Related Research Articles
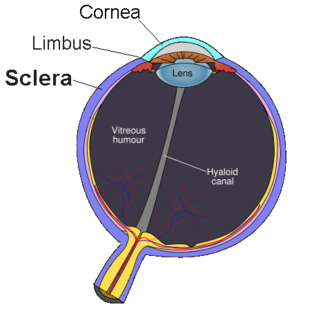
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some elastic fiber. In humans, the whole sclera is white, contrasting with the coloured iris, but in other mammals the visible part of the sclera matches the colour of the iris, so the white part does not normally show. In the development of the embryo, the sclera is derived from the neural crest. In children, it is thinner and shows some of the underlying pigment, appearing slightly blue. In the elderly, fatty deposits on the sclera can make it appear slightly yellow. Many people with dark skin have naturally darkened sclerae, the result of melanin pigmentation.
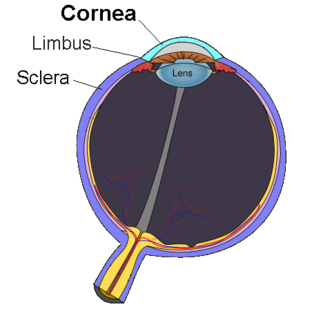
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. The cornea, with the anterior chamber and lens, refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK.

Rheum is a thin mucus naturally discharged from the eyes, nose, or mouth during sleep. Rheum dries and gathers as a crust in the corners of the eyes or the mouth, on the eyelids, or under the nose. It is formed by a combination of mucus, nasal mucus, blood cells, skin cells, or dust. Rheum from the eyes is particularly common. Dried rheum is commonly called sleep, sleepy-seeds, sleepy buds, sleepy bugs, sleepy sand, sleepies, sleepers, eye crust, eye goop, cheese, eye boogers, dream candy, winkies, goggles, sleepy dirt, chicken in your eye, or sleepy dust.

Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle was a German physician, pathologist, and anatomist. He is credited with the discovery of the loop of Henle in the kidney. His essay, "On Miasma and Contagia," was an early argument for the germ theory of disease. He was an important figure in the development of modern medicine.
Blinking is a bodily function; it is a semi-autonomic rapid closing of the eyelid. A single blink is determined by the forceful closing of the eyelid or inactivation of the levator palpebrae superioris and the activation of the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi, not the full open and close. It is an essential function of the eye that helps spread tears across and remove irritants from the surface of the cornea and conjunctiva.

Cherry eye is a disorder of the nictitating membrane (NM), also called the third eyelid, present in the eyes of dogs and cats. Cherry eye is most often seen in young dogs under the age of two. Common misnomers include adenitis, hyperplasia, adenoma of the gland of the third eyelid; however, cherry eye is not caused by hyperplasia, neoplasia, or primary inflammation. In many species, the third eyelid plays an essential role in vision by supplying oxygen and nutrients to the eye via tear production. Normally, the gland can turn inside-out without detachment. Cherry eye results from a defect in the retinaculum which is responsible for anchoring the gland to the periorbita. This defect causes the gland to prolapse and protrude from the eye as a red fleshy mass. Problems arise as sensitive tissue dries out and is subjected to external trauma Exposure of the tissue often results in secondary inflammation, swelling, or infection. If left untreated, this condition can lead to dry eye syndrome and other complications.

A red eye is an eye that appears red due to illness or injury. It is usually injection and prominence of the superficial blood vessels of the conjunctiva, which may be caused by disorders of these or adjacent structures. Conjunctivitis and subconjunctival hemorrhage are two of the less serious but more common causes.
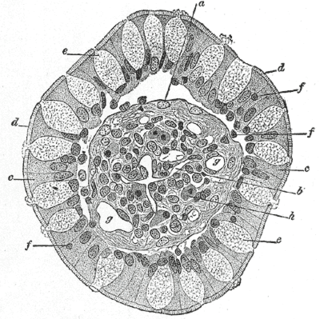
Goblet cells are simple columnar goblet shaped like epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin MUC5AC. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting vesicles into a duct, but may use apocrine methods, budding off their secretions, when under stress. The term goblet refers to the cell's goblet-like shape. The apical portion is shaped like a cup, as it is distended by abundant mucus laden granules; its basal portion lacks these granules and is shaped like a stem.
Enucleation is the removal of the eye that leaves the eye muscles and remaining orbital contents intact. This type of ocular surgery is indicated for a number of ocular tumors, in eyes that have suffered severe trauma, and in eyes that are otherwise blind and painful.

The ophthalmic nerve is the first branch of the trigeminal nerve. The ophthalmic nerve is a sensory nerve mostly carrying general somatic afferent fibers that transmit sensory information to the CNS from structures of the eyeball, the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, the lining of the upper part of the nasal cavity and air cells, and the meninges of the anterior cranial fossa. Some of ophthalmic nerve branches also convey parasympathetic fibers.
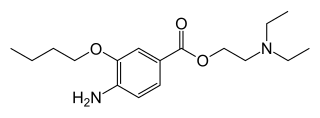
Oxybuprocaine (INN), also known as benoxinate or BNX, is an ester-type local anesthetic, which is used especially in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. Oxybuprocaine is sold by Novartis under the brand names Novesine or Novesin.
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams, ointments, aerosols, sprays, lotions, and jellies. Examples include benzocaine, butamben, dibucaine, lidocaine, oxybuprocaine, pramoxine, proparacaine, proxymetacaine, and tetracaine.

A corneal ulcer, or ulcerative keratitis, is an inflammatory condition of the cornea involving loss of its outer layer. It is very common in dogs and is sometimes seen in cats. In veterinary medicine, the term corneal ulcer is a generic name for any condition involving the loss of the outer layer of the cornea, and as such is used to describe conditions with both inflammatory and traumatic causes.

The anterior ciliary arteries are seven small arteries in each eye-socket that supply the conjunctiva, sclera and the rectus muscles. They are derived from the muscular branches of the ophthalmic artery.

The Tenon capsule, also known as the fascial sheath of the eyeball or the fascia bulbi, is a thin membrane which envelops the eyeball from the optic nerve to the corneal limbus, separating it from the orbital fat and forming a socket in which it moves.

The equine eye is one of the largest of any land mammal. Its visual abilities are directly related to the animal's behavior; for example, it is active during both day and night, and it is a prey animal. Both the strengths and weaknesses of the horse's visual abilities should be taken into consideration when training the animal, as an understanding of the horse's eye can help to discover why the animal behaves the way it does in various situations.

Mammals normally have a pair of eyes. Although mammalian vision is not so excellent as bird vision, it is at least dichromatic for most of mammalian species, with certain families possessing a trichromatic color perception.

The ocular immune system protects the eye from infection and regulates healing processes following injuries. The interior of the eye lacks lymph vessels but is highly vascularized, and many immune cells reside in the uvea, including mostly macrophages, dendritic cells, and mast cells. These cells fight off intraocular infections, and intraocular inflammation can manifest as uveitis or retinitis. The cornea of the eye is immunologically a very special tissue. Its constant exposure to the exterior world means that it is vulnerable to a wide range of microorganisms while its moist mucosal surface makes the cornea particularly susceptible to attack. At the same time, its lack of vasculature and relative immune separation from the rest of the body makes immune defense difficult. Lastly, the cornea is a multifunctional tissue. It provides a large part of the eye's refractive power, meaning it has to maintain remarkable transparency, but must also serve as a barrier to keep pathogens from reaching the rest of the eye, similar to function of the dermis and epidermis in keeping underlying tissues protected. Immune reactions within the cornea come from surrounding vascularized tissues as well as innate immune responsive cells that reside within the cornea.

Conjunctivochalasis is a common eye surface condition characterized by the presence of excess folds of the conjunctiva located between the globe of the eye and the eyelid margin.
References
| This article about the eye is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |