
The Global Environment Facility (GEF) is a multilateral environmental fund that provides grants and blended finance for projects related to biodiversity, climate change, international waters, land degradation, persistent organic pollutants (POPs), mercury, sustainable forest management, food security, and sustainable cities in developing countries and countries with economies in transition. It is the largest source of multilateral funding for biodiversity globally and distributes more than $1 billion a year on average to address inter-related environmental challenges.

Forestation is a vital ecological process where forests are established and grown through afforestation and reforestation efforts. Afforestation involves planting trees on previously non-forested lands, while reforestation focuses on replanting trees in areas that were once deforested. This process plays an important role in restoring degraded forests, enhancing ecosystems, promoting carbon sequestration, and biodiversity conservation.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."
The Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) was built by the Group on Earth Observations (GEO) on the basis of a 10-Year Implementation Plan running from 2005 to 2015. GEOSS seeks to connect the producers of environmental data and decision-support tools with the end users of these products, with the aim of enhancing the relevance of Earth observations to global issues. GEOSS aims to produce a global public infrastructure that generates comprehensive, near-real-time environmental data, information and analyses for a wide range of users. The Secretariat Director of Geoss is Barbara Ryan.
The International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP) is the petroleum industry's global forum in which members identify and share best practices to achieve improvements in health, safety, the environment, security, social responsibility, engineering and operations.
Forest management is a branch of forestry concerned with overall administrative, legal, economic, and social aspects, as well as scientific and technical aspects, such as silviculture, forest protection, and forest regulation. This includes management for timber, aesthetics, recreation, urban values, water, wildlife, inland and nearshore fisheries, wood products, plant genetic resources, and other forest resource values. Management objectives can be for conservation, utilisation, or a mixture of the two. Techniques include timber extraction, planting and replanting of different species, building and maintenance of roads and pathways through forests, and preventing fire.

The Development Bank of Southern Africa (DBSA) is a development finance institution wholly owned by the Government of South Africa. The bank intends to "accelerate sustainable socio-economic development in the Southern African Development Community (SADC) by driving financial and non-financial investments in the social and economic infrastructure sectors".

Deforestation in Nigeria refers to the extensive and rapid clearing of forests within the borders of Nigeria. This environmental issue has significant impacts on both local and global scales.
Conservation finance is the practice of raising and managing capital to support land, water, and resource conservation. Conservation financing options vary by source from public, private, and nonprofit funders; by type from loans, to grants, to tax incentives, to market mechanisms; and by scale ranging from federal to state, national to local.

Sustainable gardening includes the more specific sustainable landscapes, sustainable landscape design, sustainable landscaping, sustainable landscape architecture, resulting in sustainable sites. It comprises a disparate group of horticultural interests that can share the aims and objectives associated with the international post-1980s sustainable development and sustainability programs developed to address that humans are now using natural biophysical resources faster than they can be replenished by nature.
The environmental impact of agriculture is the effect that different farming practices have on the ecosystems around them, and how those effects can be traced back to those practices. The environmental impact of agriculture varies widely based on practices employed by farmers and by the scale of practice. Farming communities that try to reduce environmental impacts through modifying their practices will adopt sustainable agriculture practices. The negative impact of agriculture is an old issue that remains a concern even as experts design innovative means to reduce destruction and enhance eco-efficiency. Though some pastoralism is environmentally positive, modern animal agriculture practices tend to be more environmentally destructive than agricultural practices focused on fruits, vegetables and other biomass. The emissions of ammonia from cattle waste continue to raise concerns over environmental pollution.

The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) was a study led by Pavan Sukhdev from 2007 to 2011. It is an international initiative to draw attention to the global economic benefits of biodiversity. Its objective is to highlight the growing cost of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation and to draw together expertise from the fields of science, economics and policy to enable practical actions. TEEB aims to assess, communicate and mainstream the urgency of actions through its five deliverables—D0: science and economic foundations, policy costs and costs of inaction, D1: policy opportunities for national and international policy-makers, D2: decision support for local administrators, D3: business risks, opportunities and metrics and D4: citizen and consumer ownership.

The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was established in July 1970 when the White House and the United States Congress came together due to the public's demand for cleaner natural resources. The purpose of the EPA is to repair the damage done to the environment and to set up new criteria to allow Americans to make a clean environment a reality. The ultimate goal of the EPA is to protect human health and the environment.

Forest Trends is a non-profit organization founded in 1998 and based in Washington, DC, that connects with economic tools and incentives for maintaining ecosystems. Its mission is four-fold: to expand the value of forests to society, to promote sustainable forest management and conservation by creating and capturing market values for ecosystem services, to support innovative projects and companies that are developing these markets and to enhance the livelihoods of local communities living in and around those forests.
The Benguela Current Commission, or BCC, is a multi-sectoral inter-governmental, initiative of Angola, Namibia and South Africa. It promotes the sustainable management and protection of the Benguela Current Large Marine Ecosystem, or BCLME. The BCC was established in January 2007 through the signing of an Interim Agreement between the governments of Angola, Namibia and South Africa. Then, on 18 March 2013, the three governments signed the Benguela Current Convention, an environmental treaty that entrenches the Benguela Current Commission as a permanent inter-governmental organization.
Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Institute (ABMI) is an agency that monitors and reports on biodiversity status throughout the province of Alberta, Canada, that is funded equally by the government of Alberta and the oil and gas industry. The Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Institute is based in Edmonton, Alberta. According to Alberta Innovates-Technology Futures (AITF), a key partner in the ABMI, the ABMI, which acts as "an early warning system by monitoring the cumulative effects of biodiversity change in regions throughout Alberta" is "the largest project of its kind ever attempted in Canada." Collaborating agencies include the government-industry research agency Alberta Innovates-Technology Futures, the University of Alberta, University of Calgary and the Royal Alberta Museum. Along with the Alberta Forest Management Planning Standard, the ABMI are key components to implementing resource planning based on ecosystem management principles. Alberta Environment and Parks consults the Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Agency's reports in monitoring and preservation of species, setting benchmarks for biodiversity for land use plans. If industry contributes to the endangerment of a species that falls below these benchmarks, the Government of Alberta can order remedial action.
The Voluntary Principles on Security and Human Rights is a collaborative effort by governments, major multinational extractive companies, and NGOs to provide guidance to companies on tangible steps that they can take to minimize the risk of human rights abuses in communities located near extraction sites. The principles documents provide guidance to companies in developing practices that maintain the safety and security of their operations while respecting the human rights of those who come into contact with security forces related to those operations. The Principles give guidance on risk assessment, public safety and security, human rights abuses, and the interaction between companies and private and public security.

Due to its geographical and natural diversity, Indonesia is one of the countries most susceptible to the impacts of climate change. This is supported by the fact that Jakarta has been listed as the world's most vulnerable city, regarding climate change. It is also a major contributor as of the countries that has contributed most to greenhouse gas emissions due to its high rate of deforestation and reliance on coal power.
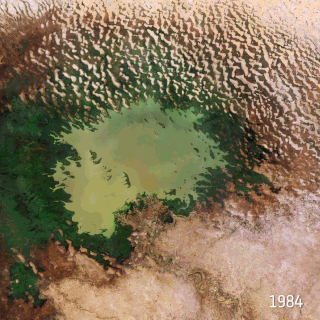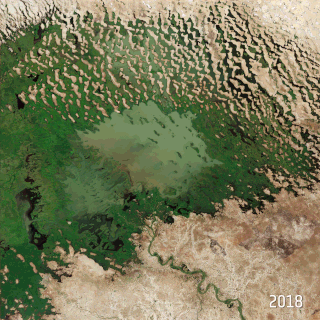
Climate change in Nigeria is evident from temperature increase, rainfall variability. It is also reflected in drought, desertification, rising sea levels, erosion, floods, thunderstorms, bush fires, landslides, land degradation, more frequent, extreme weather conditions and loss of biodiversity. All of which continues to negatively affect human and animal life and also the ecosystems in Nigeria. Although, depending on the location, regions experience climate change with significant higher temperatures during the dry seasons while rainfalls during rainy seasons help keep the temperature at milder levels. The effects of climate change prompted the World Meteorological Organization, in its 40th Executive Council 1988, to establish a new international scientific assessment panel to be called the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The 2007 IPCC's fourth and final Assessment Report (AR4) revealed that there is a considerable threat of climate change that requires urgent global attention. The report further attributed the present global warming to largely anthropogenic practices. The Earth is almost at a point of no return as it faces environmental threats which include atmospheric and marine pollution, global warming, ozone depletion, the dangers of pollution by nuclear and other hazardous substances, and the extinction of various wildlife species.

In Nigeria, firewood is a traditional source of energy for domestic and commercial use. Fuel wood is derived from cutting and burning wood materials such as logs and twigs. It has long been prevalent among rural and sometimes urban dwellers.










