
Edinburgh Castle is a historic castle in Edinburgh, Scotland. It stands on Castle Rock, which has been occupied by humans since at least the Iron Age. There has been a royal castle on the rock since at least the reign of Malcolm III in the 11th century, and the castle continued to be a royal residence until 1633. From the 15th century, the castle's residential role declined, and by the 17th century it was principally used as a military garrison. Its importance as a part of Scotland's national heritage was recognised increasingly from the early 19th century onwards, and various restoration programmes have been carried out over the past century and a half.

Stirling Castle, located in Stirling, is one of the largest and most historically and architecturally important castles in Scotland. The castle sits atop an intrusive crag, which forms part of the Stirling Sill geological formation. It is surrounded on three sides by steep cliffs, giving it a strong defensive position. Its strategic location, guarding what was, until the 1890s, the farthest downstream crossing of the River Forth, has made it an important fortification in the region from the earliest times.

Castle Menzies in Scotland is the ancestral seat of the Clan Menzies and the Menzies Baronets. It is located a little to the west of the small village of Weem, near Aberfeldy in the Highlands of Perthshire, close to the former site of Weem Castle, destroyed c. 1502.

Methven Castle is a privately owned 17th-century house situated east of Methven, in Perth and Kinross, Scotland.

Craigmillar Castle is a ruined medieval castle in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is three miles (4.8 km) south-east of the city centre, on a low hill to the south of the modern suburb of Craigmillar. The Preston family of Craigmillar, the local feudal barons, began building the castle in the late 14th century and building works continued through the 15th and 16th centuries. In 1660, the castle was sold to Sir John Gilmour, Lord President of the Court of Session, who breathed new life into the ageing castle. The Gilmours left Craigmillar in the 18th century for a more modern residence, nearby Inch House, and the castle fell into ruin. It is now in the care of Historic Environment Scotland as a scheduled monument, and is open to the public.

Duns Castle, Duns, Berwickshire is a historic house in Scotland, the oldest part of which, the massive Norman Keep or Pele Tower, supposedly dates from 1320. The castle and most of the structures on the property are designated as a scheduled ancient monument.

The Canongate is a street and associated district in central Edinburgh, the capital city of Scotland. The street forms the main eastern length of the Royal Mile while the district is the main eastern section of Edinburgh's Old Town.

Clan MacDowall or MacDouall is a Lowlands Scottish clan.
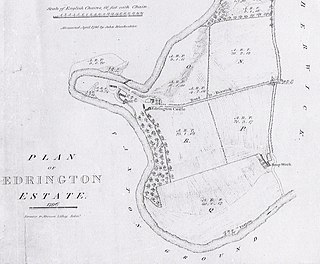
Edrington is a medieval estate occupying the lower part of Mordington parish in Berwickshire, Scotland, five miles (8.0 km) west of Berwick-upon-Tweed. From probably the 14th century, if not earlier, a castle occupied the steep hill above the mill of the same name on the Whiteadder Water. The castle ruin is still marked on today's Ordnance Survey maps, and still appears in locality references in The Berwickshire News. The principal farm of the estate is Edrington Mains.
Nunraw is an estate in East Lothian, Scotland. It includes the White Castle, a hillfort, situated on the edge of the Lammermuir Hills, two miles south of the village of Garvald, Nunraw House was formerly used as the Guesthouse for retreatants at Sancta Maria Abbey the Cistercian monastery on the hillside nearby. Sir James Balfour Paul, Lord Lyon King of Arms, writing in 1905 stated that Whitecastle and Nunraw are the same place and that the lairds there were often referred to by one or the other of these territorial designations.

Prudhoe Castle is a ruined medieval English castle situated on the south bank of the River Tyne at Prudhoe, Northumberland, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and a Grade I listed building.

Achanduin Castle,, is a castle, now in ruins, located about 5.0 kilometres (3.1 mi) west of Achnacroish on the north-western coastline of the island of Lismore, in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The castle overlooks Loch Linnhe and Bernera Island. The ruins are thought to date back to the thirteenth century. Achanduin Castle had long been thought to have been built by the Bishop of Argyll, though recent research has proved this to be unlikely. The castle was likely built by the MacDougalls around 1290 who held it throughout the fourteenth century. The castle was also thought to have been held by the Bishops of Argyll until the mid sixteenth century. It is a scheduled ancient monument.

Rosyth Castle is a fifteenth-century ruined tower house on the perimeter of Rosyth Naval Dockyard, Fife, Scotland.

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century, the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music, science and politics.

Estate houses in Scotland or Scottish country houses, are large houses usually on landed estates in Scotland. They were built from the sixteenth century, after defensive castles began to be replaced by more comfortable residences for royalty, nobility and local lairds. The origins of Scottish estate houses are in aristocratic emulation of the extensive building and rebuilding of royal residences, beginning with Linlithgow, under the influence of Renaissance architecture. In the 1560s the unique Scottish style of the Scots baronial emerged, which combined features from medieval castles, tower houses, and peel towers with Renaissance plans, in houses designed primarily for residence rather than defence.

Cleish Castle is a 16th-century tower house in Kinross-shire, Scotland. It is sited 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) south-west of Kinross and 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) west of the hamlet of Cleish. It was built by the Colville family, who owned it until 1775. It was restored and remodelled in the mid 19th century, and restored again in the 20th century. It remains a private residence and is a category A listed building. The grounds of the castle are included in the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland, the national listing of significant Scottish gardens.

Barra Castle is an unusual L-plan tower house dating from the early 16th century, about two miles south of Oldmeldrum, above the Lochter Burn, in the parish of Bourtie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It occupies the site of the Battle of Inverurie (1308), in which Robert Bruce defeated John Comyn, Earl of Buchan.

The Royal Court of Scotland was the administrative, political and artistic centre of the Kingdom of Scotland. It emerged in the tenth century and continued until it ceased to function when James VI inherited the throne of England in 1603. For most of the medieval era, the king had no "capital" as such. The Pictish centre of Forteviot was the chief royal seat of the early Gaelic Kingdom of Alba that became the Kingdom of Scotland. In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries Scone was a centre for royal business. Edinburgh only began to emerge as the capital in the reign of James III but his successors undertook occasional royal progress to a part of the kingdom. Little is known about the structure of the Scottish royal court in the period before the reign of David I when it began to take on a distinctly feudal character, with the major offices of the Steward, Chamberlain, Constable, Marischal and Lord Chancellor. By the early modern era the court consisted of leading nobles, office holders, ambassadors and supplicants who surrounded the king or queen. The Chancellor was now effectively the first minister of the kingdom and from the mid-sixteenth century he was the leading figure of the Privy Council.
Ardblair Castle is an L-plan castle, dating from the 16th century, around 0.75 miles (1.21 km) west of Blairgowrie in Perth and Kinross, Scotland. This castle is the subject of a green lady ghostlore story.

Gardening in Scotland, the design of planned spaces set aside for the display, cultivation, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature in Scotland began in the Middle Ages.



















