Related Research Articles

Uintah County is a county in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2010 United States Census the population was 32,588. Its county seat and largest city is Vernal. The county was named for the portion of the Ute Indian tribe that lived in the basin.

Fort Duchesne is a census-designated place (CDP) in Uintah County, Utah, United States. The population was 714 at the 2010 census, an increase from the 2000 figure of 621.

Ute are the Indigenous people of the Ute tribe and culture among the Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin. They had lived in sovereignty in the regions of present-day Utah and Colorado in the Southwestern United States for many centuries until European settlers colonized their lands. The state of Utah is named after the Ute tribe.
Chief Walkara was a Shoshone leader of the Utah Indians known as the Timpanogo and Sanpete Band. It is not completely clear what cultural group the Utah or Timpanogo Indians belonged to, but they are listed as Shoshone. He had a reputation as a diplomat, horseman and warrior, and a military leader of raiding parties, and in the Wakara War.
The Ute Mountain Ute Tribe is one of three federally recognized tribes of the Ute Nation, and are mostly descendants of the historic Weeminuche Band who moved to the Southern Ute reservation in 1897. Their reservation is headquartered at Towaoc, Colorado on the Ute Mountain Ute Indian Reservation in southwestern Colorado, northwestern New Mexico and small sections of Utah.

Meeker Massacre and the White River War, Ute War, or the Ute Campaign, were conflicts that began when the Utes attacked an Indian agency on September 29, 1879, killing the Indian agent Nathan Meeker and his 10 male employees for his misdeeds, and then took women and children as hostages. United States Army forces were called in from Fort Steele in Wyoming. Following the killing of Meeker and others, there was a Ute attack at Milk Creek on U.S. troops led by Major Thomas T. Thornburgh, which killed the major and 13 troops within minutes. Relief troops were called in, which resulted in a further conflict of the Utes trying to regain their lands.
The Tintic War was a short series of skirmishes occurring in February 1856 in the Tintic and Cedar Valleys of Utah, occurring after the conclusion of the Walker War. It was named after a subchief of the Ute and involved several clashes between settlers and natives, mostly over the natives' theft of cattle because of drought.

The Southern Ute Indian Reservation is a Native American reservation in southwestern Colorado near the northern New Mexico state line. Its territory consists of land from three counties; in descending order of surface area they are La Plata, Archuleta, and Montezuma Counties. The reservation has a land area of 1,058.785 sq mi (2,742.24 km²). Its largest communities are Ignacio and Arboles. The only other community that is recognized as a separate place by the Census Bureau is the CDP of Southern Ute, which lies just southeast of Ignacio.
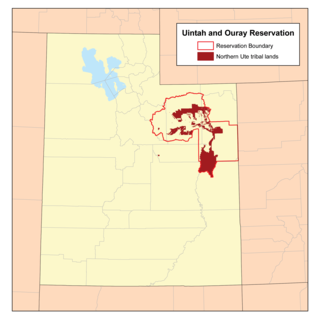
The Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation is located in northeastern Utah, United States. It is the homeland of the Ute Indian Tribe, and is the largest of three Indian reservations inhabited by members of the Ute Tribe of Native Americans.

The Uinta Basin is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains forms the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold.

The Black Hawk War, or Black Hawk's War, is the name of the estimated 150 battles, skirmishes, raids, and military engagements taking place from 1865 to 1872, primarily between Mormon settlers in Sanpete County, Sevier County and other parts of central and southern Utah, and members of 16 Ute, Southern Paiute, Apache and Navajo tribes, led by a local Ute war chief, Antonga Black Hawk. The conflict resulted in the abandonment of some settlements and hindered Mormon expansion in the region.

The Ute Indian Tribe of the Uinta and Ouray Reservation is a Federally Recognized Tribe of Indians in northeastern Utah, United States. Three bands of Utes comprise the Ute Indian Tribe: the Whiteriver Band, the Uncompahgre Band and the Uintah Band. The Tribe has a membership of more than three thousand individuals, with over half living on the Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation. The Ute Indian Tribe operates its own tribal government and oversees approximately 1.3 million acres of trust land which contains significant oil and gas deposits.
The Northern Ute Tribe is one of three ethnically-related Ute Tribes. The Northern Ute Tribe occupies and administers the Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation in northeastern Utah. The population of the Northern Ute Tribe is approximately 3,500.

The Timpanogos were a tribe of Native Americans who inhabited a large part of central Utah—particularly, the area from Utah Lake eastward to the Uinta Mountains and south into present-day Sanpete County. In some accounts they were called the Timpiavat, Timpanogot, Timpanogotzi, Timpannah, Tempenny and other names. During the mid-19th century, when Mormon pioneers entered the territory, the Timpanogos were one of the principal tribes in Utah based on population, area occupied and influence. Scholars have had difficulty identifying their language; most communication was carried out in Spanish or English, and many of their leaders spoke several native dialects of the Numic branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family.

Pahvant was a band of Ute people that lived in present-day Utah. Called the "Water People", they fished and hunted waterfowl. They were also farmers and hunter-gatherers. In the 18th century they were known to be friendly and attentive, but after a chief's father was killed by emigrating white settlers, a group of Pahvant Utes killed John Williams Gunnison and seven of his men during his exploration of the area. The bodies of water of their homeland were dried up after Mormons had diverted the water for irrigation. Having intermarried with the Paiutes, they were absorbed into the Paiute Indian Tribe of Utah and relocated to reservations.
White River Utes are a Native American band, made of two earlier bands, the Yampa from the Yampa River Valley and the Parianuche Utes who lived along the Grand Valley in Colorado and Utah.

Chipeta or White Singing Bird was a Native American woman, and the second wife of Chief Ouray of the Uncompahgre Ute tribe. Born a Kiowa Apache, she was raised by the Utes in what is now Conejos, Colorado. An advisor and confidant of her husband, Chipeta continued as a leader of her people after his death in 1880.
The Uintah tribe, once a small band of the Ute people, and now is a tribe of multiple bands of Utes that were classified as Uintahs by the U.S. government when they were relocated to the Ute Indian Tribe of the Uintah and Ouray Reservation. The bands included the San Pitch, Pahvant, Seuvartis, Timpanogos and Cumumba Utes.

The San Pitch Utes were members of a band of Ute people that lived in the Sanpete Valley and Sevier River Valley and along the San Pitch River. They may have originally been Shoshonean, and were generally considered as part of the Timpanogos.

The Seuvarits Utes are a band of the Northern Ute tribe of Native Americans that traditionally inhabited the area surrounding present-day Moab, Utah, near the Grand River and the Green River. The Seuvarits were among the Ute bands that were involved in the Black Hawk War. The Seuvarits and other Ute bands were eventually relocated onto reservations by the United States government after their population severely declined after exposure to disease and war during the latter half of the 19th century.
References
- 1 2 Bakken, Gordon Morris; Kindell, Alexandra (February 24, 2006). "Utes". Encyclopedia of Immigration and Migration in the American West. SAGE. ISBN 978-1-4129-0550-3.