
Kevin Abosch is an Irish conceptual artist and pioneer in cryptoart known for his works in photography, blockchain, sculpture, installation, AI and film. Abosch's work addresses the nature of identity, value and human currency and has been exhibited throughout the world, often in civic spaces, including The Hermitage Museum, The National Gallery of Ireland, The National Museum of China, The Irish Museum of Modern Art, The Museum of Contemporary Art Vojvodina, The Bogotá Museum of Modern Art, ZKM, Galerie nationale du Jeu de Paume, and Dublin Airport.

A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a collection of binary data which is designed to work as a medium of exchange. Individual coin ownership records are stored in a ledger, which is a computerized database using strong cryptography to secure transaction records, to control the creation of additional coins, and to verify the transfer of coin ownership. Cryptocurrencies are generally fiat currencies, as they are not backed by or convertible into a commodity. Some crypto schemes use validators to maintain the cryptocurrency. In a proof-of-stake model, owners put up their tokens as collateral. In return, they get authority over the token in proportion to the amount they stake. Generally, these token stakers get additional ownership in the token over time via network fees, newly minted tokens or other such reward mechanisms.
Coinbase Global, Inc., branded Coinbase, is an American company that operates a cryptocurrency exchange platform. Coinbase operates remote-first, and lacks an official physical headquarters. The company was founded in 2012 by Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam, and as of March 2021 was the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the United States by trading volume.

Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. Amongst cryptocurrencies, Ether is second only to Bitcoin in market capitalization.
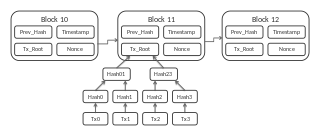
A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. The timestamp proves that the transaction data existed when the block was published in order to get into its hash. As blocks each contain information about the block previous to it, they form a chain, with each additional block reinforcing the ones before it. Therefore, blockchains are resistant to modification of their data because once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks.

Ethereum Classic is an open source, blockchain-based distributed computing platform featuring smart contract (scripting) functionality. It supports a modified version of Nakamoto consensus via transaction-based state transitions executed on a public Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Cardano is a public blockchain platform. It is open-source and decentralized, with consensus achieved using proof of stake. It can facilitate peer-to-peer transactions with its internal cryptocurrency, Ada.
An initial coin offering (ICO) or initial currency offering is a type of funding using cryptocurrencies. It is often a form of crowdfunding, although a private ICO which does not seek public investment is also possible. In an ICO, a quantity of cryptocurrency is sold in the form of "tokens" ("coins") to speculators or investors, in exchange for legal tender or other cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ether. The tokens are promoted as future functional units of currency if or when the ICO's funding goal is met and the project successfully launches.

CryptoKitties is a blockchain game on Ethereum developed by Canadian studio Dapper Labs that allows players to purchase, collect, breed and sell virtual cats. It is one of the earliest attempts to deploy blockchain technology for recreation and leisure. The game's popularity in December 2017 congested the Ethereum network, causing it to reach an all-time high in the number of transactions and slowing it down significantly.
A non-fungible token (NFT) is an idiosyncratic and non-interchangeable unit of data stored on a digital ledger (blockchain). NFTs can be associated with reproducible items such as photos, videos, 3D models, audio, and other types of digital files as unique items. NFTs use blockchain technology to provide a public proof of ownership. Copies of the original file are not restricted to the owner of the NFT, and can be copied and shared like any file. The lack of interchangeability (fungibility) distinguishes NFTs from blockchain cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin.

The DFINITY Foundation is a nonprofit organization that develops the Internet Computer, a decentralized, open-source, general-purpose blockchain designed to host smart contracts.
Decentraland is a decentralised 3D virtual reality platform that consists of 90,601 parcels of land. Virtual estate in Decentraland are NFTs which can be bought by the cryptocurrency MANA, which is based on the Ethereum blockchain. It was opened to the public in February 2020, and is overseen by the nonprofit Decentraland Foundation.
Anthony Di Iorio is a Canadian entrepreneur primarily known as a co-founder of Ethereum and an early investor in Bitcoin. Di Iorio is the founder and CEO of the blockchain company Decentral, and the associated Jaxx wallet. He also served as the first chief digital officer of the Toronto Stock Exchange. In February 2018, Forbes estimated his net worth at $750 million–$1 billion.
Paxos Trust Company is a New York-based financial institution and technology company specializing in blockchain. The company's product offerings include a cryptocurrency brokerage service, asset tokenization services, and settlement services. ItBit, a bitcoin exchange run by Paxos, was the first bitcoin exchange to be licensed by the New York State Department of Financial Services, granting the company the ability to be the custodian and exchange for customers in the United States.
Bancor Protocol is a standard for decentralized exchange networks used to allow for the automated conversion of cryptocurrency tokens into other tokens, including across blockchains, without the need for an order book or counterparty to facilitate the exchange. Bancor invented the world’s first blockchain-based automated liquidity pool, or automated market maker (AMM) called a Smart Token, a digital currency with an embedded converter that allows it to be issued or exchanged automatically for any token in its network. Bancor Network consists of all the different tokens utilizing the Bancor Protocol and connected through BNT, the Bancor Network Token, which serves as the hub token for the network through which any token can be converted into any other token.

CryptoPunks is a non-fungible token (NFT) collection on the Ethereum blockchain. The project was launched in June 2017 by the Larva Labs studio, a two-person team consisting of Canadian software developers Matt Hall and John Watkinson. The experimental project was inspired by the London punk scenes, the cyberpunk movement and electronic music artists Daft Punk. The crypto art blockchain project was an inspiration for the ERC-721 standard for NFTs and the modern crypto art movement, which has since become a part of the cryptocurrency and decentralized finance ecosystems on multiple blockchains.
Prince Jacon "Osinachi" Igwe is a Nigerian visual artist and non-fungible token creator. He is known for using Microsoft Word as his medium. He is the Chief Creative Officer for SocialStack, a social token protocol on Ethereum and Celo. He launched his own social currency $OSINA. He has been described as “Africa’s foremost crypto artist.”
A rare Pepe or RarePepe is a type of crypto art created by various artists world wide between 2016 and 2018, based on Pepe the Frog and traded as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) recorded on the CounterParty platform.
Curio Cards are collectible digital artworks located on the Ethereum blockchain. Created in 2017, Curio Cards are commonly viewed as the first digital art collectibles on the Ethereum blockchain. In October 2021, a complete collection of Curio Cards, including the card "17b" misprint, was sold for ETH393 ($1,267,320) at the Christie's Post-War to Present auction.







