
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a set of networking protocols on the Internet Protocol (IP) that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices, to seamlessly discover each other's presence on the network and establish functional network services. UPnP is intended primarily for residential networks without enterprise-class devices.
MPEG-7 is a multimedia content description standard. It was standardized in ISO/IEC 15938. This description will be associated with the content itself, to allow fast and efficient searching for material that is of interest to the user. MPEG-7 is formally called Multimedia Content Description Interface. Thus, it is not a standard which deals with the actual encoding of moving pictures and audio, like MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. It uses XML to store metadata, and can be attached to timecode in order to tag particular events, or synchronise lyrics to a song, for example.
Health Level Seven, abbreviated to HL7, is a range of global standards for the transfer of clinical and administrative health data between applications with the aim to improve patient outcomes and health system performance. The HL7 standards focus on the application layer, which is "layer 7" in the Open Systems Interconnection model. The standards are produced by Health Level Seven International, an international standards organization, and are adopted by other standards issuing bodies such as American National Standards Institute and International Organization for Standardization. There are a range of primary standards that are commonly used across the industry, as well as secondary standards which are less frequently adopted.
Message-oriented middleware (MOM) is software or hardware infrastructure supporting sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. MOM allows application modules to be distributed over heterogeneous platforms and reduces the complexity of developing applications that span multiple operating systems and network protocols. The middleware creates a distributed communications layer that insulates the application developer from the details of the various operating systems and network interfaces. APIs that extend across diverse platforms and networks are typically provided by MOM.
The Data Distribution Service (DDS) for real-time systems is an Object Management Group (OMG) machine-to-machine standard that aims to enable dependable, high-performance, interoperable, real-time, scalable data exchanges using a publish–subscribe pattern.
TV-Anytime is a set of specifications for the controlled delivery of multimedia content to a user's local storage. It seeks to exploit the evolution in convenient, high capacity storage of digital information to provide consumers with a highly personalized TV experience. Users will have access to content from a wide variety of sources, tailored to their needs and personal preferences. TV-Anytime specifications are specified by the TV-Anytime Forum.

The WiMedia Alliance was a non-profit industry trade group that promoted the adoption, regulation, standardization and multi-vendor interoperability of ultra-wideband (UWB) technologies. It existed from about 2002 through 2009.
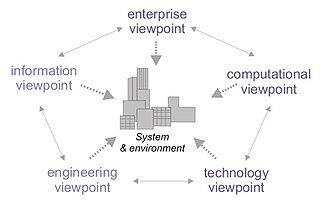
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
IEC 60870 part 6 in electrical engineering and power system automation, is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed part 6 to provide a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems which is compatible with ISO standards and ITU-T recommendations.
The ISO base media file format (ISOBMFF) is a container file format that defines a general structure for files that contain time-based multimedia data such as video and audio. It is standardized in ISO/IEC 14496-12, a.k.a. MPEG-4 Part 12, and was formerly also published as ISO/IEC 15444-12, a.k.a. JPEG 2000 Part 12.
The Open Smart Grid Protocol (OSGP) is a family of specifications published by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) used in conjunction with the ISO/IEC 14908 control networking standard for smart grid applications. OSGP is optimized to provide reliable and efficient delivery of command and control information for smart meters, direct load control modules, solar panels, gateways, and other smart grid devices. With over 5 million OSGP based smart meters and devices deployed worldwide it is one of the most widely used smart meter and smart grid device networking standards.
Storage security is a specialty area of security that is concerned with securing data storage systems and ecosystems and the data that resides on these systems.