A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)
In organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane. They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, grease, rubber, resin, and caulk.

Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication and passive daytime radiative cooling.
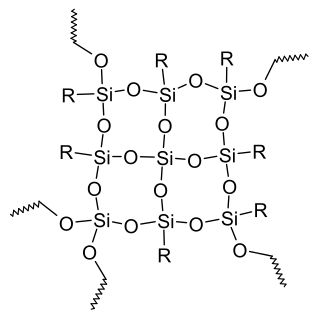
Silicone resins are a type of silicone material which is formed by branched, cage-like oligosiloxanes with the general formula of RnSiXmOy, where R is a non-reactive substituent, usually methyl or phenyl, and X is a functional group: hydrogen, hydroxyl, chlorine or alkoxy. These groups are further condensed in many applications, to give highly crosslinked, insoluble polysiloxane networks.

In organosilicon chemistry, a siloxane is an organic compound containing a functional group of two silicon atoms bound to an oxygen atom: Si−O−Si. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H[OSiH2]nOH and [OSiH2]n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones [−R2Si−O−SiR2−]n, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group R3SiO− is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility.
In inorganic chemistry, chlorosilanes are a group of reactive, chlorine-containing chemical compounds, related to silane and used in many chemical processes. Each such chemical has at least one silicon-chlorine bond. Trichlorosilane is produced on the largest scale. The parent chlorosilane is silicon tetrachloride.

Silicone rubber is an elastomer composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations. Silicone rubbers are often one- or two-part polymers, and may contain fillers to improve properties or reduce cost. Silicone rubber is generally non-reactive, stable, and resistant to extreme environments and temperatures from −55 to 300 °C while still maintaining its useful properties. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber can be found in a wide variety of products, including voltage line insulators; automotive applications; cooking, baking, and food storage products; apparel such as undergarments, sportswear, and footwear; electronics; medical devices and implants; and in home repair and hardware, in products such as silicone sealants.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.

Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, also known as D5 and D5, is an organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]5. It is a colorless and odorless liquid that is slightly volatile.

Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO or MM) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O[Si(CH3)3]2. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl chloride. The molecule is the protypical disiloxane and resembles a subunit of polydimethylsiloxane.
A silicone oil is any liquid polymerized siloxane with organic side chains. The most important member is polydimethylsiloxane. These polymers are of commercial interest because of their relatively high thermal stability and their lubricating properties.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.

Methyltrichlorosilane, also known as trichloromethylsilane, is a monomer and organosilicon compound with the formula CH3SiCl3. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor similar to that of hydrochloric acid. As methyltrichlorosilane is a reactive compound, it is mainly used a precursor for forming various cross-linked siloxane polymers.
This glossary of chemistry terms is a list of terms and definitions relevant to chemistry, including chemical laws, diagrams and formulae, laboratory tools, glassware, and equipment. Chemistry is a physical science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions; it features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.

Silicon monoxide is the chemical compound with the formula SiO where silicon is present in the oxidation state +2. In the vapour phase, it is a diatomic molecule. It has been detected in stellar objects and has been described as the most common oxide of silicon in the universe.
In organosilicon chemistry, polysilazanes are polymers in which silicon and nitrogen atoms alternate to form the basic backbone. Since each silicon atom is bound to two separate nitrogen atoms and each nitrogen atom to two silicon atoms, both chains and rings of the formula [R2Si−NR]n occur. R can be hydrogen atoms or organic substituents. If all substituents R are hydrogen atoms, the polymer is designated as perhydropolysilazane, polyperhydridosilazane, or inorganic polysilazane ([H2Si−NH]n). If hydrocarbon substituents are bound to the silicon atoms, the polymers are designated as Organopolysilazanes. Molecularly, polysilazanes [R2Si−NH]n are isoelectronic with and close relatives to polysiloxanes [R2Si−O]n (silicones).

Dibutyltin dilaurate is an organotin compound with the formula (CH310CO2)2Sn(CH2CH2CH2CH3)2. It is a colorless viscous and oily liquid. It is used as a catalyst.

Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, also called D4, is an organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]4. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is a common cyclomethicone. It is widely used in cosmetics.
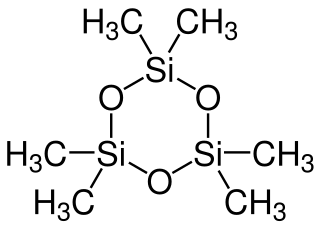
Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane, also known as D3 and D3, is the organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]3. It is a colorless or white volatile solid. It finds limited use in organic chemistry. The larger tetrameric and pentameric siloxanes, respectively octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane and decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, are of significant industrial interest, whereas 1,000–10,000 tonnes per year of the trimer is manufactured and/or imported in the European Economic Area.



![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)






