
Conservation and restoration of immovable cultural property describes the process through which the material, historical, and design integrity of any immovable cultural property are prolonged through carefully planned interventions. The individual engaged in this pursuit is known as an architectural conservator-restorer. Decisions of when and how to engage in an intervention are critical to the ultimate conservation-restoration of cultural heritage. Ultimately, the decision is value based: a combination of artistic, contextual, and informational values is normally considered. In some cases, a decision to not intervene may be the most appropriate choice.

The National Theatre of Albania was the main theatre in Tirana, Albania. In March 2020, the National Theatre of Albania was selected by Europa Nostra among the 7 most endangered monuments in Europe, as an exceptional example of modern Italian architecture from the 1930s and one of the most prominent cultural centers in Albania, facing impending threat of demolition. On 17 May 2020, the National Theatre building was demolished.
Holy Trinity Church of Lavdar, also known as the Holy Trinity Church of Tudas is a 15th century Albanian orthodox church built in the Byzantine style by the medieval Albanian noble family of Muzaka. It is located near the villages Lavdar and Tudas in the region of Opar in Korçë county, southeastern Albania. Noted for its distinguished architecture and frescoes, it was declared a Cultural Monument of Albania in 1963.

Despite being a relatively small country, Albania is exceedingly rich in biodiversity. Its ecosystems and habitats support over 5,550 species of vascular and non-vascular plants and more than 15,600 species of coniferous and non-coniferous evergreens, most of which are threatened at global and European levels. The country has made recent efforts to expand its network of protected areas which now include: 11 national parks, 1 marine park, 718 nature monuments, 23 managed nature reserves, 11 protected landscapes, 4 World Heritage Sites, 4 Ramsar sites and other protected areas of various categories, that when combined, account for 21.36% of the territory. Furthermore, a biosphere reserve, 45 important plant areas and 16 important bird areas are found in the country.

The Old Stone Bridge in Prizren is a cultural heritage monument in Prizren, Kosovo. This monument is of the "Archaeological" category, approved with number 2345/48.
Protected areas of Ukraine are special areas of Ukraine established with the goal of protecting the natural and cultural heritage of the country from excessive changes as a result of human activity. The protection of the areas is the responsibility of the government of Ukraine, specifically the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine.

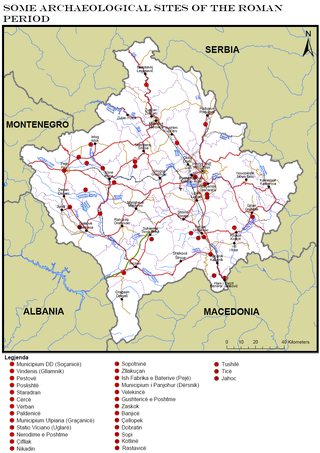
Archaeology of Kosovo as a field of study and research was started in the second half of the 20th century. Kosovo's field of archaeology has developed in tandem with the historical study, studies of ancient authors' sources, classic philological studies, theological data research, topographic studies and ground survey, analysis of toponyms, deciphering of epigraphic and historiographic data. First data about antique monuments in Kosovo, were documented from the end of the 19th until the beginning of the Second World War, a time period when Kosovo was visited by researchers, guides, and archaeologists such as: Evans, Boue, Hahn, Kanitz, Tomaschek, Domaschevski, Arpad, Vulic, Jirecek, Patsch, Domenico Mustilli, etc.

Kosovo is a partially recognized state and disputed territory located in the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The majority of Kosovars are ethnically Albanian. Kosovo has an expansive cultural heritage, including monuments, clothing items, museums, and traditional food.
Monuments of Kosovo comprise all the monuments that are located in Kosovo.
Part of a series of articles upon Archaeology of Kosovo
The cultural monuments of the Czech Republic are protected properties designated by the Ministry of Culture of the Czech Republic. Cultural monuments that constitute the most important part of the Czech cultural heritage may be declared national cultural monuments by a regulation of the Government of the Czech Republic. Government may also proclaim a territory, whose character and environment is determined by a group of immovable cultural monuments or archaeological finds, as a whole, as a monument reservation. Ministry of Culture may proclaim a territory of a settlement with a smaller number of cultural monuments, historical environment or part of a landscape area that display significant cultural values as a monument zone.
Mitrovica is one of the oldest settlements in Kosovo and a very important urban ensemble. There are many traces which have special interest and prove early civilization of the territory of Mitrovica, in particular from the Illyrian inhabitation in antiquity.

Historical monuments in Pristina are made up of 21 monuments out of a total of 426 protected monuments all over Kosovo. A large number of these monuments date back to the Byzantine and Ottoman periods. Since 1945, the Yugoslav authorities followed the idea of constructing a modern Pristina by relying in the urban development motto “destroy the old, build the new” and this resulted with major changes in the structure of the buildings, their function and their surrounding environment. However, numerous types of monuments have been preserved, including four mosques, a restored orthodox church, an Ottoman bath, a public fountain, a clock tower, several traditional houses as well as European-influenced architecture buildings such as the Museum of Kosovo. These symbolize the historical and cultural character of Pristina as it was developed throughout centuries in the spirit of conquering empires.
The architecture of Kosovo dates back to the Neolithic period and includes the Copper, Bronze and Iron Ages, Antiquity and the Medieval period. It has been influenced by the presence of different civilizations and religions as evidenced by the structures which have survived to this day. Local builders have combined building techniques of conquering empires with the materials at hand and the existing conditions to develop their own varieties of dwellings.

The Monumental Complex of the Albanian League of Prizren is a museum complex and cultural heritage monument located in the historic city of Prizren, Kosovo. This monument belongs to the "architectural" category, approved with number 414/77 and is under state protection. The Complex is now home to photographs, documents, objects, clothing and other cultural artifacts that date from the time of the League of Prizren.
The Vrućevce Mosque is a cultural heritage monument built in 1826 in Vrućevce, Kamenica, Kosovo. Built of clay-mortared stone, the mosque lies halfway between Vrućevce and Marovce, and the two villages share it as a place of worship. There is no minaret.

The Architectural complex in Maletaj is a cultural heritage monument located in Maletaj (Gumnisht), Vushtrri, Kosovo. This monument is of the "Architectural" category, approved with number.

The Mazhiq Mosque or the Mosque of Mazhiq is a cultural heritage monument of Kosovo, located 13 km from Mitrovica, in the village of Mazhiq. The mosque was built around the 15th century and today is almost fully destroyed, having lost its original function. This monument is classified as "architectural" and has been approved with the number 004 in the list of monuments of Kosovo. Together with St. Peter's Basilica Church in Stantërg, located around 2 km away and also in ruins, they stand as important religious and cultural landmarks in the region of Shala e Bajgorës.











