Related Research Articles
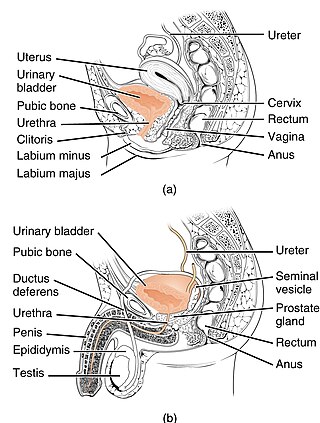
The urethra is the tube that connects the mammalian urinary bladder to the urinary meatus. In placental mammals, the urethra transports urine through the penis or vulva during urination and semen through the penis during ejaculation.

The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.

The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.
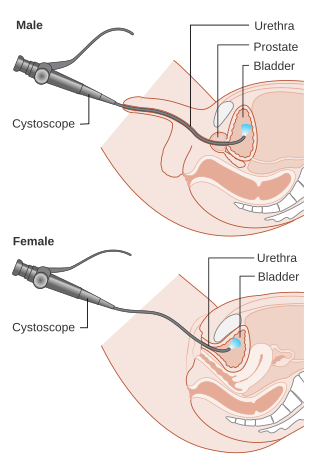
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.

Urination is the release of urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Urine is released through the urethra and exits the penis or vulva through the urinary meatus in placental mammals, but is released through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, pissing, and euphemistically going number one. The process of urination is under voluntary control in healthy humans and other animals, but may occur as a reflex in infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day.

Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis. UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others.

The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. Stenosis is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children.
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination.

Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections.

Hydronephrosis describes hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dilation of the entire upper urinary tract.
Feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD) is a generic category term to describe any disorder affecting the bladder or urethra of cats.
In urology, voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) is a frequently performed technique for visualizing a person's urethra and urinary bladder while the person urinates (voids). It is used in the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux, among other disorders. The technique consists of catheterizing the person in order to fill the bladder with a radiocontrast agent, typically diatrizoic acid. Under fluoroscopy the radiologist watches the contrast enter the bladder and looks at the anatomy of the patient. If the contrast moves into the ureters and back into the kidneys, the radiologist makes the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux, and gives the degree of severity a score. The exam ends when the person voids while the radiologist is watching under fluoroscopy. Consumption of fluid promotes excretion of contrast media after the procedure. It is important to watch the contrast during voiding, because this is when the bladder has the most pressure, and it is most likely this is when reflux will occur. Despite this detailed description of the procedure, at least as of 2016 the technique had not been standardized across practices.

Bladder stones or uroliths are a common occurrence in animals, especially in domestic animals such as dogs and cats. Occurrence in other species, including tortoises, has been reported as well. The stones form in the urinary bladder in varying size and numbers secondary to infection, dietary influences, and genetics. Stones can form in any part of the urinary tract in dogs and cats, but unlike in humans, stones of the kidney are less common and do not often cause significant disease, although they can contribute to pyelonephritis and chronic kidney disease. Types of stones include struvite, calcium oxalate, urate, cystine, calcium phosphate, and silicate. Struvite and calcium oxalate stones are by far the most common. Bladder stones are not the same as bladder crystals but if the crystals coalesce unchecked in the bladder they can become stones.

The detrusor muscle, also detrusor urinae muscle, muscularis propria of the urinary bladder and muscularis propria, is smooth muscle found in the wall of the bladder. The detrusor muscle remains relaxed to allow the bladder to store urine, and contracts during urination to release urine. Related are the urethral sphincter muscles which envelop the urethra to control the flow of urine when they contract.

The urethral sphincters are two muscles used to control the exit of urine in the urinary bladder through the urethra. The two muscles are either the male or female external urethral sphincter and the internal urethral sphincter. When either of these muscles contracts, the urethra is sealed shut.

Cystometry, also known as flow cystometry, is a clinical diagnostic procedure used to evaluate bladder function. Specifically, it measures contractile force of the bladder when voiding. The resulting chart generated from cystometric analysis is known as a cystometrogram (CMG), which plots intravesical pressure against the volume of fluid in the bladder.
Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC) or feline interstitial cystitis or cystitis in cats, is one of the most frequently observed forms of feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD). Feline cystitis means "inflammation of the bladder in cats". The term idiopathic means unknown cause; however, certain behaviours have been known to aggravate the illness once it has been initiated. It can affect both males and females of any breed of cat. It is more commonly found in female cats; however, when males do exhibit cystitis, it is usually more dangerous.
Suprapubic aspiration is a procedure to take a urine sample. It involves putting a needle through the skin just above the pubic bone into the bladder. It is typically used as a method to collect urine in child less than 2 years of age who is not yet toilet trained in an effort to diagnose a urinary tract infection.
A urethral bulking injection is a gynecological procedure and medical treatment used to treat involuntary leakage of urine: urinary incontinence in women. Injectional materials are used to control stress incontinence. Bulking agents are injected into the mucosa surrounding the bladder neck and proximal urethra. This reduces the diameter of the urethra and creates resistance to urine leakage. After the procedure, the pressure forcing the urine from the bladder through the urethra is resisted by the addition of the bulking agent in the tissue surrounding the proximal urethra. Most of the time this procedure prevents urinary stress incontinence in women.
The genitourinary tract, or simply the urinary tract, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The kidney is the most frequently injured. Injuries to the kidney commonly occur after automobile or sports-related accidents. A blunt force is involved in 80-85% of injuries. Major decelerations can result in vascular injuries near the kidney's hilum. Gunshots and knife wounds and fractured ribs can result in penetrating injuries to the kidney.
References
- ↑ "Cystocentesis". Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine. Archived from the original on 7 October 2013. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- ↑ Morgan, Rhea. "Cystocentesis". Wurtsboro Veterinary Clinic. Archived from the original on 6 October 2013. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- ↑ A Distended Bladder is a conditions that occurs when the Blatter becomes inflamed or enlarged due to pressure, internal or external.