Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (EVPM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance and progress in an objective manner.

Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities.
In computer science, best, worst, and average cases of a given algorithm express what the resource usage is at least, at most and on average, respectively. Usually the resource being considered is running time, i.e. time complexity, but it could also be memory or other resource. Best case is the function which performs the minimum number of steps on input data of n elements. Worst case is the function which performs the maximum number of steps on input data of size n. Average case is the function which performs an average number of steps on input data of n elements.
Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a method of planning and managing projects that emphasizes the resources required to execute project tasks. It was developed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt. It differs from more traditional methods that derive from critical path and PERT algorithms, which emphasize task order and rigid scheduling. A critical chain project network strives to keep resources levelled, and requires that they be flexible in start times.

The program (or project) evaluation and review technique (PERT) is a statistical tool used in project management, which was designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project.
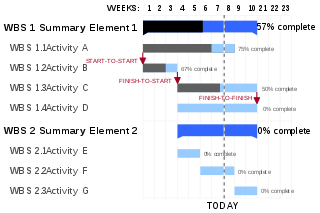
A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule, named after its inventor, Henry Gantt (1861–1919), who designed such a chart around the years 1910–1915. Modern Gantt charts also show the dependency relationships between activities and current schedule status.
In project management, float or slack is the amount of time that a task in a project network can be delayed without causing a delay to:
Agile software development is an approach to software development under which requirements and solutions evolve through the collaborative effort of self-organizing and cross-functional teams and their customer(s)/end user(s). It advocates adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continual improvement, and it encourages rapid and flexible response to change.

Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financial loss and uncertainty about its extent.

The precedence diagram method (PDM) is a tool for scheduling activities in a project plan. It is a method of constructing a project schedule network diagram that uses boxes, referred to as nodes, to represent activities and connects them with arrows that show the dependencies. It is also called the activity-on-node (AON) method.
Extreme programming (XP) is an agile software development methodology used to implement software projects. This article details the practices used in this methodology. Extreme programming has 12 practices, grouped into four areas, derived from the best practices of software engineering.

Critical Chain is a novel by Dr. Eliyahu Goldratt using the Critical Chain theory of Project Management as the major theme. It is really a teaching method for the theory.

A risk register (PRINCE2) is a scatterplot used as risk management tool and to fulfill regulatory compliance acting as a repository for all risks identified and includes additional information about each risk, e.g. nature of the risk, reference and owner, mitigation measures.

Event chain methodology is a network analysis technique that is focused on identifying and managing events and relationship between them that affect project schedules. It is an uncertainty modeling schedule technique. Event chain methodology is an extension of quantitative project risk analysis with Monte Carlo simulations. It is the next advance beyond critical path method and critical chain project management. Event chain methodology helps to mitigate the effect of motivational and cognitive biases in estimating and scheduling. It improves accuracy of risk assessment and helps to generate more realistic risk adjusted project schedules.

Event chain diagrams are visualizations that show the relationships between events and tasks and how the events affect each other.
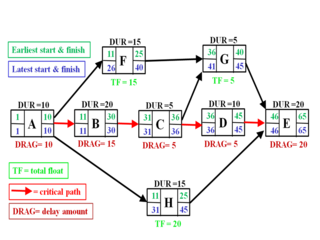
Critical path drag is a project management metric developed by Stephen Devaux as part of the Total Project Control (TPC) approach to schedule analysis and compression in the critical path method of scheduling. Critical path drag is the amount of time that an activity or constraint on the critical path is adding to the project duration. Alternatively, it is the maximum amount of time that one can shorten the activity before it is no longer on the critical path or before its duration becomes zero.
Drag cost is a project management metric developed by Stephen Devaux as part of the Total Project Control (TPC) approach to project schedule and cost analysis. It is the amount by which a project’s expected return on investment (ROI) is reduced due to the critical path drag of a specific critical path activity Task or other specific schedule factor such as a schedule lag or other delaying constraint.
Intaver Institute is a software development company that develops a suite of project management, risk analysis and risk management applications. Intaver Institute's product is project risk management and risk analysis software suite RiskyProject. Intaver Institute is a privately owned company headquartered in Naples, Florida, United States and Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Devaux's Index of Project Performance is a project management performance metric formulated by Stephen Devaux as part of the total project control (TPC) approach to project and program value analysis. It is an index that integrates the three variables of a project into a single value-based index where:









