Related Research Articles
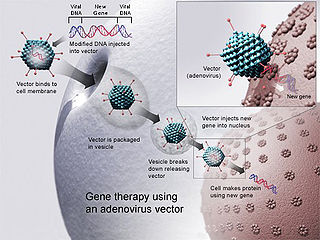
Human genetic enhancement or human genetic engineering refers to human enhancement by means of a genetic modification. This could be done in order to cure diseases, prevent the possibility of getting a particular disease, to improve athlete performance in sporting events, or to change physical appearance, metabolism, and even improve physical capabilities and mental faculties such as memory and intelligence. These genetic enhancements may or may not be done in such a way that the change is heritable.

Medical research, also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research", – involving fundamental scientific principles that may apply to a preclinical understanding – to clinical research, which involves studies of people who may be subjects in clinical trials. Within this spectrum is applied research, or translational research, conducted to expand knowledge in the field of medicine.

Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug. The entire process – from concept through preclinical testing in the laboratory to clinical trial development, including Phase I–III trials – to approved vaccine or drug typically takes more than a decade.

The Children's Tumor Foundation (CTF) is a 501(c)(3) foundation dedicated to improving the health and well-being of individuals and families affected by NF, a group of genetic conditions known as neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis. Their four-part mission includes propelling drug research and development through a series of strategic investments, strengthening patient support, increasing public awareness of NF and establishing best practices in clinical care for affected individuals. The Foundation is incorporated in all 50 states with active chapters and affiliates in 37 states. CTF is the largest private funder of all forms of NF research.

The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research aims to find a cure for Parkinson's disease (PD) founded in 2000 by Michael J. Fox. It concentrates on funding research and ensuring the development of improved therapies for people with Parkinson's.

The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) is one of the world's largest nonprofit organization serving people with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. The NPF provides information and services to help people manage their condition while supporting research to find a cure. In addition to serving more than 3 million people annually through patient and professional health education and advocacy initiatives, the NPF has funded more than $10 million in psoriatic disease research grants and fellowships.

The ALS Association is an American nonprofit organization that funds global amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) research, provides care services and programs to people affected by ALS through its nationwide network of chapters, and works with ALS advocates around the country for state and federal policies that serve people living with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease. The ALS Association is broken up into distinct chapters, each servicing a particular geographic area of the United States and all working under the umbrella of a national charter and administrator.
Alzheimer's Research UK (ARUK) is a dementia research charity in the United Kingdom, founded in 1992 as the Alzheimer's Research Trust.
Alzheimer Research Forum (ARF), or Alzforum is a website which uses web technology to accelerate research into Alzheimer's disease.
Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) is a multisite study that aims to improve clinical trials for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). This cooperative study combines expertise and funding from the private and public sector to study subjects with AD, as well as those who may develop AD and controls with no signs of cognitive impairment. Researchers at 63 sites in the US and Canada track the progression of AD in the human brain with neuroimaging, biochemical, and genetic biological markers. This knowledge helps to find better clinical trials for the prevention and treatment of AD. ADNI has made a global impact, firstly by developing a set of standardized protocols to allow the comparison of results from multiple centers, and secondly by its data-sharing policy which makes available all at the data without embargo to qualified researchers worldwide. To date, over 1000 scientific publications have used ADNI data. A number of other initiatives related to AD and other diseases have been designed and implemented using ADNI as a model. ADNI has been running since 2004 and is currently funded until 2021.

Rudolph Emile 'Rudy' Tanzi is the Joseph P. and Rose F. Kennedy Professor of Neurology at Harvard University, Vice-chair of Neurology, Director of the Genetics and Aging Research Unit, and co-director of the Henry and Allison McCance Center for Brain Health at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Dr. Tanzi has been investigating the genetics of neurological disease since the 1980s when he participated in the first study that used genetic markers to find a disease gene. Dr. Tanzi co-discovered all three familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease (FAD) genes and several other neurological disease genes including that responsible for Wilson’s disease. As the leader of the Cure Alzheimer's Fund Alzheimer's Genome Project, Dr. Tanzi has carried out multiple genome wide association studies of thousands of Alzheimer's families leading to the identification of novel AD candidate genes, including CD33 and the first two rare mutations causing late-onset AD in the ADAM10 gene. His research on the role of zinc and copper in AD has led to clinical trials at Prana Biotechnology. He is also working on gamma secretase modulators for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's. He also serves as Chair of the Cure Alzheimer's Fund Research Leadership Group and Director the Cure Alzheimer's Fund Alzheimer's Genome Project™.
Translational bioinformatics (TBI) is a field that emerged in the 2010s to study health informatics, focused on the convergence of molecular bioinformatics, biostatistics, statistical genetics and clinical informatics. Its focus is on applying informatics methodology to the increasing amount of biomedical and genomic data to formulate knowledge and medical tools, which can be utilized by scientists, clinicians, and patients. Furthermore, it involves applying biomedical research to improve human health through the use of computer-based information system. TBI employs data mining and analyzing biomedical informatics in order to generate clinical knowledge for application. Clinical knowledge includes finding similarities in patient populations, interpreting biological information to suggest therapy treatments and predict health outcomes.
The Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF) is a nonprofit organization founded in 1998 by co-chairmen Leonard A. Lauder and Ronald S. Lauder of the Estée Lauder Companies cosmetics family and led by Howard Fillit, a geriatrician and neuroscientist. The ADDF provides funding to scientists who are conducting promising, innovative Alzheimer's disease drug research worldwide. The ADDF funds early-stage research and early-phase clinical trials that might otherwise go unfunded. By supporting research projects around the world, it seeks to increase the chances of finding treatments for Alzheimer's disease, related dementias and cognitive aging. The ADDF has invested nearly $65 million to fund some 450 Alzheimer's drug discovery programs and clinical trials in academic centers and biotechnology companies in 18 countries.
Translational neuroscience is the field of study which applies neuroscience research to translate or develop into clinical applications and novel therapies for nervous system disorders. The field encompasses areas such as deep brain stimulation, brain machine interfaces, neurorehabilitation and the development of devices for the sensory nervous system such as the use of auditory implants, retinal implants, and electronic skins.
Multiple Sclerosis Discovery Forum (MSDF) is a non-profit online resource created to speed progress toward a cure for multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases by enabling faster sharing of information and free discussion among MS researchers in academia, industry, and the clinic.

Giulio Maria Pasinetti is the Program Director of the Center on Molecular Integrative Neuroresilience and is the Saunders Family Chair in Neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS) in New York City. Pasinetti is a Professor of Neurology, Psychiatry, Neuroscience, and Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine at ISMMS.

Alzheon is an American clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company based in Framingham, Massachusetts. The company is developing medicines for patients with Alzheimer's disease and other neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Robert David Moir was an Australian-born medical research scientist who theorized that the over-accumulation of beta-amyloid, which had formed to protect the brain against microbes, aided the development of Alzheimer's disease in the human brain.

Simufilam (PTI-125) is an Investigational New Drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It is being developed by the American pharmaceutical firm Cassava Sciences. The drug is in phase III clinical trials as of October 2023. There are two phase III clinical studies: RETHINK-ALZ, a 52-week trial, is set to complete in 2024, and REFOCUS-ALZ, spanning 76 weeks, is projected to finish in 2025.
Alzheimer's disease (AD) in African Americans is becoming a rising topic of interest in AD care, support, and scientific research, as African Americans are disproportionately affected by AD. Recent research on AD has shown that there are clear disparities in the disease among racial groups, with higher prevalence and incidence in African Americans than the overall average. Pathologies for Alzheimer’s also seem to manifest differently in African Americans, including with neuroinflammation markers, cognitive decline, and biomarkers. Although there are genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s, these account for few cases in all racial groups.
References
- ↑ GuideStar. Archived 2015-02-15 at the Wayback Machine . Accessed 26 March 2014.
- ↑ Better Business Bureau. Archived 2014-05-04 at the Wayback Machine . Accessed 26 March 2014.
- ↑ Charity Navigator. . Accessed 5 March 2014.
- ↑ Cure Alzheimer's Fund
- ↑ Tjan, Anthony. "Can the VC Model Help Cure Alzheimer's?". HuffPost. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ↑ Cure Alzheimer's Fund. . Accessed March 5, 2014.
- ↑ "Cure Alzheimer's Fund donates $5.4 million". Massachusetts General Hospital. October 26, 2012. Retrieved October 19, 2019.
- ↑ Don Seifferi (May 3, 2013). "Betting on a cure for Alzheimer's". Boston Business Journal. Retrieved October 19, 2019.
- ↑ Alice Park (November 3, 2008). "The Top 10 Everything of 2008". Time . Retrieved October 19, 2019.
- ↑ "Charity Navigator - Rating for Cure Alzheimer's Fund". Charity Navigator.