Related Research Articles

A dermoid cyst is a teratoma of a cystic nature that contains an array of developmentally mature, solid tissues. It frequently consists of skin, hair follicles, and sweat glands, while other commonly found components include clumps of long hair, pockets of sebum, blood, fat, bone, nail, teeth, eyes, cartilage, and thyroid tissue.
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Steatocystoma multiplex, is a benign, autosomal dominant congenital condition resulting in multiple cysts on a person's body. Steatocystoma simplex is the solitary counterpart to steatocystoma multiplex.

Hidrocystoma is an adenoma of the sweat glands.

Mucinous carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from epithelial cells; these line certain internal organs and skin, and produce mucin. Over 40 percent of all mucinous carcinomas are colorectal.
Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition with punctate symmetric palmoplantar keratoderma, with the keratoderma and fragility of the nails beginning around age 12. In addition to palmoplantar keratoderma, other symptoms include hypodontia, hypotrichosis, nail dystrophies, and eyelid cysts. Patients may also develop syringofibroadenoma and squamous cell carcinomas.
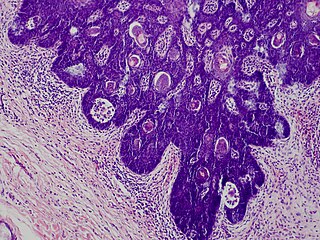
Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma abbreviated as (FSCH) is a rare cutaneous hamartoma consisting of dilated folliculosebaceous units invested in mesenchymal elements. it typically affects adults, have a predilection for the central face or scalp, with less than 1.5 cm dimension. Clinically, the lesions are asymptomatic, rubbery to firm in consistency, and usually occur on or above the neck in of cases, Histopathologically, FSCH shares several similar features to sebaceous trichofolliculoma, but it is usually possible to differentiate these two tumors.
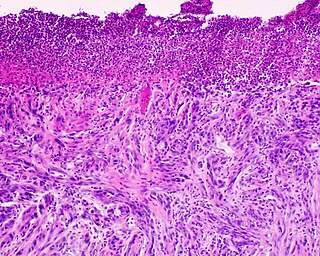
Desmoplastic melanoma is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by a deeply infiltrating type of melanoma with an abundance of fibrous matrix. It usually occurs in the head and neck region of older people with sun-damaged skin. Diagnosis can be difficult as it has a similar appearance to sclerosing melanocytic nevi as well as some nonmelanocytic skin lesions such as scars, fibromas, or cysts.

Spiradenoma, also spiroma or eccrine spiradenoma, is a cutaneous condition that is typically characterized, clinically, as a solitary, deep-seated dermal nodule of approximately one centimeter, occurring on the ventral surface of the body. Spiradenoma lesions are benign sudoriferous tumors, and have also been described as cystic epitheliomas of the sweat glands.
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a cutaneous condition characterized by a tumor that usually presents on the chest, scalp, or vulva of middle- to older-aged persons.
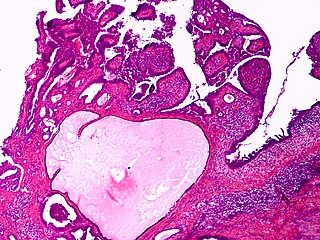
Apocrine gland carcinoma is a cutaneous condition characterized by skin lesions which form in the axilla or anogenital regions.

Pilomatricoma, is a benign skin tumor derived from the hair matrix. These neoplasms are relatively uncommon and typically occur on the scalp, face, and upper extremities. Clinically, pilomatricomas present as a subcutaneous nodule or cyst with unremarkable overlying epidermis that can range in size from 0.5-3.0 cm, but the largest reported case was 24 cm.
Multiple familial trichoepithelioma is a cutaneous condition characterized by multiple cystic and solid nodules appearing on the face.

Proliferating trichilemmal cysts are a cutaneous condition characterized by proliferations of squamous cells forming scroll-like structures.
Verrucous cysts are a cutaneous condition that resemble epidermoid cysts except that the lining demonstrates papillomatosis.
Cutaneous columnar cysts are a cutaneous condition, a group of different cysts lined by columnar epithelium. Types of cysts included in this group are:

Bronchogenic cysts are small, solitary cysts or sinuses, most typically located in the region of the suprasternal notch or behind the manubrium.
Median raphe cysts are a cutaneous condition of the penis due to developmental defects near the glans.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
| This Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, cysts article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |