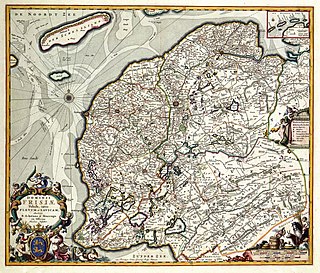
The Lordship of Frisia or Lordship of Friesland was a feudal dominion in the Netherlands. It was formed in 1498 by King Maximilian I and reformed in 1524 when Emperor Charles V conquered Frisia.

The Lordship of Overijssel or Overissel is a former division of the Netherlands named for its position along the river Issel.

The Lordship of Utrecht was formed in 1528 when Charles V of Habsburg conquered the Bishopric of Utrecht, during the Guelders Wars.

The Hof van Holland, Zeeland en West-Friesland was the High Court of the provinces of Holland, West Friesland and Zeeland, instituted as a separate entity of the government of the Counties of Holland and Zeeland in 1428, under the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands, and continued with little change under the Dutch Republic, Batavian Republic, and the Kingdom of Holland, until its dissolution in 1811 by the First French Empire. It should not be confused with the Hoge Raad van Holland en Zeeland which was the supreme court, founded in 1582 by the States-General of the Netherlands and intended for the entire Dutch Republic. The Hof was in practice the main Appellate court in Holland and Zeeland, and in number of cases-handled the most important in the entire Dutch Republic and its Precedents played an important role in the development of Roman-Dutch law, which is still influential in Southern Africa.















