
A fixed-wing aircraft is a flying machine, such as an airplane or aeroplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft, and ornithopters. The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft and airplanes that use wing morphing are all examples of fixed-wing aircraft.

The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine, typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressed air from the compressor is heated by the fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s.
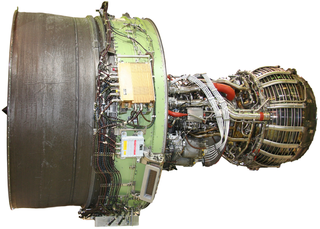
The General Electric GEnx is an advanced dual rotor, axial flow, high-bypass turbofan jet engine in production by GE Aviation for the Boeing 787 and 747-8. The GEnx is intended to replace the CF6 in GE's product line.

SSVOBB is the acronym for Stichting Studenten Vliegtuigontwikkeling, -bouw en -beheer which is Dutch for Foundation for Students in Airplane development, manufacturing and management.

An airplane or aeroplane is a powered, fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, transportation of goods and people, military, and research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne-kilometres of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be remotely or computer-controlled such as drones.
Composite gear housing refers to the use of composite materials to enclose the components of motor transmissions. Fiber reinforced composite materials are used primarily for weight reduction. Carbon fiber reinforced plastic material is commonly used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Manufacturing Engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical,chemical, electrical and industrial engineering. Manufacturing engineering requires the ability to plan the practices of manufacturing; to research and to develop tools, processes, machines and equipment; and to integrate the facilities and systems for producing quality products with the optimum expenditure of capital.

The Royal Netherlands Aerospace Centre is the National Aerospace Laboratory of the Netherlands and is one of its major technological institutes. These institutes perform a large part of the applied research in the Netherlands, each within its own specific field of technology. As an independent non-profit organisation, the NLR is the aerospace-knowledge enterprise in the Netherlands and provides high-quality technical support to the aerospace sector.
An RF switch matrix is a system of discrete electronic components that are integrated to route radio frequency (RF) signals between multiple inputs and multiple outputs. Popular applications requiring RF matrices are ground systems, test equipment, and communication systems.
NASA spinoff technologies are commercial products and services which have been developed with the help of NASA, through research and development contracts, such as Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) or STTR awards, licensing of NASA patents, use of NASA facilities, technical assistance from NASA personnel, or data from NASA research. Information on new NASA technology that may be useful to industry is available in periodical and website form in "NASA Tech Briefs", while successful examples of commercialization are reported annually in the NASA publication "Spinoffs". The Spinoff publication has documented more than 2,000 technologies over time.
The Australian Research Centre for Aerospace Automation (ARCAA) was a research centre of the Queensland University of Technology. ARCAA conducted research into all aspects of aviation automation, with a particular research focus on autonomous technologies which support the more efficient and safer utilisation of airspace, and the development of autonomous aircraft and on-board sensor systems for a wide range of commercial applications.

The history of human-powered aircraft (HPA) started in the early twentieth century. HPAs are aircraft belonging to the class of vehicles known as human-powered vehicles. Early attempts at human-powered flight were unsuccessful because of the difficulty of achieving the high power-to-weight ratio. Prototypes often used ornithopter principles which were not only too heavy to meet this requirement but aerodynamically unsatisfactory.

Tailored fiber placement (TFP) is a textile manufacturing technique based on the principle of sewing for a continuous placement of fibrous material for composite components. The fibrous material is fixed with an upper and lower stitching thread on a base material. Compared to other textile manufacturing processes fiber material can be placed near net-shape in curvilinear patterns upon a base material in order to create stress adapted composite parts.

The Clean Sky Joint Undertaking (CSJU) is a public-private partnership between the European Commission and the European aeronautics industry that coordinates and funds research activities to deliver significantly quieter and more environmentally friendly aircraft. The CSJU manages the Clean Sky Programme (CS) and the Clean Sky 2 Programme (CS2), making it Europe’s foremost aeronautical research body.

The Pipistrel Panthera is a lightweight, all-composite, highly efficient four-seat aircraft under development by Pipistrel of Slovenia.
Airglow is a pedal-driven human-powered aircraft. It was designed and developed by brothers John and Mark McIntyre of Cambridgeshire, England.
The Formula Student Team Delft is a Dutch Formula Student team based in Delft and composed mostly of students from the Delft University of Technology. The team is known for designing constructing lightweight Formula Student racing cars and competing in the global Formula Student competition since 2001. Having won Formula Student UK three times and Formula Student Germany six times, FS Team Delft is currently among the highest ranked teams in the Formula Student competition.
The term "smart structures" is commonly used for structures which have the ability to adapt to environmental conditions according to the design requirements. As a rule, the adjustments are designed and performed in order to increase the efficiency or safety of the structure. Combining "smart structures" with the "sophistication" achieved in materials science, information technology, measurement science, sensors, actuators, signal processing, nanotechnology, cybernetics, artificial intelligence, and biomimetics, one can talk about Smart Intelligent Structures. In other words, structures which are able to sense their environment, self-diagnose their condition and adapt in such a way so as to make the design more useful and efficient.
The Information Age is generally understood to have arrived with the Internet as it was developed through the 1970s and rolled out throughout the 1980s, and continues evolving to this day. So too the adoption of digital techniques in aviation also arrived progressively at around the same time and also continues today.
Automated conveyor roller condition monitoring is an emerging field that has risen out of the need to make bulk handling conveyors more reliable.











