Related Research Articles
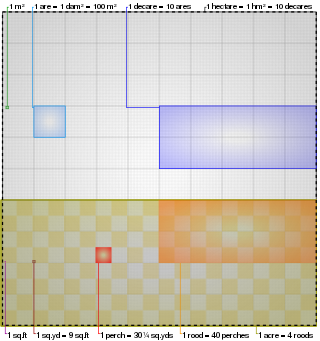
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one eighth of a mile, equivalent to any of 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in horse racing, where in many countries it is the standard measurement of race lengths, and agriculture, where it is used to measure rural field lengths and distances.
The rod, perch, or pole is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units it is defined as 16+1⁄2 feet, equal to exactly 1⁄320 of a mile, or 5+1⁄2 yards, and is exactly 5.0292 meters. The rod is useful as a unit of length because integer multiples of it can form one acre of square measure (area). The 'perfect acre' is a rectangular area of 43,560 square feet, bounded by sides 660 feet long and 66 feet wide or, equivalently, 40 rods by 4 rods. An acre is therefore 160 square rods or 10 square chains.

Hatillo is a town and municipality located in Puerto Rico's north coast, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Lares and Utuado to the south, Camuy to the west, and Arecibo to the east. According to the 2000 US Census Hatillo is spread over nine barrios and Hatillo Pueblo. It is part of the San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo Metropolitan Statistical Area.
The chain is a unit of length equal to 66 feet, used in both the US customary and Imperial unit systems. It is subdivided into 100 links. There are 10 chains in a furlong, and 80 chains in one statute mile. In metric terms, it is 20.1168 m long. By extension, chainage is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, as given by an odometer.
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the leuga, the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries.
There are a number of Spanish units of measurement of length or area that are virtually obsolete due to metrication. They include the vara, the cordel, the league and the labor. The units of area used to express the area of land are still encountered in some transactions in land today.

A manzana is a unit of area used in Argentina and in many Central American countries, originally defined as 10,000 square varas in Spanish customary units. In other Spanish-speaking regions, the term has the meaning of a city block.

Toro Negro State Forest is one of the 21 forests that make up the public forests system in Puerto Rico. It is also Puerto Rico's highest cloud forest. It is in the Cordillera Central region of the island and covers 8,204 cuerdas, of mountains. Toro Negro's mountains have heights reaching up to 4,400 feet (1,300 m) and include Cerro de Punta, Cerro Jayuya and Cerro Rosa, the three highest peaks in the island. Nested among these mountains is Lake Guineo, the island's highest lake. The forest has 18 kilometers (11 mi) of trails, an observation tower, two natural swimming pools (Spanish:"charcos"), camping and picnic areas, nine rivers, and numerous creeks and waterfalls. The forest spans areas within the municipalities of Ponce, Jayuya, Orocovis, Ciales, and Juana Díaz, and consists of seven non-contiguous tracts of land. The largest contiguous segment of the forest is located in the municipalities of Ponce and Jayuya. Some 40% of the area of Toro Negro State Forest is located in Ponce's Barrio Anón.
In Guatemala the metric system is official but it uses a mixture of U.S., metric and Spanish customary units.

Isla de Ratones is a small uninhabited island off the southern coast of Puerto Rico, off the coast of Ponce. The island is part of barrio Canas in the municipality of Ponce. The island gained attention in 2010 when the Puerto Rican Bird Society made it a target for the eradication of the black rat. While named as one single island, it is actually composed of two islands separated by a few feet of shallow water during high tide, which become a single island at low tide.

Isla de Jueyes are a group of three small uninhabited islands off the southern coast of Puerto Rico. Together with Caja de Muertos, Gatas, Morrillito, Ratones, Cardona, and Isla del Frío, Isla de Jueyes is one of seven islands ascribed to the municipality of Ponce. At an area of just 2.89 cuerdas, they are also the smallest of these seven islands. Like Isla del Frío, the islands are considered part of barrio Vayas.
The History of measurement systems in Pakistan begins in early Indus Valley civilization when pastoral societies used barter to exchange goods or services and needed units of measurement.
A number of units of measurement were used in Costa Rica to measure measurements in length, mass, area, capacity, etc. In Costa Rica, metric system has been adopted since 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, by a joint convention among Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Honduras for length, mass, volume etc. In Honduras, the metric system was adopted in 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, under a joint convention between Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and El Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Nicaragua to measure measurements in mass, area, volume, etc. In Nicaragua, the metric system was adopted in 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, by a joint convention between Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and El Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Paraguay to measure quantities including length, mass, area, capacity, etc. Metric system had been optional since 1890, and adopted since 1899 in Paraguay.
Several units of measurements are used in Puerto Rico. The units of measure in use in Puerto Rico are based on the United States customary units with two major exceptions: roadway distance signs are measured in kilometers and gasoline is sold by the liter.
The caballería was a unit of land measurement in the Spanish viceroyalties in the Americas during the times of the Spanish Empire in the 16th through 19th centuries. It was equivalent to 78.58 hectares. The unit came from Spain, where it had already been in use.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Archived at the WayBack Machine on 16 August 2013, from the original Units: C: cuerda. Russ Rowlett. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Units - Cuerda. Sizes.com. Puerto Rico Act 135, section 4 (page 100), 1913–14, as amended by Act No. 3, 1913–14: A cuerda, quote: "a unit of land area, approximately 3,930 square meters (approximately 0.971 acres)...In land measurements and records, the measurement by cuerda customarily used in Porto [sic] Rico...equivalent to 3,930.395625 square meters..."
- 1 2 Menocal Villagran, Juan Carlos (2011). "La Importancia para el Notario de Conocer el Sistema de Conversión de Medidas Agrarias al Sistema Métrico Décimal e Interpretatión Básica de Planos (Tesis)" (PDF) (in Spanish). Guatemala City: Facultad de Ciencias Jurídicas y Sociales, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala. pp. 66–8.