A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a system of money in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound Sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies.

In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.

A banknote—also called a bill, paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commercial banks, which were legally required to redeem the notes for legal tender when presented to the chief cashier of the originating bank. These commercial banknotes only traded at face value in the market served by the issuing bank. Commercial banknotes have primarily been replaced by national banknotes issued by central banks or monetary authorities.

Legal tender is a form of money that courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which when offered ("tendered") in payment of a debt extinguishes the debt. There is no obligation on the creditor to accept the tendered payment, but the act of tendering the payment in legal tender discharges the debt.
MEI Conlux is a manufacturer of electronic banknote validators, coin acceptors and changers. MEI was spun off to private investment interests in July 2006. In December 2012, it was sold to Crane Co., which also manufactures vending machines. A new division was created inside the company by merging former CPS and MEI into CPI.
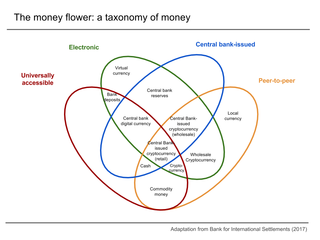
Digital currency is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital currencies include cryptocurrency, virtual currency and central bank digital currency. Digital currency may be recorded on a distributed database on the internet, a centralized electronic computer database owned by a company or bank, within digital files or even on a stored-value card.

Skrill is part of Paysafe Limited (“Paysafe”) (PSFE.WS), a global payments platform. Skrill is one of its digital wallet brands and was established in 2001 to offer multiple online payment and money transfer services.
A currency detector or currency validator is a device that determines whether notes or coins are genuine or counterfeit. These devices are used in a wide range of automated machines, such as retail kiosks, supermarket self checkout machines, arcade gaming machines, payphones, launderette washing machines, car park ticket machines, automatic fare collection machines, public transport ticket machines, and vending machines.

Crane Co. is an American industrial products company based in Stamford, Connecticut. Founded by Richard Teller Crane in 1855, it became one of the leading manufacturers of bathroom fixtures in the United States, until 1990, when that division was sold off. In 1960 it began the process of becoming a holding company with a diverse portfolio. Its business segments are Aerospace & Electronics, Engineered Materials, Payment and Merchandising Technology, Fluid Handling, and Controls. Industries served by these segments include chemical industries, commercial construction, food and beverage, general and commercial aviation, and power generation.

Crane Currency supplies central banks with design services, currency papers, and banknote printing services as well as anti-counterfeiting technology to issuing authorities and brand owners.

A debate exists within the United States government and American society at large over whether the one-cent coin, the penny, should be eliminated as a unit of currency in the United States. The penny costs more to produce than the one cent it is worth, meaning the seigniorage is negative – the government loses money on every penny that is created. Several bills introduced in the U.S. Congress would have ceased production of pennies, but none have been approved. Such bills would leave the five-cent coin, or nickel, as the lowest-value coin minted in the United States.

Fractional currency, also referred to as shinplasters, was introduced by the United States federal government following the outbreak of the Civil War. These low-denomination banknotes of the United States dollar were in use between 21 August 1862 and 15 February 1876, and issued in denominations of 3, 5, 10, 15, 25, and 50 cents across five issuing periods. The complete type set below is part of the National Numismatic Collection, housed at the National Museum of American History, part of the Smithsonian Institution.

Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are: medium of exchange, a unit of account, a store of value and sometimes, a standard of deferred payment.

A currency-counting machine is a machine that counts money—either stacks of banknotes or loose collections of coins. Counters may be purely mechanical or use electronic components. The machines typically provide a total count of all money, or count off specific batch sizes for wrapping and storage.

The United States dollar is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100 cents, and authorized the minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color.

GRG Banking is a Chinese listed enterprise, specialized in the financial self-service industry. GRG Banking is engaged in research and development, manufacturing, sales and service, software development for automated teller machines, AFCs(Automated fare collection) and other currency recognition and processing equipment.
Ripple is a real-time gross settlement system, currency exchange and remittance network that is open to financial institutions worldwide and was created by Ripple Labs Inc., a US-based technology company. Released in 2012, Ripple is built upon a distributed open source protocol, and supports tokens representing fiat currency, cryptocurrency, commodities, or other units of value such as frequent flier miles or mobile minutes. Ripple purports to enable "secure, instantly and nearly free global financial transactions of any size with no chargebacks". The ledger employs the native cryptocurrency known as XRP.

BitPay is a bitcoin payment service provider headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. It was founded in May 2011 by Tony Gallippi and Stephen Pair. BitPay provides Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash payment processing services for merchants.
Ripple Labs, Inc. is an American technology company which develops the Ripple payment protocol and exchange network. Originally named Opencoin and renamed in 2015, the company was founded in 2012 and is based in San Francisco, California.














