
Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians. The Greeks referred to them as the Getae and the Romans called them Daci.

Sarmizegetusa Regia, also Sarmisegetusa, Sarmisegethusa, Sarmisegethuza, Ζαρμιζεγεθούσα (Zarmizegethoúsa) or Ζερμιζεγεθούση (Zermizegethoúsē), was the capital and the most important military, religious and political centre of the Dacians before the wars with the Roman Empire. Erected on top of a 1200 m high mountain, the fortress, comprising six citadels, was the core of a strategic defensive system in the Orăştie Mountains.

Built in murus dacicus style, the six Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains, in Romania, were created in the 1st centuries BC and AD as protection against Roman conquest, and played an important role during the Roman-Dacian wars.

The Dacians were a Thracian people who were the ancient inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians spoke the Dacian language, a sub-group of Thracian, but were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC.

Burebista was a Thracian king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61 BC to 45/44 BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian Kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, and modern day Romania and Moldova. In the 7th and 6th centuries BC it became home to the Thracian peoples, including the Getae and the Dacians. From the 4th century to the middle of the 2nd century BC the Dacian peoples were influenced by La Tène Celts who brought new technologies with them into Dacia. Sometime in the 2nd century BC the Dacians expelled the Celts from their lands. Dacians often warred with neighbouring tribes, but the relative isolation of the Dacian peoples in the Carpathian Mountains allowed them to survive and even to thrive. By the 1st century BC the Dacians had become the dominant tribe.
Hunedoara County is a county (județ) of Romania, in Transylvania, with its capital city at Deva. The county is part of the Danube–Criș–Mureș–Tisa Euroregion.

The so-called Free Dacians is the name given by some modern historians to those Dacians who putatively remained outside, or emigrated from, the Roman Empire after the emperor Trajan's Dacian Wars. Dio Cassius named them Dakoi prosoroi meaning "neighbouring Dacians".

The Kosons are the only gold coins that have been minted by the Dacians, named after the Greek alphabet inscription "ΚΟΣΩΝ" on them. It is thought that "Koson" is the name of an otherwise historically unrecorded Dacian king, though he may be identical to the Cotison mentioned by Horace and Suetonius.

Murus Dacicus is a construction method for defensive walls and fortifications developed in ancient Dacia sometime before the Roman conquest. It is a mix between traditional construction methods particular to Dacian builders and methods imported from Greek and Roman architecture and masonry, and – although somewhat similar construction techniques were used before, during and long after the period – it has peculiarities that make it unique.

Club Sportiv Municipal Dacia Orăștie 2010, commonly known as CSM Dacia Orăștie, or simply as Dacia Orăștie, is a Romanian amateur football club based in Orăștie, Hunedoara County, founded in 1935 and re-founded in 2009.

Comosicus was a Dacian king and high priest who lived in the 1st century BC. The only reference to Comosicus is a passage in the writings of the Roman historian Jordanes.

The history of Dacian warfare spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 2nd century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Dacia, populated by a collection of Thracian, Ionian, and Dorian tribes. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Dacian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Dacians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Dacians too.
The dacicus was a gold coin issued during the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian (50–96) in honor of his claimed victory against the Dacians in the 1st century. The terms of peace with Decebalus, the Dacian king, were severely criticised by contemporaneous authors, who considered this treaty shameful to the Romans as the treaty granted Decebalus an annual subsidy of 8 million sesterces. For the remainder of Domitian's reign, Dacia remained a relatively peaceful client kingdom, but Decebalus used the Roman money to fortify his defences and continued to defy Rome until the reign of Trajan.
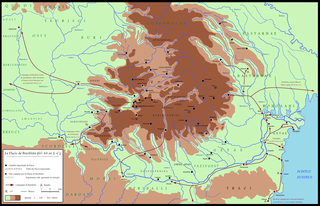
Dava was a Geto-Dacian name for a city, town or fortress. Generally, the name indicated a tribal center or an important settlement, usually fortified. Some of the Dacian settlements and the fortresses employed the Murus Dacicus traditional construction technique.
Romanian archaeology begins in the 19th century.

Situated at the top of a steep hill, the Dacian fortress of Căpâlna was built in the second half of the 1st century BC as a military defense, guarding the entrance from the Sebeș Valley to the capital of the Dacian kingdom, Sarmizegetusa Regia.

Dacian fortress of Bănița is one of the six Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains, in Romania. Together with the other Dacian fortresses in the area, it was designated as an UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1999.
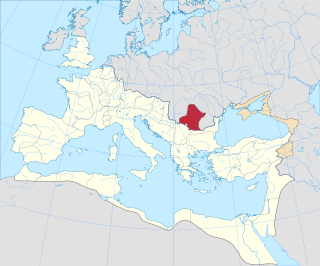
Roman Dacia was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat. During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians.














