
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south of the ecliptic, which is the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The orbital paths of the Moon and major planets are within the belt of the zodiac.

A horoscope is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ōra and scopos meaning "time" and "observer". It is claimed by proponents of astrology that a horoscope can be used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology, although practices surrounding astrology have been recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers.

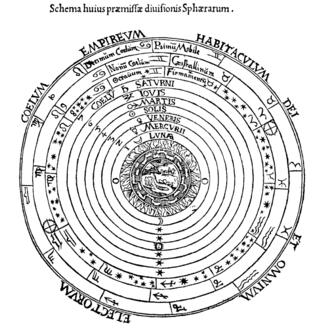
Western astrology is the system of astrology most popular in Western countries. Western astrology is historically based on Ptolemy's Tetrabiblos, which in turn was a continuation of Hellenistic and ultimately Babylonian traditions.

Most horoscopic traditions of astrology systems divide the horoscope into a number of houses whose positions depend on time and location rather than on date. In Hindu astrological tradition these are known as Bhāvas. The houses of the horoscope represent different fields of experience wherein the energies of the signs and planets operate—described in terms of physical surroundings as well as personal life experiences.

In astrology, sidereal and tropical are terms that refer to two different systems of ecliptic coordinates used to divide the ecliptic into twelve "signs". Each sign is divided into 30 degrees, making a total of 360 degrees. The terms sidereal and tropical may also refer to two different definitions of a year, applied in sidereal solar calendars or tropical solar calendars.

In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the vernal equinox. The astrological signs are Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by the Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Over the centuries, Western astrology's zodiacal divisions have shifted out of alignment with the constellations they were named after by axial precession of the Earth while Hindu astrology measurements correct for this shifting. Astrology was developed in Chinese and Tibetan cultures as well but these astrologies are not based upon the zodiac but deal with the whole sky.

The Age of Aquarius, in astrology, is either the current or forthcoming astrological age, depending on the method of calculation. Astrologers maintain that an astrological age is a product of the Earth's slow precessional rotation and lasts for 2,160 years, on average.

An astrological age is a time period in astrological theory which astrologers say, parallels major changes in the development of Earth's inhabitants, particularly relating to culture, society, and politics. There are twelve astrological ages corresponding to the twelve zodiacal signs in western astrology. Advocates believe that when one cycle of the twelve astrological ages, called a Great Year, is completed, another cycle of twelve ages begins. The length of one cycle of twelve ages is 25,772 years.

Astrology has used the concept of classical elements from antiquity up until the present. In Western astrology and Sidereal astrology four elements are used: Fire, Earth, Air, and Water.

In astrology, exaltation is one of the five essential dignities of a planet. The exaltation is a place of awareness for the planet, whereas the fall is a position of weakness concerning the function of the planet. The sign position directly opposite a planet's sign of exaltation is considered to be its fall.

In astrology, a cusp is the imaginary line that separates a pair of consecutive signs in the zodiac or houses in the horoscope.

Pisces (♓︎) is the twelfth and final astrological sign in the zodiac. It is a negative, mutable sign. It spans 330° to 360° of celestial longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this area between February 19 and March 20. In classical interpretations, the symbol of the fish is derived from the ichthyocentaurs, who aided Aphrodite when she was born from the sea.

Ayanamsa, also ayanabhāga, is the Sanskrit term for many systems used in Hindu astrology to account for the precession of equinoxes. There are also systems of ayanamsa used in Western sidereal astrology, such as the Fagan/Bradley Ayanamsa.

Brigadier Roy Charles Whitworth George Firebrace was a British Army officer, who served as Head of the British Military Mission in Moscow during the Second World War. He was also a sidereal astrologer, founder and editor of the journal Spica, and a co-founder of the Astrological Association of Great Britain.
In astrology, certain stars are considered significant. Historically, all of the various heavenly bodies considered by astrologers were considered "stars", whether they were stars, planets, other stellar phenomena like novas and supernovas, or other solar system phenomena like comets and meteors.
Walter Berg is a British astrologer, known for his system of a 13-sign sidereal astrology (13), "a sidereal system that uses the actual star constellations of the true zodiac". He has published several best selling books on horoscopy and divination in Japan and has appeared regularly on Fuji Television.
Locational astrology is any of various types of astrology that factor in specific locations of the Earth. The different types also carry a range of astrological techniques.

Ophiuchus has sometimes been suggested in sidereal astrology as a 13th astrological sign in addition to the 12 signs of the tropical zodiac. The constellation Ophiuchus, as defined by the 1930 International Astronomical Union's constellation boundaries, is situated behind the Sun from November 29 to December 18.

The theory of synoptical astrology was created by László Wladimir Orosz, Hungarian philosopher and astrologer.










