
Thrace is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split between Bulgaria, Greece and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria, northeastern Greece and the European part of Turkey.

Dacian is an extinct Indo-European language that was spoken in the Carpathian region in antiquity. In the 1st century, it was probably the predominant language of the ancient regions of Dacia and Moesia and possibly of some surrounding regions. The language was probably extinct by the 7th century AD.

In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians (Παίονες).
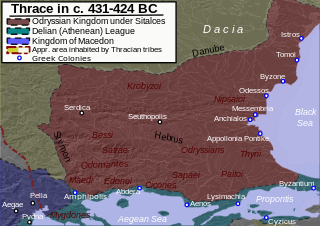
The Odrysian Kingdom was a state union of over 40 Thracian tribes and 22 kingdoms that existed between the 5th century BC and the 1st century AD. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria, spreading to parts of Southeastern Romania, parts of Northern Greece and parts of modern-day European Turkey.

The Getae, , or Gets were several Thracian tribes that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form Get and plural Getae may be derived from a Greek exonym: the area was the hinterland of Greek colonies on the Black Sea coast, bringing the Getae into contact with the ancient Greeks from an early date. Several scholars, especially in the Romanian historiography, posit the identity between the Getae and their westward neighbours, the Dacians.

Teres I, was the first king of the Odrysian state of Thrace. Thrace had nominally been part of the Persian empire since 516 BC during the rule of Darius the Great, and was re-subjugated by Mardonius in 492 BC.

The Bessi were an independent Thracian tribe who lived in a territory ranging from Moesia to Mount Rhodope in southern Thrace, but are often mentioned as dwelling about Haemus, the mountain range that separates Moesia from Thrace and from Mount Rhodope to the northern part of Hebrus. Herodotus described them as a sort of priestly-caste among the Satrae, the Bessi being interpreters of the prophetic utterances given by a priestess in an oracular shrine of Dionysus located on a mountain-top.
Paeonian, sometimes spelled Paionian, is a poorly-attested, extinct language spoken by the ancient Paeonians until late antiquity.
The Moesi was a Thracian tribe which inhabited present day Northern Bulgaria and Serbia, which gave its name to the Roman province of Moesia after its defeat in 29 BC. Moesia was first established as a separate province in 45–46 AD.
The linguistic classification of the ancient Thracian language has long been a matter of contention and uncertainty, and there are widely varying hypotheses regarding its position among other Paleo-Balkan languages. It is not contested, however, that the Thracian languages were Indo-European languages which had acquired satem characteristics by the time they are attested.
Thracology is the scientific study of Ancient Thrace and Thracian antiquities and is a regional and thematic branch of the larger disciplines of ancient history and archaeology. A practitioner of the discipline is a Thracologist. Thracology investigates the range of ancient Thracian culture from 1000 BC up to the end of Roman rule in the 4th–7th centuries AD. Modern Thracology started with the work of Wilhelm Tomaschek in the late 19th century.

Beglik Tash, is a prehistoric rock sanctuary situated on the southern Black Sea coast of Bulgaria, a few kilometers north of the city of Primorsko. It was re-used by the Thracian tribes in the Iron Age.
Koilaletoi or Coilaletae or Coelaletae is the name of a Thracian tribe. Other parts of this tribe were, the Coelaletae Maiores and Coelaletae Minores. They are mentioned by Tacitus.
The Tyrageti, Tyragetae, or Tyrangitae, literally, the Getae of the Tyras, were a sub-tribe of the Getae Thracians, situated on the river Tyras. They were regarded as an immigrant tribe of European Sarmatia dwelling E. of the river Tyras, near the Harpii and Tagri, and, according to Ptolemy, the northern neighbours of Lower Moesia. Pliny calls them, with more correct orthography, Tyragetae, and represents them as dwelling on a large island in the Tyras.

The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Thrace. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Thracian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Thracians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Thracian tribes.
Thracian clothing refers to types of clothing worn mainly by Thracians, Dacians but also by some Greeks. Its best literal descriptions are given by Herodotus and Xenophon in his Anabasis. Depictions are found in a great number of Greek vases and there are a few Persian representations as well. In contrast to shapes and patterns we have very little evidence on the colours used.
Krobyzoi is a Thracian, Getae or Dacian tribe.










