In biological classification, the order is
- a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. The well-known ranks in descending order are: life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species, with order fitting in between class and family. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order.
- a taxonomic unit in the rank of order. In that case the plural is orders.
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the protein the viral capsid is made of. The coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form into hairpin loops that are important during replication. Parvovirus virions are small compared to most viruses, at 23–28 nanometers in diameter, and contain the genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid that has a rugged surface.
Pseudoviridae is a family of viruses, which includes three genera.
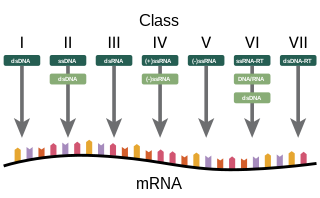
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.

Iridoviridae is a family of viruses with double-stranded DNA genomes. Amphibians, fish, and invertebrates such as arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 22 species in this family, divided among two subfamilies and seven genera.
Animal viruses are viruses that infect animals. Viruses infect all cellular life and although viruses infect every animal, plant, fungus and protist species, each has its own specific range of viruses that often infect only that species.
Marnaviridae is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order Picornavirales. The first species of this family that was isolated is Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus (HaRNAV) in the genus Marnavirus, that infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, Heterosigma akashiwo. Using a sequence-based framework an additional twenty marine RNA viruses have been added to the family.

Nudiviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family Nudiviridae. Insects and marine crustaceans serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this family, assigned to 4 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: death in larvae, chronic disease in adults.

Positive-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome.
Yuyuevirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family Yueviridae, which in turn is the only family in the order Goujianvirales and class Yunchangviricetes. Two species are recognized: Beihai yuyuevirus and Shahe yuyuevirus.
Yingvirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family Qinviridae, which is the only family in Muvirales, which is the only order in Chunqiuviricetes. There are eight species in the genus.
Riboviria is a realm of viruses that includes all viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication. It includes RNA viruses that encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, as well as reverse-transcribing viruses that encode an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called RNA replicase, produces RNA from RNA. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDp), also called reverse transcriptase (RT), produces DNA from RNA. These enzymes are essential for replicating the viral genome and transcribing viral genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation of viral proteins.
Smacoviridae is a family of single-stranded DNA viruses. The genomes of this family are small. The name Smacoviridae stands for 'small circular genome virus'. The genomes are circular single-stranded DNA and encode rolling-circle replication initiation proteins (Rep) and unique capsid proteins. As of 2021, 12 genera and 84 species are recognized in this family. The viruses in this taxon were isolated from faecal samples from insects and vertebrates by metagenomic methods. Little is known about their biology.

Duplodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all double-stranded DNA viruses that encode the HK97 fold major capsid protein. The HK97 fold major capsid protein is the primary component of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Viruses in the realm also share a number of other characteristics, such as an icosahedral capsid, an opening in the viral capsid called a portal, a protease enzyme that empties the inside of the capsid prior to DNA packaging, and a terminase enzyme that packages viral DNA into the capsid.
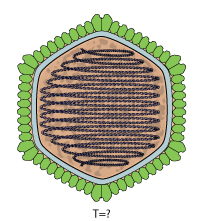
Portogloboviridae is a family of DNA viruses that infect archaea. It is a proposed family of the realm Varidnaviria. Viruses in the family are related to Halopanivirales. The capsid proteins of these viruses and their characteristics are of evolutionary importance for the origin of the other Varidnaviria viruses since they seem to retain primordial characters.

Ribozyviria is a realm of satellite nucleic acids. Established in ICTV TaxoProp 2020.012D, the realm is named after the presence of genomic and antigenomic ribozymes of the Deltavirus type. Additional common features include a rod-like structure, a RNA-binding "delta antigen" encoded in the genome, and animal hosts. Most lineages of this realm are poorly understood, the notable exception being members of the genus Deltavirus, the causal agents of Hepatitis D in humans.
Daazvirus is a genus of viruses in the realm Ribozyviria, containing the single species Daazvirus cynopis.
Deevirus is a genus of viruses in the realm Ribozyviria, containing the single species Deevirus actinopterygii. Various ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) serve as its hosts.
Dobrovirus is a genus of viruses in the realm Ribozyviria, containing the single species Dobrovirus bufonis.









