Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or another organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information.

Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single SSO ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems.
Identity and access management or Identity management (IdM), is a framework of policies and technologies to ensure that the right users have the appropriate access to technology resources. IAM systems fall under the overarching umbrellas of IT security and data management. Identity and access management systems not only identify, authenticate, and control access for individuals who will be utilizing IT resources but also the hardware and applications employees need to access.
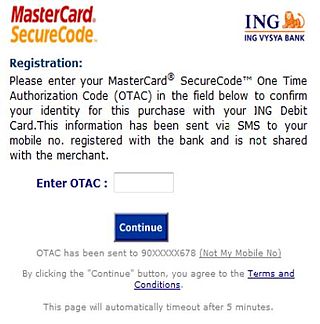
A one-time password (OTP), also known as a one-time PIN, one-time passcode, one-time authorization code (OTAC) or dynamic password, is a password that is valid for only one login session or transaction, on a computer system or other digital device. OTPs avoid several shortcomings that are associated with traditional (static) password-based authentication; a number of implementations also incorporate two-factor authentication by ensuring that the one-time password requires access to something a person has as well as something a person knows.

Shibboleth is a single sign-on log-in system for computer networks and the Internet. It allows people to sign in using just one identity to various systems run by federations of different organizations or institutions. The federations are often universities or public service organizations.
A digital identity is data stored on computer systems relating to an individual, organization, application, or device. For individuals, it involves the collection of personal data that is essential for facilitating automated access to digital services, confirming one's identity on the internet, and allowing digital systems to manage interactions between different parties. It is a component of a person's social identity in the digital realm, often referred to as their online identity.
The eCRM or electronic customer relationship management encompasses all standard CRM functions with the use of the net environment i.e., intranet, extranet and internet. Electronic CRM concerns all forms of managing relationships with customers through the use of information technology (IT).
Appointment scheduling software or meeting scheduling tools allows businesses and professionals to manage appointments and bookings. This type of software is also known as appointment booking software and online booking software.
Electronic authentication is the process of establishing confidence in user identities electronically presented to an information system. Digital authentication, or e-authentication, may be used synonymously when referring to the authentication process that confirms or certifies a person's identity and works. When used in conjunction with an electronic signature, it can provide evidence of whether data received has been tampered with after being signed by its original sender. Electronic authentication can reduce the risk of fraud and identity theft by verifying that a person is who they say they are when performing transactions online.
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PET) are technologies that embody fundamental data protection principles by minimizing personal data use, maximizing data security, and empowering individuals. PETs allow online users to protect the privacy of their personally identifiable information (PII), which is often provided to and handled by services or applications. PETs use techniques to minimize an information system's possession of personal data without losing functionality. Generally speaking, PETs can be categorized as either hard or soft privacy technologies.

An information card is a personal digital identity that people can use online, and the key component of an identity metasystem. Visually, each i-card has a card-shaped picture and a card name associated with it that enable people to organize their digital identities and to easily select one they want to use for any given interaction. The information card metaphor has been implemented by identity selectors like Windows CardSpace, DigitalMe or Higgins Identity Selector.
Web access management (WAM) is a form of identity management that controls access to web resources, providing authentication management, policy-based authorizations, audit and reporting services (optional) and single sign-on convenience.

"Cloud computing is a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to ISO.

Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.
Cloud computing security or, more simply, cloud security, refers to a broad set of policies, technologies, applications, and controls utilized to protect virtualized IP, data, applications, services, and the associated infrastructure of cloud computing. It is a sub-domain of computer security, network security, and, more broadly, information security.

A Microsoft account or MSA is a single sign-on personal user account for Microsoft customers to log in to consumer Microsoft services, devices running on one of Microsoft's current operating systems, and Microsoft application software.
A personal data service (PDS) gives the user a central point of control for their personal information. The user's data attributes being managed by the service may be stored in a co-located repository, or they may be stored in multiple external distributed repositories, or a combination of both. Attributes from a PDS may be accessed via an API. Users of the same PDS instance may be allowed to selectively share sets of attributes with other users. A data ecosystem is developing where such sharing among projects or "operators" may become practicable.
Do Not Track legislation protects Internet users' right to choose whether or not they want to be tracked by third-party websites. It has been called the online version of "Do Not Call". This type of legislation is supported by privacy advocates and opposed by advertisers and services that use tracking information to personalize web content. Do Not Track (DNT) is a formerly official HTTP header field, designed to allow internet users to opt-out of tracking by websites—which includes the collection of data regarding a user's activity across multiple distinct contexts, and the retention, use, or sharing of that data outside its context. Efforts to standardize Do Not Track by the World Wide Web Consortium did not reach their goal and ended in September 2018 due to insufficient deployment and support.

Banking as a service (BaaS) is the provision of banking products to non-bank third parties through APIs.
A data management platform (DMP) is a software platform used for collecting and managing data. DMPs allow businesses to identify audience segments, which can be used to target specific users and contexts in online advertising campaigns. They may use big data and artificial intelligence algorithms to process and analyze large data sets about users from various sources. Advantages of using DMPs include data organization, increased insight on audiences and markets, and more effective advertisement budgeting. On the other hand, DMPs often have to deal with privacy concerns due to the integration of third-party software with private data. This technology is continuously being developed by global entities such as Nielsen and Oracle.







