
In computer networking, a thin client is a simple (low-performance) computer that has been optimized for establishing a remote connection with a server-based computing environment. The server does most of the work, which can include launching software programs, performing calculations, and storing data. This contrasts with a fat client or a conventional personal computer; the former is also intended for working in a client–server model but has significant local processing power, while the latter aims to perform its function mostly locally.
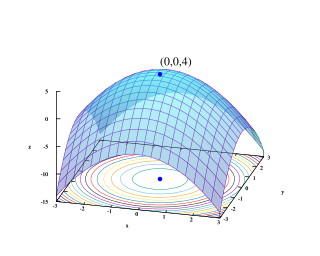
Mathematical optimization or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. Optimization problems of sorts arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries.

In computer science, inter-process communication or interprocess communication (IPC) refers specifically to the mechanisms an operating system provides to allow the processes to manage shared data. Typically, applications can use IPC, categorized as clients and servers, where the client requests data and the server responds to client requests. Many applications are both clients and servers, as commonly seen in distributed computing.
freedesktop.org (fd.o) is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free-software desktop environments for the X Window System (X11) and Wayland on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington from Red Hat in March 2000. The project's servers are hosted by Portland State University, which in turn are sponsored by HP, Intel and Google.
Desktop COmmunication Protocol (DCOP) was an inter-process communication (IPC) daemon by KDE used in K Desktop Environment 3. The design goal for the protocol was to allow applications to interoperate, and share complex tasks. Essentially, DCOP was a ‘remote control’ system, which allowed applications or scripts to enlist the help of other applications. DCOP is built on top of the X11 Inter-Client Exchange protocol.
In mathematics, nonlinear programming (NLP) is the process of solving an optimization problem where some of the constraints or the objective function are nonlinear. An optimization problem is one of calculation of the extrema of an objective function over a set of unknown real variables and conditional to the satisfaction of a system of equalities and inequalities, collectively termed constraints. It is the sub-field of mathematical optimization that deals with problems that are not linear.

A multi-agent system is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents. Multi-agent systems can solve problems that are difficult or impossible for an individual agent or a monolithic system to solve. Intelligence may include methodic, functional, procedural approaches, algorithmic search or reinforcement learning.
In computing, D-Bus is a Message-oriented middleware mechanism that allows communication between multiple processes running concurrently on the same machine. D-Bus was developed as part of the freedesktop.org project, initiated by Havoc Pennington from Red Hat to standardize services provided by Linux desktop environments such as GNOME and KDE.
In mathematical optimization, constrained optimization is the process of optimizing an objective function with respect to some variables in the presence of constraints on those variables. The objective function is either a cost function or energy function, which is to be minimized, or a reward function or utility function, which is to be maximized. Constraints can be either hard constraints, which set conditions for the variables that are required to be satisfied, or soft constraints, which have some variable values that are penalized in the objective function if, and based on the extent that, the conditions on the variables are not satisfied.
Distributed constraint optimization is the distributed analogue to constraint optimization. A DCOP is a problem in which a group of agents must distributedly choose values for a set of variables such that the cost of a set of constraints over the variables is minimized.

KDE Platform 4 was a collection of libraries and software frameworks by KDE that served as technological foundation for KDE Software Compilation 4 distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). KDE Platform 4 was the successor to KDElibs and the predecessor of KDE Frameworks. KDE Platform 4 is the only version of KDE Platform, see KDE’s brand repositioning.
In computing, the term remote desktop refers to a software or operating system feature that allows a personal computer's desktop environment to be run remotely on one system, while being displayed on a separate client device. Remote desktop applications have varying features. Some allow attaching to an existing user's session and "remote controlling", either displaying the remote control session or blanking the screen. Taking over a desktop remotely is a form of remote administration.
Wt is an open-source widget-centric web framework for the C++ programming language. It has an API resembling that of Qt framework, also using a widget-tree and an event-driven signal/slot system.
AIMMS is a prescriptive analytics software company with offices in the Netherlands, United States, China and Singapore.

Teradici is a privately held software company founded in 2004, with its head office in Metropolitan Vancouver, BC. Teradici initially developed a protocol (PCoIP) for compressing and decompressing images and sound when remotely accessing blade servers, and implemented it in hardware. This technology was later expanded to thin clients/zero clients for general Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. Teradici's protocol or hardware is used by HP, Dell-Wyse, Amulet Hotkey, Samsung, Amazon Web Services, Fujitsu, and VMware.
Adaptive web design (AWD) promotes the creation of multiple versions of a web page to better fit the user's device, as opposed to a single static page which loads the same on all devices or a single page which reorders and resizes content responsively based on the device/screen size/browser of the user.
Workforce optimization (WFO) is a business strategy that integrates business performance considerations with workforce management. The strategy involves automating processes, data visibility, compliance on legislation and solving business problems related to staffing. It is used by call centers to improve workforce management and agent performance.

Google Duo is a video chat mobile app developed by Google, available on the Android and iOS operating systems. It was announced at Google's developer conference on May 18, 2016, and began its worldwide release on August 16, 2016. It is also available to use via Google's Chrome web browser on desktop and laptop computers.





