The centimetre–gram–second system of units is a variant of the metric system based on the centimetre as the unit of length, the gram as the unit of mass, and the second as the unit of time. All CGS mechanical units are unambiguously derived from these three base units, but there are several different ways in which the CGS system was extended to cover electromagnetism.
In mathematics, the determinant is a scalar-valued function of the entries of a square matrix. The determinant of a matrix A is commonly denoted det(A), det A, or |A|. Its value characterizes some properties of the matrix and the linear map represented, on a given basis, by the matrix. In particular, the determinant is nonzero if and only if the matrix is invertible and the corresponding linear map is an isomorphism.
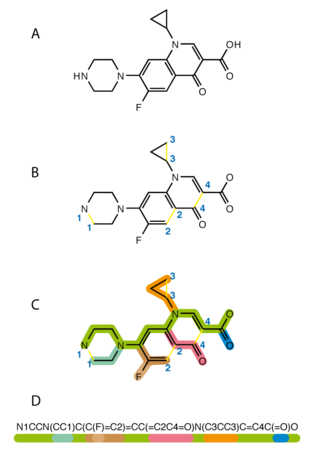
The Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES) is a specification in the form of a line notation for describing the structure of chemical species using short ASCII strings. SMILES strings can be imported by most molecule editors for conversion back into two-dimensional drawings or three-dimensional models of the molecules.

In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances. However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables.
In fluid dynamics, the Darcy–Weisbach equation is an empirical equation that relates the head loss, or pressure loss, due to friction along a given length of pipe to the average velocity of the fluid flow for an incompressible fluid. The equation is named after Henry Darcy and Julius Weisbach. Currently, there is no formula more accurate or universally applicable than the Darcy-Weisbach supplemented by the Moody diagram or Colebrook equation.

A longest common subsequence (LCS) is the longest subsequence common to all sequences in a set of sequences. It differs from the longest common substring: unlike substrings, subsequences are not required to occupy consecutive positions within the original sequences. The problem of computing longest common subsequences is a classic computer science problem, the basis of data comparison programs such as the diff utility, and has applications in computational linguistics and bioinformatics. It is also widely used by revision control systems such as Git for reconciling multiple changes made to a revision-controlled collection of files.

The asymptotic gain model is a representation of the gain of negative feedback amplifiers given by the asymptotic gain relation:
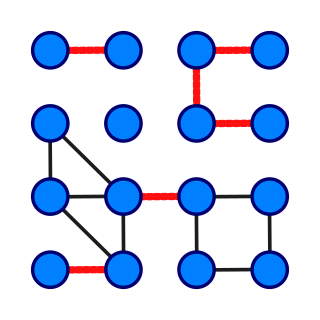
In graph theory, a bridge, isthmus, cut-edge, or cut arc is an edge of a graph whose deletion increases the graph's number of connected components. Equivalently, an edge is a bridge if and only if it is not contained in any cycle. For a connected graph, a bridge can uniquely determine a cut. A graph is said to be bridgeless or isthmus-free if it contains no bridges.
In coding theory, a linear code is an error-correcting code for which any linear combination of codewords is also a codeword. Linear codes are traditionally partitioned into block codes and convolutional codes, although turbo codes can be seen as a hybrid of these two types. Linear codes allow for more efficient encoding and decoding algorithms than other codes.
Many letters of the Latin alphabet, both capital and small, are used in mathematics, science, and engineering to denote by convention specific or abstracted constants, variables of a certain type, units, multipliers, or physical entities. Certain letters, when combined with special formatting, take on special meaning.
Rietveld refinement is a technique described by Hugo Rietveld for use in the characterisation of crystalline materials. The neutron and X-ray diffraction of powder samples results in a pattern characterised by reflections at certain positions. The height, width and position of these reflections can be used to determine many aspects of the material's structure.
A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a "mirrored" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current.

In hyperbolic geometry, a hypercycle, hypercircle or equidistant curve is a curve whose points have the same orthogonal distance from a given straight line.

In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins C1/C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPC gene.
In combinatorial optimization, the Gomory–Hu tree of an undirected graph with capacities is a weighted tree that represents the minimum s-t cuts for all s-t pairs in the graph. The Gomory–Hu tree can be constructed in |V| − 1 maximum flow computations. It is named for Ralph E. Gomory and T. C. Hu.
Symbolic circuit analysis is a formal technique of circuit analysis to calculate the behaviour or characteristic of an electric/electronic circuit with the independent variables, the dependent variables, and the circuit elements represented by symbols.
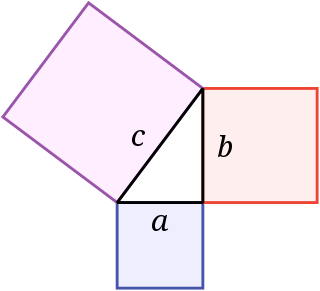
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic Era. Although usually associated with clothing and household linens, sewing is used in a variety of crafts and industries, including shoemaking, upholstery, sailmaking, bookbinding and the manufacturing of some kinds of sporting goods. Sewing is the fundamental process underlying a variety of textile arts and crafts, including embroidery, tapestry, quilting, appliqué and patchwork.
The HCS clustering algorithm is an algorithm based on graph connectivity for cluster analysis. It works by representing the similarity data in a similarity graph, and then finding all the highly connected subgraphs. It does not make any prior assumptions on the number of the clusters. This algorithm was published by Erez Hartuv and Ron Shamir in 2000.









