Related Research Articles

Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.

Mecamylamine is a non-selective, non-competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) that was introduced in the 1950s as an antihypertensive drug. In the United States, it was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in 2009 but was brought to market in 2013 as Vecamyl and eventually was marketed by Turing Pharmaceuticals.
Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company founded in 1992. The company is headquartered in San Diego, California, and led by CEO Kevin Gorman. Neurocrine develops treatments for neurological and endocrine-related diseases and disorders. In 2017, the company's drug valbenazine (Ingrezza) was approved in the US to treat adults with tardive dyskinesia (TD).

Desvenlafaxine, sold under the brand name Pristiq among others, is a medication used to treat depression. It is an antidepressant of the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class and is taken by mouth. It is recommended that the need for further treatment be occasionally reassessed. It may be less effective than its parent compound venlafaxine, although some studies have found comparable efficacy.
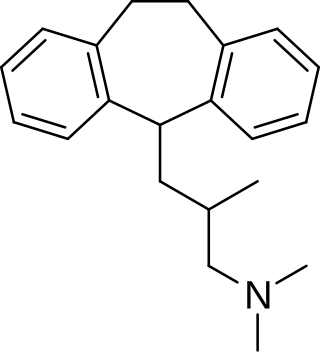
Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Indiplon is a nonbenzodiazepine, hypnotic sedative that was developed in two formulations—an immediate-release formulation for sleep onset, and a modified-release version for sleep maintenance.
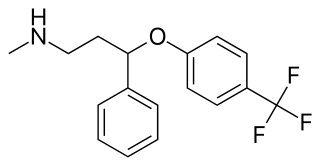
Fluoxetine, sold under the brand name Prozac, among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), anxiety, bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. It is also approved for treatment of major depressive disorder in adolescents and children 8 years of age and over. It has also been used to treat premature ejaculation. Fluoxetine is taken by mouth.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission. The naturally-occurring and potent SNDRI cocaine is widely used recreationally and often illegally for the euphoric effects it produces.
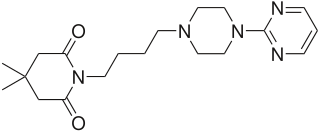
Gepirone, sold under the brand name Exxua, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It is taken orally.
The number of new psychiatric drugs, and especially antidepressants on the market in Japan, is significantly less than Western countries.

Bicifadine (DOV-220,075) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) discovered at American Cyanamid as an analgesic drug candidate, and licensed to DOV Pharmaceutical in 1998 after American Cyanamid was acquired by Wyeth.
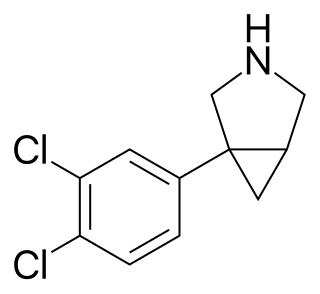
DOV 216,303 is an experimental antidepressant drug originally developed by DOV Pharmaceutical and was licensed to Merck & Co. in 2004; Merck and DOV terminated their relationship in December 2006.
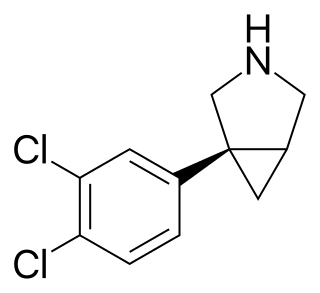
DOV-102,677 is a psychoactive drug being developed by Merck and is currently in clinical trials. It is a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), or serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI). It is the (−)-enantiomer of DOV-216,303, and its (+)-enantiomer is DOV-21,947 (amitifadine).

Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.

Wyeth was a pharmaceutical company until it was purchased by Pfizer in 2009. The company was founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1860 as John Wyeth and Brother. Its headquarters moved to Collegeville, Pennsylvania, and Madison, New Jersey, before its headquarters were consolidated with Pfizer's in New York City after the 2009 merger.

Amitifadine is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) or so-called triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI) which is or was being developed by Euthymics Bioscience It was under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder, but in May 2013, it was reported that the drug failed to show superior efficacy to placebo in a phase IIb/IIIa clinical trial. It was suggested that this may have been due to the drug being underdosed. In September 2017, development of amitifadine for the treatment of major depressive disorder was finally officially discontinued. As of September 2017, it is still listed as being under development for the treatment of alcoholism and smoking withdrawal.
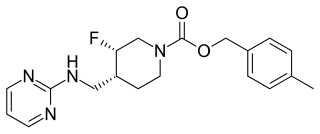
Rislenemdaz is an orally active, selective NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist which is under development by Cerecor in the United States as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). In November 2013, phase II clinical trials were initiated, and in the same month, rislenemdaz received Fast Track Designation from the Food and Drug Administration for TRD.

Centanafadine (INN) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) that began its development with Euthymics Bioscience after they acquired DOV Pharmaceutical. It was developed as a treatment for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin with a ratio of 1:6:14, respectively. In 2011, Euthymics Bioscience spun off its development of centanafadine to a new company called Neurovance. In March 2017, Otsuka Pharmaceutical acquired Neurovance and the rights to centanafadine. As of January 2018, Otsuka's pipeline indicates it is in Phase II and III clinical trials for a number of different applications to medical conditions.

Aurora Biosciences was a biotechnology company founded in 1995 in San Diego to commercialize fluorescence assays based on Roger Y. Tsien's discoveries concerning green fluorescent protein and its uses in basic research - work for which Tsien eventually won the 2008 Nobel Prize in chemistry along with two other chemists.
Phil Skolnick is an American neuroscientist and pharmacologist most widely known for his work on the psychopharmacology of depression and anxiety, as well as on addiction medicine. Author of more than 500 published papers, Skolnick's most notable accomplishments include elucidating the role of the NMDA system in depression therapeutics, demonstrating the existence of endogenous benzodiazepine receptor ligands, and spearheading the National Institute on Drug Abuse's partnership to develop a naloxone atomizer for reversal of acute opioid overdose. Skolnick's work also laid the foundation for the development of ketamine as a rapid-acting antidepressant.
References
- 1 2 Neubauer, DN. "Indiplon". pp 453-464 in GABA and Sleep: Molecular, Functional and Clinical Aspects. Eds Jaime M. Monti, Seithikurippu Ratnas Pandi-Perumal, Hanns Möhler. Springer Science & Business Media, 2010 ISBN 9783034602266
- ↑ Edgar Online. IPO Deal Data Archived 15 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine Page accessed 15 July 2015
- ↑ Hess, Diane, Drugmaker's IPO Is a Big Headache Archived 11 February 2005 at the Wayback Machine , TheStreet.com, 1 May 2002. Retrieved 5 November 2007.
- Simpson, Stephen D. A Pain DOV Pharmaceutical Couldn't Cure, Motley Fool, 26 April 2006. Retrieved 5 November 2007.
- ↑ Krauskopf, Lewis, Investors Suing Hackensack, N.J.-Based DOV Pharmaceutical over Stock Losses, The Record (Hackensack, New Jersey), 2 May 2002. Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ↑ Maeillo, Michael, The Coldest IPO..., Forbes.com, 2 September 2002. Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ↑ DOV IPO sinks on first day, CNN.com, 25 April 2002. Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ↑ "Press Release: Dr. Phil Skolnick Now Leads NIDA's Medications Development Efforts". National Institute on Drug Abuse. 1 April 2010.
- ↑ "Press Release: DOV Pharmaceutical, Inc. Announces Reorganization of Senior Management". DOV Pharmaceutical via PRNewswire. 5 July 2006.
- ↑ McCoy, Michael (12 March 2012). "Happy Results for a Depression Drug". Chemical & Engineering News Archive. 90 (11): 20–22. doi:10.1021/cen-09011-cover3. ISSN 0009-2347.
- ↑ Fierce Biotech 22 July 2010 Euthymics lands $24M to fund antidepressant work
- ↑ Bunyan, Clytie (5 September 2010). "Oklahoma attorney helps with Mass. bioscience startup". NewsOK.com.
- 1 2 Marks, DM; Pae, CU; Patkar, AA (September 2008). "Triple reuptake inhibitors: a premise and promise". Psychiatry Investig. 5 (3): 142–7. doi:10.4306/pi.2008.5.3.142. PMC 2796030 . PMID 20046357.
- ↑ [https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1066833/000114420404018172/v08017_ex10-51.txt SEC Filing: Wyeth-DOV Restated License Agreement] Page accessed July 15, 2015
- ↑ Chemical and Engineering News. 12 August 2004 Merck and DOV Pharmaceutical In Drug Pact
- ↑ Dov 8 December 2006 DOV Pharmaceutical Announces Termination Of License Agreement With Merck & Co., Inc. (MRK)
- 1 2 3 4 Edgar Online. Data as of May 2004 IPO Deal Data: Business Description Archived 15 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine Page accessed 15 July 2015
- ↑ "10-K For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007". Dov Pharmaceutical via SEC Edgar. 31 March 2008.
DOV 216,303 was originally in development for depression; however as the patented composition of matter claim has expired, there are no ongoing clinical trials of DOV 216,303 and none are planned.