Related Research Articles

Cri du chat syndrome is a rare genetic disorder due to a partial chromosome deletion on chromosome 5. Its name is a French term referring to the characteristic cat-like cry of affected children. It was first described by Jérôme Lejeune in 1963. The condition affects an estimated 1 in 50,000 live births across all ethnicities and is more common in females by a 4:3 ratio.
Müllerian agenesis, also known as Müllerian aplasia, vaginal agenesis, or Mayer–Rokitansky–Küster–Hauser syndrome, is a congenital malformation characterized by a failure of the Müllerian ducts to develop, resulting in a missing uterus and variable degrees of vaginal hypoplasia of its upper portion. Müllerian agenesis is the cause in 15% of cases of primary amenorrhoea. Because most of the vagina does not develop from the Müllerian duct, instead developing from the urogenital sinus, along with the bladder and urethra, it is present even when the Müllerian duct is completely absent. Because ovaries do not develop from the Müllerian ducts, affected people might have normal secondary sexual characteristics but are infertile due to the lack of a functional uterus. However, biological motherhood is possible through uterus transplantation or use of gestational surrogates.

Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infant's skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development combined with a significant reduction in IQ.

Popliteal pterygium syndrome (PPS) is an inherited condition affecting the face, limbs, and genitalia. The syndrome goes by a number of names including the popliteal web syndrome and, more inclusively, the facio-genito-popliteal syndrome. The term PPS was coined by Gorlin et al. in 1968 on the basis of the most unusual anomaly, the popliteal pterygium.

SCARF syndrome is a rare syndrome characterized by skeletal abnormalities, cutis laxa, craniostenosis, ambiguous genitalia, psychomotor retardation, and facial abnormalities. These characteristics are what make up the acronym SCARF. It shares some features with Lenz-Majewski hyperostotic dwarfism. It is a very rare disease with an incidence rate of approximately one in a million newborns. It has been clinically described in two males who were maternal cousins, as well as a 3-month-old female. Babies affected by this syndrome tend to have very loose skin, giving them an elderly facial appearance. Possible complications include dyspnea, abdominal hernia, heart disorders, joint disorders, and dislocations of multiple joints. It is believed that this disease's inheritance is X-linked recessive.

Baller–Gerold syndrome (BGS) is a rare genetic syndrome that involves premature fusion of the skull bones and malformations of facial, forearm and hand bones. The symptoms of Baller–Gerold syndrome overlap with features of a few other genetics disorders: Rothmund–Thomson syndrome and RAPADILINO syndrome. The prevalence of BGS is unknown, as there have only been a few reported cases, but it is estimated to be less than 1 in a million. The name of the syndrome comes from the researchers Baller and Gerold who discovered the first three cases.
Hecht Scott syndrome is a rare genetic disease that causes congenital limb formation. The main characterisation is the aplasia or hypoplasia of bones of the limb. It is currently presenting in less than 1 in 1,000,000 newborns. It has been known to be more commonly present in males. It was first diagnosed in 2005 by Courtens et al. who recognised the malformations with his present case and four others that were similarly described in literature.

Kleeblattschaedel is a rare malformation of the head where there is a protrusion of the skull and broadening of the face. This condition is a severe type of craniosynostosis.

Van Den Berghe Dequeker syndrome, also known as ulnar hypoplasia-split foot syndrome is a very rare congenital limb malformation syndrome which is characterized by severe ulnar hypoplasia, absence of the index to pinky finger in both hands, and split-foot.
Fibular aplasia-ectrodactyly syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by aplasia/hypoplasia of the fibula, ectrodactyly, and/or brachydactyly/syndactyly. Additional symptoms include shortness of the femur and tibial/knee/hip/ankle defects. This disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Saito–Kuba–Tsuruta syndrome, also known as Fibulo-ulnar hypoplasia-renal anomalies syndrome, is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by fibulo-ulnar dysplasia associated with renal abnormalities. It is associated with neo-natal respiratory failure soon after birth.
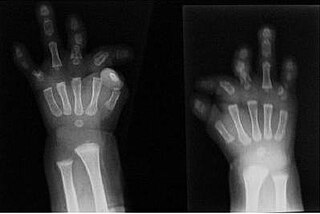
Du Pan syndrome, also known as fibular hypoplasia and complex brachydactyly is an extremely rare genetic disorder which is characterized by hypoplasia, aplasia or dysplasia of the fibula, under-developee/abnormally developed hands and feet and rather complex brachydactyly. Unlike other rare genetic disorders, Du Pan syndrome doesn't affect traits like intellect or the appearance of the head and trunk To this day, 18 cases have been reported in medical literature. This disorder is associated with mutations in the CDCP1 gene, in chromosome 20q11.2. The mode of inheritance varies family from family, but it is most commonly inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, rare cases have families where the mode of inheritance is autosomal dominant.

Craniosynostosis and dental anomalies is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by craniosynostosis, maxillary hypoplasia, and dental anomalies. Dental anomalies seen in this condition include malocclusion, delayed and ectopic tooth eruption, and/or supernumerary teeth. Syndactyly, clinodactyly, and other digit anomalies may also be present.
Craniosynostosis with anomalies of the cranial base and digits is a syndrome characterized by premature craniosynostosis, synchrondosis at the skull base, absent thumbs, absence of the middle phalanges in fingers 2 and 5, and proximally positioned halluces.
Craniosynostosis, Adelaide type (CRSA) is a syndrome characterized by cone-shaped epiphyses, phalangeal hypoplasia, and carpal bone malsegmentation along with craniosynostosis.

Craniosynostosis, Philadelphia type is a rare autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by sagittal craniosynostosis (scaphocephaly) and soft tissue syndactyly of the hands and feet. This condition is considered a form of acrocephalosyndactyly.

Craniosynostosis-Dandy-Walker malformation-hydrocephalus syndrome is an autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by sagittal craniosynostosis (scaphocephaly), Dandy-Walker malformation, hydrocephalus, and craniofacial dysmorphisms including hypertelorism, micrognathia, and positional ear deformities.

Craniorhiny is a rare autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by craniosynostosis (oxycephaly) and facial anomalies around the nose base and lips.

Low anterior hairline is a condition in which the frontal hairline which defines the top and sides of the forehead is unusually low. This can mean that either the distance between the trichion (hairline) and glabella at the midline is more than 2 SD below the mean, or that this distance is apparently (subjectively) decreased.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Craniosynostosis-fibular aplasia syndrome (Concept Id: C1857492)". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2023-09-14.
- 1 2 3 "218550 - CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS WITH FIBULAR APLASIA". www.omim.org. Retrieved 2023-09-14.
- ↑ "Resources: Craniosynostosis-fibular aplasia syndrome". Rare Disease InfoHub. Retrieved September 14, 2023.