Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as MF4.
DV is a family of codecs and tape formats used for storing digital video, launched in 1995 by a consortium of video camera manufacturers led by Sony and Panasonic. It includes the recording or cassette formats DV, MiniDV, DVCAM, Digital8, HDV, DVCPro, DVCPro50 and DVCProHD. DV has been used primarily for video recording with camcorders in the amateur and professional sectors.

The Emergency Broadcast System (EBS), sometimes called the Emergency Action Notification System (EANS), was an emergency warning system used in the United States. It was the most commonly used, along with the Emergency Override system. It replaced the previous CONELRAD system and was used from 1963 to 1997, at which point it was replaced by the Emergency Alert System.

A Dolby noise-reduction system, or Dolby NR, is one of a series of noise reduction systems developed by Dolby Laboratories for use in analog audio tape recording. The first was Dolby A, a professional broadband noise reduction system for recording studios that was first demonstrated in 1965, but the best-known is Dolby B, a sliding band system for the consumer market, which helped make high fidelity practical on cassette tapes, which used a relatively noisy tape size and speed. It is common on high-fidelity stereo tape players and recorders to the present day, although Dolby has as of 2016 ceased licensing the technology for new cassette decks. Of the noise reduction systems, Dolby A and Dolby SR were developed for professional use. Dolby B, C, and S were designed for the consumer market. Aside from Dolby HX, all the Dolby variants work by companding: compressing the dynamic range of the sound during recording, and expanding it during playback.

The Emergency Alert System (EAS) is a national warning system in the United States designed to allow authorized officials to broadcast emergency alerts and warning messages to the public via cable, satellite and broadcast television and AM, FM and satellite radio. Informally, Emergency Alert System is sometimes conflated with its mobile phone counterpart Wireless Emergency Alerts (WEA), a different but related system. However, both the EAS and WEA, among other systems, are coordinated under the Integrated Public Alert and Warning System (IPAWS). The EAS, and more broadly IPAWS, allows federal, state, and local authorities to efficiently broadcast emergency alert and warning messages across multiple channels. The EAS became operational on January 1, 1997, after being approved by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in November 1994, replacing the Emergency Broadcast System (EBS), and largely supplanted Local Access Alert systems, though Local Access Alert systems are still used from time to time. Its main improvement over the EBS, and perhaps its most distinctive feature, is its application of a digitally encoded audio signal known as Specific Area Message Encoding (SAME), which is responsible for the characteristic "screeching" or "chirping" sounds at the start and end of each message. The first signal is the "header" which encodes, among other information, the alert type and locations, or the specific area that should receive the message. The last short burst marks the end-of-message. These signals are read by specialized encoder-decoder equipment. This design allows for automated station-to-station relay of alerts to only the area the alert was intended for.

A mixing console or mixing desk is an electronic device for mixing audio signals, used in sound recording and reproduction and sound reinforcement systems. Inputs to the console include microphones, signals from electric or electronic instruments, or recorded sounds. Mixers may control analog or digital signals. The modified signals are summed to produce the combined output signals, which can then be broadcast, amplified through a sound reinforcement system or recorded.

Scratching, sometimes referred to as scrubbing, is a DJ and turntablist technique of moving a vinyl record back and forth on a turntable to produce percussive or rhythmic sounds. A crossfader on a DJ mixer may be used to fade between two records simultaneously.

A recording studio is a specialized facility for recording and mixing of instrumental or vocal musical performances, spoken words, and other sounds. They range in size from a small in-home project studio large enough to record a single singer-guitarist, to a large building with space for a full orchestra of 100 or more musicians. Ideally, both the recording and monitoring spaces are specially designed by an acoustician or audio engineer to achieve optimum acoustic properties.

An acetate disc is a type of phonograph record generally used from the 1930s to the late 1950s for recording and broadcast purposes. Despite their name, "acetate" discs do not contain any acetate.
Broadcast automation incorporates the use of broadcast programming technology to automate broadcasting operations. Used either at a broadcast network, radio station or a television station, it can run a facility in the absence of a human operator. They can also run in a live assist mode when there are on-air personnel present at the master control, television studio or control room.

An equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure level, over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness when presented with pure steady tones. The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon and is arrived at by reference to equal-loudness contours. By definition, two sine waves of differing frequencies are said to have equal-loudness level measured in phons if they are perceived as equally loud by the average young person without significant hearing impairment.

In radio and television, broadcast delay is an intentional delay when broadcasting live material, technically referred to as a deferred live. Such a delay may be to prevent mistakes or unacceptable content from being broadcast. Longer delays lasting several hours can also be introduced so that the material is aired at a later scheduled time to maximize viewership. Tape delays lasting several hours can also be edited down to remove filler material or to trim a broadcast to the network's desired run time for a broadcast slot, but this is not always the case.
Transtar was the first radio network to provide 24-hour music programming to local affiliates. The slate of 24-hour networks is now owned by Westwood One and operated by Dial Global. The studios were located in Valencia, California.
Television crew positions are derived from those of film crew, but with several differences.

2-inch quadruplex videotape was the first practical and commercially successful analog recording video tape format. It was developed and released for the broadcast television industry in 1956 by Ampex, an American company based in Redwood City, California. The first videotape recorder using this format was built the same year. This format revolutionized broadcast television operations and television production, since the only recording medium available to the TV industry until then was motion picture film.

A loop bin duplicator is a specialized audio tape machine used in the duplication of pre-recorded audio cassettes and 8-track cartridges.
This glossary of terms used in broadcasting is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related to both radio and television broadcasting, along with the industry in general.

The Fidelipac, commonly known as a "NAB cartridge" or simply "cart", is a magnetic tape sound recording format, used for radio broadcasting for playback of material over the air such as radio commercials, jingles, station identifications, and music, and for indoor background music. Fidelipac is the official name of this industry standard audio tape cartridge. It was developed in 1954 by inventor George Eash, and commercially introduced in 1959 by Collins Radio Co. at the 1959 NAB Convention. The cartridge was often used at radio stations until the late 1990s, when such formats as MiniDisc and computerized broadcast automation predominated.

WSJM-FM is a commercial radio station licensed to Benton Harbor, Michigan and also serving nearby St. Joseph. The station broadcasts a News/Talk/Sports radio format. It is owned by Mid-West Family Broadcasting with studios on East Napier Avenue in Southwest Benton Harbor.
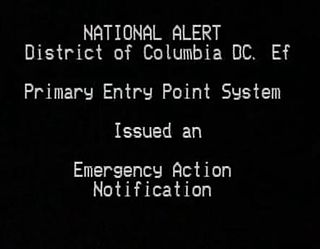
A National Emergency Message, formerly known until 2022 as an Emergency Action Notification, is the national activation of the Emergency Alert System (EAS) used to alert the residents of the United States of a national or global emergency such as a nuclear war or any other mass casualty situation. This alert can only be activated by the president of the United States or a designated representative thereof, such as the vice president. The Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) also carried the Emergency Action Notification. Except for the 2011 national test, which utilized the Emergency Action Notification alert type, no president has ever issued a National Emergency Message.