Cuenca Province was a province of Gran Colombia. With the 1824 reform of the subdivisions of Gran Colombia, it became part of the Azuay Department.
Cuenca Province was a province of Gran Colombia. With the 1824 reform of the subdivisions of Gran Colombia, it became part of the Azuay Department.

The Second Republic of Venezuela is the name used to refer to the reestablished Venezuelan Republic declared by Simón Bolívar on 7 August 1813. This declaration followed the defeat of Domingo Monteverde by Bolívar during the Admirable Campaign in the west and Santiago Mariño in his campaign in the east.
The Republic came to an end in the following year, when Caracas was reoccupied by the Royalists on 16 July 1814, after a series of defeats at the hands of José Tomás Boves.

Maynas is one of the eight provinces in the Loreto Region in northeastern Peru. Its capital, Iquitos, is also Loreto's regional capital and the largest city in the Peruvian Amazon Rainforest.
Cundinamarca may refer to:

A department is an administrative or political division in several countries. Departments are the first-level divisions of 11 countries, nine in the Americas and two in Africa. An additional 10 countries use departments as second-level divisions, eight in Africa, and one each in the Americas and Europe.

The Gran Colombia–Peru War of 1828 and 1829 was the first international conflict fought by the Republic of Peru, which had gained its independence from Spain in 1821, and Gran Colombia, that existed between 1819 and 1830.

La Gran Colombia University is a private university located in Bogotá, D.C., Colombia. It was founded on May 24, 1951, by Julio César García Valencia, recognized Colombian historian of the Twentieth century.

Gran Colombia, or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Panama, and Venezuela, along with parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil, and claimed the Essequibo region. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiographically to distinguish it from the current Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state.

La Libertad Province is a province of the Colombian Department of Boyacá. The province is formed by 4 municipalities. The province bears its name for the liberty gained from the Spanish Empire after the independence of Gran Colombia.

The Isthmus Department, or Department of Panama, was one of the departments of the Republic of Gran Colombia and later of the Republic of Colombia. It was created in 1824 and named after the Isthmus of Panama. It covered the territory of what is now the country of Panama and some coastal territories farther northward along the Caribbean shoreline of present-day Costa Rica and Nicaragua.
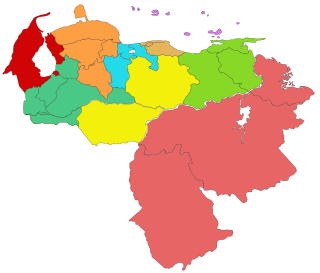
The Zulian Region is one of the 10 administrative regions into which Venezuela is divided for its development plans. This region is coterminous with Zulia State and is administrated by CORPOZULIA. The people from this region seek autonomy from the central government.
The Republic of Gran Colombia was a former independent country in northern South America, a post-Spanish colonial country that existed from 1819 to 1831. Its initial subdivisions, created in 1820, were revised and expanded in 1824 to 12 departments.

New Andalusia Province or Province of Cumaná (1537–1864) was a province of the Spanish Empire, and later of Gran Colombia and Venezuela. It included the territory of present-day Venezuelan states Sucre, Anzoátegui and Monagas. Its most important cities were the Capital City Cumaná and New Barcelona.
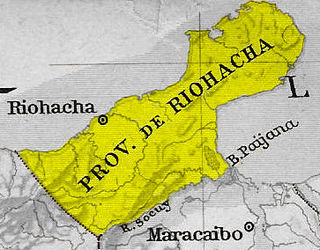
Riohacha Province was a province of Gran Colombia. With the 1824 changes in the subdivisions of Gran Colombia, it became part of Magdalena Department. Riohacha[a], is a city in the Riohacha Municipality in the northern Caribbean Region of Colombia by the mouth of the Ranchería River and the Caribbean Sea. Riohacha is the capital city of La Guajira Department.

Barcelona Province (1811–1864) was one of the provinces of Venezuela which signed the 1811 Venezuelan Declaration of Independence from the Spanish Empire. It became one of the provinces of Gran Colombia after Venezuela's independence from Gran Colombia in 1830. During the times of Gran Colombia, it was part of the Orinoco Department.

Neiva Province was one of the provinces of Gran Colombia. With the 1824 changes in the subdivisions of Gran Colombia, it became part of the Cundinamarca Department.

Carabobo Province (1824–1864) was one of the provinces of Gran Colombia, and later one of the provinces of Venezuela, after Venezuelan independence in 1830. It was split from Caracas Province. In Gran Colombia it belonged to the Venezuela Department which was created in 1824.

Apure Province was a province of Gran Colombia, and later one of the provinces of Venezuela, after Venezuelan independence in 1830. It was created in 1823, being split from Barinas Province, with the Uribante River and Apure River marking the border. The following year, Gran Colombia was reorganised into four Departments, with the Apure Department consisting of Apure Province and Barinas Province. Its capital was Achaguas, for which the Province was sometimes called Achaguas Province.

The Third Republic of Venezuela is the reestablished Republic of Venezuela declared by Simón Bolívar in the year 1817, during the Venezuelan War of Independence.
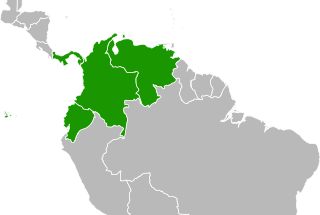
Reunification of Gran Colombia refers to the potential future reunification of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Panama under a single government. There have been attempts of reunification since 1903, when Panama separated from Colombia. People in favor for a reunification are called "unionistas" or unionists. In 2008, Hugo Chávez, president of Venezuela, announced the proposal of the political restoration of the Gran Colombia, under the Bolivarian revolution.

The Free Province of Guayaquil was a South American state that emerged between 1820 and 1822 with the independence of the province of Guayaquil from the Spanish monarchy. The free province had a provisional government and constitution until its annexation by Gran Colombia in 1822. Its successor was the Department of Guayaquil forming part of Gran Colombia.
The Spanish province of Guayaquil had been separated from the Viceroyalty of Peru and in those days it only depended legally on the court of the Real Audiencia de Quito. About a decade later, the Departments of Guayaquil, Azuay, and Ecuador separated from Gran Colombia forming the current Ecuador.