Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, as well as misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial orthopedics.

Orthodontic retainers are custom-made devices, usually made of wires or clear plastic, that hold teeth in position after surgery or any method of realigning teeth. Once a phase of orthodontic treatment has been completed to straighten teeth, there remains a lifelong risk of relapse due to a number of factors: recoil of periodontal fibres, pressure from surrounding soft tissues, the occlusion and patient’s continued growth and development. By using retainers to hold the teeth in their new position for a length of time, the surrounding periodontal fibres adapt to changes in the bone which can help minimize any changes to the final tooth position after the completion of orthodontic treatment. Retainers may also be used to treat overjets.

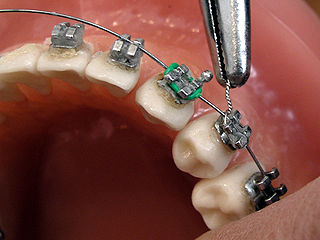
Dental braces are devices used in orthodontics that align and straighten teeth and help position them with regard to a person's bite, while also aiming to improve dental health. They are often used to correct underbites, as well as malocclusions, overbites, open bites, gaps, deep bites, cross bites, crooked teeth, and various other flaws of the teeth and jaw. Braces can be either cosmetic or structural. Dental braces are often used in conjunction with other orthodontic appliances to help widen the palate or jaws and to otherwise assist in shaping the teeth and jaws.

Clear aligners are orthodontic devices that are a transparent, plastic form of dental braces used to adjust teeth.

Orthodontic headgear is a type of orthodontic appliance typically attached to the patient's head with a strap or number of straps around the patient's head or neck. From this, a force is transferred to the mouth/jaw(s) of the subject.
Orthodontic separators are rubber bands or metal appliances used in orthodontics. Spacers are placed between the molars at the second orthodontic appointment before molar bands are applied. They are usually added a week before you get your braces, but can sometimes be added after.

In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855–1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word "malocclusion" derives from occlusion, and refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet.

A palatal expander is a device in the field of orthodontics which is used to widen the upper jaw (maxilla) so that the bottom and upper teeth will fit together better. This is a common orthodontic procedure. The use of an expander is most common in children and adolescents 8–18 years of age. It can also be used in adults, although expansion is more uncomfortable and takes longer in adults. A patient who would rather not wait several months for the end result achieved by a palatal expander may be able to opt for a surgical separation of the maxilla. Use of a palatal expander is most often followed by braces to then straighten the teeth.
Orthodontic technology is a specialty of dental technology that is concerned with the design and fabrication of dental appliances for the treatment of malocclusions, which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both.

Edward Hartley Angle was an American dentist, widely regarded as "the father of American orthodontics". He was trained as a dentist, but made orthodontics his speciality and dedicated his life to standardizing the teaching and practice of orthodontics. He founded the Angle School of Orthodontia in 1899 in St. Louis and schools in other regions of the United States. As the originator of the profession, Angle founded three orthodontic schools between 1905 and 1928 in St. Louis, Missouri, New London, Connecticut and Pasadena, California. These exclusive institutions provided the opportunity for several pioneering American orthodontists to receive their training.

Crossbite is a form of malocclusion where a tooth has a more buccal or lingual position than its corresponding antagonist tooth in the upper or lower dental arch. In other words, crossbite is a lateral misalignment of the dental arches.
Self-ligating brackets are defined as "a dental brace, which generally utilizes a permanently installed, moveable component to entrap the archwire". Self-ligating brackets have also been designed which do not require a movable component to hold the wire in place. Self-ligating braces may be classified into two categories: Passive and Active.

SureSmile is a type of customized orthodontic arch wires used by orthodontists to straighten teeth. The technique utilizes 3-D imaging, treatment planning software and a robot to create the wires. The technique is reported to decrease the time required to complete orthodontic treatment by 34% and increase the precision of the results.
Percival Raymond Begg AO was a professor at the University of Adelaide School of Dentistry and a well known orthodontist, famous for developing the "Begg technique". Permanent displays dedicated to the Begg technique can be found in the Smithsonian Institution in Washington DC, the Library of the American Dental Association in Chicago, and the PR Begg Museum at the University of Adelaide.
Lingual braces are one of the many types of the fixed orthodontic treatment appliances available to patients needing orthodontics. They involve attaching the orthodontic brackets on the inner sides of the teeth. The main advantage of lingual braces is their near invisibility compared to the standard braces, which are attached on the buccal (cheek) sides of the tooth. Lingual braces were invented by Craven Kurz in 1976.
Dr. William J. Clark is a Scottish orthodontist known for developing Twin Block Appliance in Orthodontics. This appliance was developed by Dr. Clark in 1977 in Scotland and since then this appliance has been used in correction of Class 2 malocclusions with retrognathic mandible. He also developed invisible TransForce Appliance in 2004.
Dr. Robert M. Ricketts was an American orthodontist known for many contributions in the field of orthodontics. Most important contributions were related to his development of Ricketts' Cephalometric Analysis and an .018-inch slot in an orthodontic bracket. His research focused on the growth and structural variation of the face and jaws.
Activator Appliance is an Orthodontics appliance that was developed by Viggo Andresen in 1908. This was one of the first functional appliances that was developed to correct functional jaw in the early 1900s. Activator appliance became the universal appliance that was used widely throughout Europe in the earlier part of the 20th century.
Frankel appliance or Frankel Functional Regulator is an orthodontic functional appliance which was developed by Rolf Fränkel in 1950s for treatment to patients of all ages. This appliance primarily focused on the modulation of neuromuscular activity in order to produce changes in jaw and teeth. The appliance was opposite to the Bionator appliance and Activator appliance.

Align Technology, Inc. is an American manufacturer of 3D digital scanners and Invisalign clear aligners used in orthodontics. It was founded in 1997 and is headquartered in Tempe, Arizona. The company manufactures the aligners in Juarez, Mexico, and its scanners in Israel and China. The company is best known for its Invisalign system, which is a clear aligner treatment used to straighten teeth.










