Related Research Articles

In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set computer (CISC), a RISC computer might require more instructions in order to accomplish a task because the individual instructions are written in simpler code. The goal is to offset the need to process more instructions by increasing the speed of each instruction, in particular by implementing an instruction pipeline, which may be simpler to achieve given simpler instructions.

A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2022, supercomputers have existed which can perform over 1018 FLOPS, so called exascale supercomputers. For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.

The Cray-1 was a supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research. Announced in 1975, the first Cray-1 system was installed at Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1976. Eventually, eighty Cray-1s were sold, making it one of the most successful supercomputers in history. It is perhaps best known for its unique shape, a relatively small C-shaped cabinet with a ring of benches around the outside covering the power supplies and the cooling system.

Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling. As power consumption by computers has become a concern in recent years, parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multi-core processors.
Cell, a shorthand for Cell Broadband Engine Architecture, is a 64-bit multi-core microprocessor and microarchitecture that combines a general-purpose PowerPC core of modest performance with streamlined coprocessing elements which greatly accelerate multimedia and vector processing applications, as well as many other forms of dedicated computation.
The Whetstone benchmark is a synthetic benchmark for evaluating the performance of computers. It was first written in ALGOL 60 in 1972 at the Technical Support Unit of the Department of Trade and Industry in the United Kingdom. It was derived from statistics on program behaviour gathered on the KDF9 computer at NPL National Physical Laboratory, using a modified version of its Whetstone ALGOL 60 compiler. The workload on the machine was represented as a set of frequencies of execution of the 124 instructions of the Whetstone Code. The Whetstone Compiler was built at the Atomic Power Division of the English Electric Company in Whetstone, Leicestershire, England, hence its name. Dr. B.A. Wichman at NPL produced a set of 42 simple ALGOL 60 statements, which in a suitable combination matched the execution statistics.

ASCI Red was the first computer built under the Accelerated Strategic Computing Initiative (ASCI), the supercomputing initiative of the United States government created to help the maintenance of the United States nuclear arsenal after the 1992 moratorium on nuclear testing.
Wei Yen is a Taiwanese-American technologist and serial entrepreneur. He has been involved with several companies, including most recently as Chairman and Founder of AiLive.

NEC SX describes a series of vector supercomputers designed, manufactured, and marketed by NEC. This computer series is notable for providing the first computer to exceed 1 gigaflop, as well as the fastest supercomputer in the world between 1992–1993, and 2002–2004. The current model, as of 2018, is the SX-Aurora TSUBASA.
The Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) was a UK government agency providing computer and telecoms support to government departments.
The QCDOC is a supercomputer technology focusing on using relatively cheap low power processing elements to produce a massively parallel machine. The machine is custom-made to solve small but extremely demanding problems in the fields of quantum physics.

A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. The newest manifestation of cluster computing is cloud computing.
Manycore processors are special kinds of multi-core processors designed for a high degree of parallel processing, containing numerous simpler, independent processor cores. Manycore processors are used extensively in embedded computers and high-performance computing.

Exascale computing refers to computing systems capable of calculating at least 1018 IEEE 754 Double Precision (64-bit) operations (multiplications and/or additions) per second (exaFLOPS)"; it is a measure of supercomputer performance.
Supercomputing in India has a history going back to the 1980s. The Government of India created an indigenous development programme as they had difficulty purchasing foreign supercomputers. As of November 2024, the AIRAWAT supercomputer is the fastest supercomputer in India, having been ranked 136th fastest in the world in the TOP500 supercomputer list. AIRAWAT has been installed at the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) in Pune.

Japan operates a number of centers for supercomputing which hold world records in speed, with the K computer being the world's fastest from June 2011 to June 2012, and Fugaku holding the lead from June 2020 until June 2022.

The history of supercomputing goes back to the 1960s when a series of computers at Control Data Corporation (CDC) were designed by Seymour Cray to use innovative designs and parallelism to achieve superior computational peak performance. The CDC 6600, released in 1964, is generally considered the first supercomputer. However, some earlier computers were considered supercomputers for their day such as the 1954 IBM NORC in the 1950s, and in the early 1960s, the UNIVAC LARC (1960), the IBM 7030 Stretch (1962), and the Manchester Atlas (1962), all of which were of comparable power.

Approaches to supercomputer architecture have taken dramatic turns since the earliest systems were introduced in the 1960s. Early supercomputer architectures pioneered by Seymour Cray relied on compact innovative designs and local parallelism to achieve superior computational peak performance. However, in time the demand for increased computational power ushered in the age of massively parallel systems.
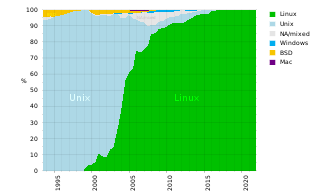
A supercomputer operating system is an operating system intended for supercomputers. Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, as fundamental changes have occurred in supercomputer architecture. While early operating systems were custom tailored to each supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been moving away from in-house operating systems and toward some form of Linux, with it running all the supercomputers on the TOP500 list in November 2017. In 2021, top 10 computers run for instance Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or some variant of it or other Linux distribution e.g. Ubuntu.

The high performance supercomputing program started in mid-to-late 1980s in Pakistan. Supercomputing is a recent area of Computer science in which Pakistan has made progress, driven in part by the growth of the information technology age in the country. Developing on the ingenious supercomputer program started in 1980s when the deployment of the Cray supercomputers was initially denied.
References
- 1 2 3 Schlansker, Michael (2011). "Cydra 5". Encyclopedia of Parallel Computing: 488–497. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-09766-4_123. ISBN 978-0-387-09765-7.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Rau, B.R.; Yen, D.W.L.; Towle, R.A. (January 1989). "The Cydra 5 departmental supercomputer: design philosophies, decisions, and trade-offs" (PDF). Computer. 22 (1): 12–35. doi:10.1109/2.19820. ISSN 0018-9162 . Retrieved 23 December 2021.