
Malbec is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. The French plantations of Malbec are now found primarily in Cahors in South West France. It is increasingly celebrated as an Argentine varietal wine and is being grown around the world.

Graves is an important subregion of the Bordeaux wine region. Graves is situated on the left bank of the Garonne River, in the upstream part of the region, southeast of the city Bordeaux and stretches over 50 kilometres (31 mi). Graves is the only Bordeaux subregion which is famed for all three of Bordeaux' three main wine types—reds, dry whites and sweet wines—although red wines dominate the total production. Graves AOC is also the name of one Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) which covers most, but not all of the Graves subregion.

A Bordeaux wine is any wine produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France. Bordeaux is centered on the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde and covering the whole area of the Gironde department,with a total vineyard area of over 120,000 hectares, making it the largest wine growing area in France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of Bordeaux wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red, with sweet white wines, dry whites, and rosé and sparkling wines collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 8,500 producers or châteaux. There are 54 appellations of Bordeaux wine.

French wine is produced all throughout France, in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France is one of the largest wine producers in the world. French wine traces its history to the 6th century BC, with many of France's regions dating their wine-making history to Roman times. The wines produced range from expensive wines sold internationally to modest wines usually only seen within France such as the Margnat wines were during the post war period.

Languedoc-Roussillon wine, including the vin de pays labeled Vin de Pays d'Oc, is produced in southern France. While "Languedoc" can refer to a specific historic region of France and Northern Catalonia, usage since the 20th century has primarily referred to the northern part of the Languedoc-Roussillon région of France, an area which spans the Mediterranean coastline from the French border with Spain to the region of Provence. The area has around 700,000 acres (2,800 km2) under vines and is the single biggest wine-producing region in the world, being responsible for more than a third of France's total wine production. In 2001, the region produced more wine than the United States.
Côtes de Toul is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) for French wine produced in the département of Meurthe-et-Moselle in the Lorraine région. The Côtes de Toul vineyards cover 110 hectares in an area close to Toul, to the west of the city of Nancy. The area of production includes the following communes: Blénod-lès-Toul, Bruley, Bulligny, Charmes-la-Côte, Domgermain, Lucey, Mont-le-Vignoble and Pagney-derrière-Barine. Annual production is 4,500 hectoliter, corresponding to 600,000 bottles.
Abouriou is a red French wine grape variety grown primarily in Southwest France and, in small quantities, California. It is a blending grape that, along with Malbec, Cabernet Sauvignon, Syrah, Fer, Cabernet Franc, and Merlot, is used to make the Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) wine of Côtes du Marmandais. Abouriou can also be made into a varietal, as it is used in some vin de pays wines. The grape is known for its low acidity and high tannin content.

The wine regions of Bordeaux are a large number of wine growing areas, differing widely in size and sometimes overlapping, which lie within the overarching wine region of Bordeaux, centred on the city of Bordeaux and covering the whole area of the Gironde department of Aquitaine.

Gaillac AOC is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) in South West France in the département of Tarn, just north of Toulouse.
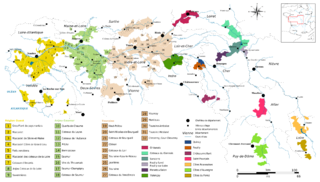
The Loire Valley wine region includes the French wine regions situated along the Loire River from the Muscadet region near the city of Nantes on the Atlantic coast to the region of Sancerre and Pouilly-Fumé just southeast of the city of Orléans in north central France. In between are the regions of Anjou, Saumur, Bourgueil, Chinon, and Vouvray. The Loire Valley itself follows the river through the Loire province to the river's origins in the Cévennes but the majority of the wine production takes place in the regions noted above. The area includes 87 appellations under the Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC), Vin Délimité de Qualité Superieure (VDQS) and Vin de pays systems. While the majority of production is white wine from the Chenin blanc, Sauvignon blanc and Melon de Bourgogne grapes, there are red wines made from Cabernet franc. In addition to still wines, rosé, sparkling and dessert wines are also produced. With Crémant production throughout the Loire, it is the second largest sparkling wine producer in France after Champagne. Among these different wine styles, Loire wines tend to exhibit characteristic fruitiness with fresh, crisp flavors-especially in their youth. The Loire Valley has a long history of winemaking dating back to the 1st century. In the High Middle Ages, the wines of the Loire Valley were the most esteemed wines in England and France, even more prized than those from Bordeaux.

In the Bordeaux wine region there are seven regional Appellations d'origine contrôlée (AOCs) that may be used throughout the Gironde department. These are Bordeaux Rouge AOC, Bordeaux Supérieur Rouge, Bordeaux Clairet, Bordeaux Rosé, Bordeaux Blanc, a dry white, Bordeaux Supérieur Blanc, a sweet white, and Crémant de Bordeaux, a sparkling méthode traditionnelle wine. The regional appellations together form the largest world-class wine vineyard, making up more than half of the production of the prestigious Bordeaux wine region, and representing more than 55% of all Bordeaux wines consumed in the world.

Provence (Provençal) wine comes from the French wine-producing region of Provence in southeast France. The Romans called the area provincia nostra, giving the region its name. Just south of the Alps, it was the first Roman province outside Italy.

Côtes de Bourg is an Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) for Bordeaux wine situated around the small town of Bourg-sur-Gironde near Bordeaux, France. The first vineyards in the area were founded by the Romans. In the Middle Ages, Bourg was a major port for wine and the vineyards developed at the same tempo as the estuary traffic. The Côtes de Bourg appellation, in the north of the patchwork of Bordeaux wines, took its first steps on the east bank of the Gironde. At the time, the inhabitants of Bourg were fishermen, sailors or winemakers and the latter benefited from the perfect combination of a commercially minded town and a soil made for the vine.

Anjou wine is produced in the Loire Valley wine region of France near the city of Angers. The wines of region are often grouped together with the wines of nearby Saumur as "Anjou-Saumur". Along with the wines produced further east in Touraine, Anjou-Saumur make what is collectively known as the "Middle Loire" (as opposed to the "Upper Loire" which includes the wine regions of Sancerre and Pouilly-Fumé. Within the Anjou wine region are several Appellation d'origine contrôlées responsible for a broad spectrum of wines including still red, white and rosé produced with varying levels of sweetness. Extending across the Deux-Sèvres, Maine-et-Loire and Vienne départements, the generic Anjou AOC appellation and its various sub-appellations encompasses vineyards across more than 151 communes.

Côtes de Duras is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) for red and white wines in South West France. Côtes de Duras is located in the department of Lot-et-Garonne, and is located immediately adjacent to the Bordeaux wine region, which is restricted to the Gironde department, as an extension of Bordeaux immediately to the east of the departmental border.
Buzet is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) for wine in South West France, in the department of Lot-et-Garonne.

Béarn is an Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée (AOC) for wine in South West France. It is located in the area of intersection of three French departments: Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Hautes-Pyrénées and Gers; and two regions: Aquitaine and Midi-Pyrénées. Some vineyards in the area of the Jurançon AOC can also produce red Béarn wine, and some in the area of the Madiran AOC may produce a rosé Béarn. Wines made in the village of Bellocq also carry the appellation Béarn-Bellocq.
Merlot blanc is a white French wine grape variety that came from a natural crossing of the Bordeaux wine grape Merlot and the Cognac grape Folle blanche. The grape is distinct from Merlot gris which is a pink-skinned color mutation of the red wine grape Merlot and is sometimes used in vin gris and rosé wines. Plantings of Merlot blanc were first discovered in 1891 but cuttings of the vine have not been widely propagated and the variety is very rare. It is not used to make the sweet White Zinfandel-style wine White Merlot that is made by some California wine producers. Those wines are made from a saignee of red Merlot wine.

Château Suau is a French vineyard located south of the village of Capian in the Bordeaux area. It sits at the highest point of the Cadillac-côtes-de-Bordeaux appellation. Château Suau produces organic wines.


















