Related Research Articles
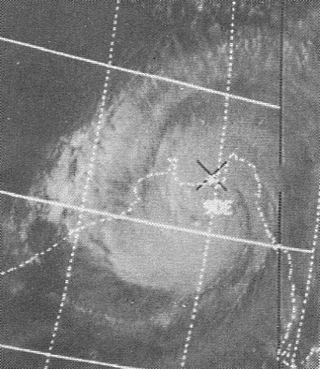
The 1970 Bhola cyclone was a devastating tropical cyclone that struck East Pakistan and India's West Bengal on November 12, 1970. It remains the deadliest tropical cyclone ever recorded and one of the world's deadliest natural disasters. At least 300,000 people lost their lives in the storm, possibly as many as 500,000, primarily as a result of the storm surge that flooded much of the low-lying islands of the Ganges Delta. Bhola was the sixth and strongest cyclonic storm of the 1970 North Indian Ocean cyclone season.

Emergency management or disaster management is the managerial function charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters. Emergency management, despite its name, does not actually focus on the management of emergencies, which can be understood as minor events with limited impacts and are managed through the day to day functions of a community. Instead, emergency management focuses on the management of disasters, which are events that produce more impacts than a community can handle on its own. The management of disasters tends to require some combination of activity from individuals and households, organizations, local, and/or higher levels of government. Although many different terminologies exist globally, the activities of emergency management can be generally categorized into preparedness, response, mitigation, and recovery, although other terms such as disaster risk reduction and prevention are also common. The outcome of emergency management is to prevent disasters and where this is not possible, to reduce their harmful impacts.

Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Mala was the strongest tropical cyclone of the 2006 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. In mid-April 2006, an area of disturbed weather formed over the southern Bay of Bengal and nearby Andaman Sea. Over a period of several days, the system became increasingly organized and was classified as a depression on April 24. Situated within a region of weak steering currents, the storm slowly intensified as it drifted in a general northward direction. It attained gale-force winds and was named Mala the next day. Conditions for strengthening improved markedly on April 27 and Mala subsequently underwent rapid intensification which culminated in the cyclone attaining its peak. Early on April 28, the cyclone had estimated winds of 185 km/h (115 mph). The Joint Typhoon Warning Center considered Mala to have been slightly stronger, classifying it as a Category 4-equivalent cyclone. Steady weakening ensued thereafter and the storm made landfall in Myanmar's Rakhine State on April 29. Rapid dissipation took place once onshore and Mala was last noted early the next morning.

The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) is a worldwide humanitarian aid organization that reaches 160 million people each year through its 192-member National Societies. It acts before, during and after disasters and health emergencies to meet the needs and improve the lives of vulnerable people. It does so with impartiality as to nationality, race, gender, religious beliefs, class and political opinions.

Cyclonic Storm Akash was the first named tropical cyclone of the 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. Warned by both India Meteorological Department (IMD) and Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), it formed from an area of disturbed weather on the Bay of Bengal on May 12, and gradually organized as it drifted northward. An eye began to develop as it approached land, and after reaching peak 3-min sustained winds of 85 km/h (55 mph) it struck about 115 km (70 mi) south of Chittagong in Bangladesh. Akash rapidly weakened over land, and advisories were discontinued on May 15.

Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Sidr was a tropical cyclone that resulted in one of the worst natural disasters in Bangladesh. The fourth named storm of the 2007 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Sidr formed in the central Bay of Bengal, and quickly strengthened to reach peak 1-minute sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph), making it a Category-5 equivalent tropical cyclone on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The storm eventually made landfall in Bangladesh on November 15, 2007, causing large-scale evacuations. At least 3,447 deaths have been blamed on the storm, with some estimates reaching 15,000.

Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Nargis was an extremely destructive and deadly tropical cyclone that caused the worst natural disaster in the recorded history of Myanmar during early May 2008. The cyclone made landfall in Myanmar on Friday, 2 May 2008, sending a storm surge 40 kilometres up the densely populated Irrawaddy delta, causing catastrophic destruction and at least 138,373 fatalities. The Labutta Township alone was reported to have 80,000 dead, with about 10,000 more deaths in Bogale. There were around 55,000 people missing and many other deaths were found in other towns and areas, although the Myanmar government's official death toll may have been under-reported, and there have been allegations that government officials stopped updating the death toll after 138,000 to minimise political fallout. The feared 'second wave' of fatalities from disease and lack of relief efforts never materialised. Damage was at $12 billion, making Nargis the costliest tropical cyclone on record in the North Indian Ocean at the time, before that record was broken by Cyclone Amphan in 2020.

Cyclonic Storm Bijli, was the first tropical cyclone to form during the 2009 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. Bijli formed from an area of Low Pressure on April 14. Later that evening, RSMC New Delhi upgraded the low-pressure area to a Depression and designated it as BOB 01. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) then issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert for the system and soon after designated it as Tropical Depression 01B. On the evening of April 15, both RSMC New Delhi and the JTWC reported that the system had intensified into a tropical storm, with the former naming it Bilji. Soon after, Bilji reached its peak intensity as it approached the coast of Bangladesh. However, on the morning of April 17, Bijli weakened to a deep depression due to land interaction, before making landfall just south of Chittagong. The remnants of Bilji continued to weaken as they tracked across northern Myanmar, before RSMC New Delhi issued their last advisory on April 18. The word Bijli refers to lightning in Hindi.

Severe Cyclonic Storm Aila was the second named tropical cyclone of the 2009 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. Warned by both the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RMSC) and Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), Aila formed over a disturbance over the Bay of Bengal on May 23, 2009 and started to intensify and organize reaching sustained wind speeds of 110 kmh (70 mph). It was the worst natural disaster to affect Bangladesh since Cyclone Sidr in November 2007. A relatively strong tropical cyclone, it caused extensive damage in India and Bangladesh.
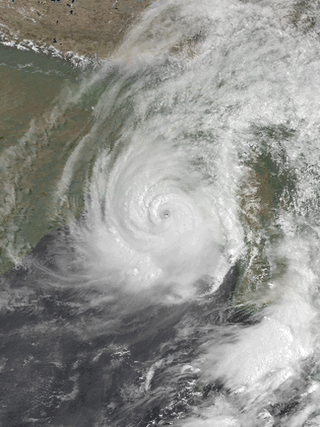
The May 1997 Bangladesh cyclone was a powerful storm that caused widespread damage and loss of life throughout Bangladesh. Originating from a near-equatorial trough on May 15, 1997, the cyclone tracked in a general northward direction throughout its existence. The system gradually intensified over the following days, reaching the equivalent of a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale by May 17. The following day, the storm attained its peak intensity with winds of 215 km/h (135 mph) according to the JTWC and 165 km/h (105 mph) according to the IMD along with a barometric pressure of 964 mbar. On May 19, the cyclone made landfall near Chittagong, Bangladesh before rapidly dissipating the next day.

Climate change in Bangladesh is a critical issue as the country is one of the most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. In the 2020 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, it ranked seventh in the list of countries most affected by climate calamities during the period 1999–2018. Bangladesh's vulnerability to climate change impacts is due to a combination of geographical factors, such as its flat, low-lying, and delta-exposed topography, and socio-economic factors, including its high population density, levels of poverty, and dependence on agriculture.

The 2002 West Bengal cyclone was a deadly tropical cyclone that affected India and Bangladesh in November 2002. The sixth tropical cyclone and fourth cyclonic storm of the 2002 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, it developed in the Bay of Bengal northeast of Sri Lanka on November 10, as a tropical depression. After tracking northeast, the system strengthened into a cyclonic storm on November 11, as maximum sustained winds exceeded 65 km/h (40 mph). On November 12, it further intensified into a severe cyclonic storm. Later that day, the storm made landfall on Sagar Island in West Bengal with winds of 100 km/h (60 mph). After moving inland, it rapidly weakened and dissipated over Bangladesh on November 12.
The 2013 Saravan earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 7.7 at 15:14 pm IRDT (UTC+4:30) on 16 April. The shock struck a mountainous area between the cities of Saravan and Khash in Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran, close to the border with Pakistan, with a duration of about 25 seconds. The earthquake occurred at an intermediate depth in the Arabian plate lithosphere, near the boundary between the subducting Arabian Plate and the overriding Eurasian Plate at a depth of about 80 km.

The Ministry of Disaster Management and Relief is a ministry of the government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh, responsible for disaster management and relief.

Severe Cyclonic Storm Mora was a moderate but deadly tropical cyclone that caused widespread devastation and severe flooding in Sri Lanka, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Northeast India in May 2017. The second named storm of the 2017 annual cyclone season, Mora developed from an area of low pressure over the southeastern Bay of Bengal on May 28. Mora reached peak strength with maximum sustained winds of 110 km/h (70 mph). The cyclone made landfall near Chittagong on the morning of May 30 and steadily weakened, dissipating early in the morning on May 31. Across its path, Mora dropped a large amount of rain, including 225mm of rainfall in Chittagong and northeast India. The storm is estimated to have caused damages nearing US$300 million.

On 12 June 2017, heavy monsoon rain triggered a series of landslides and floods in Rangamati, Chittagong and Bandarban - three hilly districts of Bangladesh - and killed at least 152 people. The weather also caused power cuts and telecommunications disruptions, making it difficult for rescuers to reach affected communities. Reaz Ahmed, head of Bangladesh's Disaster Management Department, said the landslides were the worst in the country's history.

Super Cyclonic Storm Amphan was an extremely powerful and catastrophic tropical cyclone that caused widespread damage in Eastern India, specifically in West Bengal and Odisha, and in Bangladesh, in May 2020. It was the strongest tropical cyclone to strike the Ganges Delta. It was also the fourth super cyclone that hit West Bengal and Kolkata since 15 as well as being one of the strongest storms to impact the area. Causing over US$13 billion of damage, Amphan is also the costliest cyclone ever recorded in the North Indian Ocean, surpassing the record held by Cyclone Nargis of 2008.

Very Severe Cyclonic Storm Yaas was a relatively strong and very damaging tropical cyclone that made landfall in Odisha and brought significant impacts to West Bengal during late May 2021. The second cyclonic storm, second severe cyclonic storm, and second very severe cyclonic storm of the 2021 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Yaas formed from a tropical disturbance that the Indian Meteorological Department first monitored on May 23. Conditions in the basin favored development as the system became a deep depression later that day, before intensifying into a cyclonic storm on the next day, receiving the name Yaas. The system further intensified as it turned to the northeast, becoming a severe cyclonic storm on May 24 despite moderate wind shear. Marginally favorable conditions further continued as Yaas accelerated northeastward, strengthening to a Category 1-equivalent tropical cyclone and to a very severe cyclonic storm on May 25. Yaas crossed the northern Odisha coast around 20 km south of Balasore at its peak intensity as a very severe cyclonic storm on May 26. Upon landfall, the JTWC and IMD issued their final advisories as Yaas further weakened inland while turning north-northwestwards.
References
- ↑ "Cyclone Preparedness Programme (CPP)". preparecenter.org. Global Disaster Preparedness Center. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ↑ "Cyclone poised to strike". The Daily Star. 30 May 2017. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ↑ "Flood situation worsens, ministry cancels holidays -bdnews24.com". bdnews24.com. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ↑ "Challenges for disaster risk reduction". The Daily Star. 26 February 2017. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ↑ "Early warning early action saves thousands as Cyclone Mora strikes Bangladesh". International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ↑ "Modi lauds Bangladesh's disaster management success". The Daily Star. 3 November 2016. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ↑ "IFRC launches emergency appeal to aid coastal communities in Bangladesh affected by Cyclone Roanu". ifrc.org. Retrieved 22 September 2017.