A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a system of money in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies.
Special drawing rights are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). SDRs are units of account for the IMF, and not a currency per se. They represent a claim to currency held by IMF member countries for which they may be exchanged. SDRs were created in 1969 to supplement a shortfall of preferred foreign exchange reserve assets, namely gold and U.S. dollars. The ISO 4217 currency code for special drawing rights is XDR and the numeric code is 960.

The renminbi is the official currency of the People's Republic of China. It is the world's 5th most traded currency as of April 2022.

A reserve currency is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international transactions, international investments and all aspects of the global economy. It is often considered a hard currency or safe-haven currency.

In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of the euro.
The Hong Kong dollar is the official currency of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. It is subdivided into 100 cents or 1000 mils. The Hong Kong Monetary Authority is the monetary authority of Hong Kong and the Hong Kong dollar.
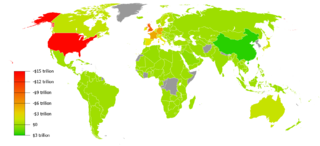
In international economics, the balance of payments of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. In other words, it is economic transactions between countries during a period of time. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.
The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
The Yuan is the base unit of a number of former and present-day currencies in Chinese.

Dynamic currency conversion (DCC) or cardholder preferred currency (CPC) is a process whereby the amount of a credit card transaction is converted at the point of sale, ATM or internet to the currency of the card's country of issue. DCC is generally provided by third party operators in association with the merchant, and not by a card issuer. Card issuers permit DCC operators to offer DCC in accordance with the card issuers' processing rules. However, using DCC, the customer is usually charged an amount in excess of the transaction amount converted at the normal exchange rate, though this may not be obviously disclosed to the customer at the time. The merchant, the merchant's bank or ATM operator usually impose a markup on the transaction, in addition to the exchange rate that would normally apply, sometimes by as much as 18%.
A freight forwarder or forwarding agent is a person or a company who co-ordinates and organizes the movement of shipments on behalf of a shipper by liaising with carriers. The carriers may use a variety of shipping modes, including ships, airplanes, trucks, and railroads, and often use multiple modes for a single shipment. A freight forwarder does not move the goods but acts as an agent in the logistics network and will carry out freight consolidation, rate negotiations, shipment tracking, customs and other documentation, among other tasks. FIATA describes a freight forwarder as the "Architect of transport".
This is a partial list of notable price fixing and bid rigging cases.

Currency intervention, also known as foreign exchange market intervention or currency manipulation, is a monetary policy operation. It occurs when a government or central bank buys or sells foreign currency in exchange for its own domestic currency, generally with the intention of influencing the exchange rate and trade policy.
Central bank liquidity swap is a type of currency swap used by a country's central bank to provide liquidity of its currency to another country's central bank. In a liquidity swap, the lending central bank uses its currency to buy the currency of another borrowing central bank at the market exchange rate, and agrees to sell the borrower's currency back at a rate that reflects the interest accrued on the loan. The borrower's currency serves as collateral.

This article includes a list of China's historical gross domestic product (GDP) values, the market value of all final goods and services produced by a nation in a given year. The GDP dollar estimates presented here are either calculated at market or government official exchange rates (nominal), or derived from purchasing power parity (PPP) calculations. This article also includes historical GDP growth.

Renminbi currency value is a debate affecting the Chinese currency unit, the renminbi. The renminbi is classified as a fixed exchange rate currency "with reference to a basket of currencies", which has drawn attention from nations which have freely floated currency and has become a source of trade friction with Western nations.

The United States dollar was established as the world's foremost reserve currency by the Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944. It claimed this status from sterling after the devastation of two world wars and the massive spending of the United Kingdom's gold reserves. Despite all links to gold being severed in 1971, the dollar continues to be the world's foremost reserve currency. Furthermore, the Bretton Woods Agreement also set up the global post-war monetary system by setting up rules, institutions and procedures for conducting international trade and accessing the global capital markets using the US dollar.
Since the late-2000s, the People's Republic of China (PRC) has sought to internationalize its official currency, the Renminbi (RMB). RMB internationalization accelerated in 2009 when China established the dim sum bond market and expanded Cross-Border Trade RMB Settlement Pilot Project, which helps establish pools of offshore RMB liquidity. The RMB was the 8th-most-traded currency in the world in 2013 and the 7th-most-traded in early 2014. By the end of 2014, RMB ranked 5th as the most traded currency, according to SWIFT's report, at 2.2% of SWIFT payment behind JPY (2.7%), GBP (7.9%), EUR (28.3%) and USD (44.6%). In February 2015, RMB became the second most used currency for trade and services, and reached the ninth position in forex trading. The RMB Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor (RQFII) quotas were also extended to five other countries — the UK, Singapore, France, Korea, Germany, and Canada, each with the quotas of ¥80 billion except Canada and Singapore (¥50bn). Previously, only Hong Kong was allowed, with a ¥270 billion quota.
In 1945, China cofounded the International Monetary Fund (IMF) with 34 other nations. China was initially represented by the Republic of China. In April 1980, representation transferred to the People's Republic of China. The Chinese-IMF relationship mainly operates around affairs associated with IMF governance and the IMF Special Drawing Rights (SDR).








