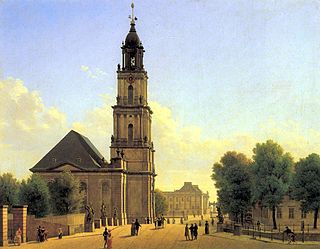Potsdam is the capital and largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some 25 kilometres southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin.

Cecilienhof Palace is a palace in Potsdam, Brandenburg, Germany, built from 1914 to 1917 in the layout of an English Tudor manor house. Cecilienhof was the last palace built by the House of Hohenzollern that ruled the Kingdom of Prussia and the German Empire until the end of World War I. It is famous for having been the location of the Potsdam Conference in 1945, in which the leaders of the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom and the United States made important decisions affecting the shape of post World War II Europe and Asia. Cecilienhof has been part of the Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1990.

The Roman Baths, situated northeast of the Charlottenhof Palace in the Sanssouci Park in Potsdam, reflect the Italiensehnsucht of its creator Frederick William IV of Prussia. Various classical Roman and antique Italian styles were melded into an architectural ensemble, created between 1829 and 1840.

Pfaueninsel is an island in the River Havel situated in Berlin-Wannsee, in the district of Steglitz-Zehlendorf in southwestern Berlin, near the border with Potsdam in Brandenburg. The island is part of the Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its outstanding Prussian architecture and is a popular destination for day-trippers. Pfaueninsel is also a nature reserve in accordance with the EU Habitats Directive and a Special Protection Area for wild birds.

The Orangery Palace is a palace located in the Sanssouci Park of Potsdam, Germany. It is also known as the New Orangery on the Klausberg, or just the Orangery. It was built on behest of the "Romantic on the Throne", King Friedrich Wilhelm IV from 1851 to 1864.

The Protestant Church of Peace is situated in the Marly Gardens on the Green Fence in the palace grounds of Sanssouci Park in Potsdam, Germany. The church was built according to the wishes and with the close involvement of the artistically gifted King Frederick William IV and designed by the court architect, Ludwig Persius. After Persius' death in 1845, the architect Friedrich August Stüler was charged with continuing his work. Building included work by Ferdinand von Arnim and Ludwig Ferdinand Hesse also. The church is located in the area covered by the UNESCO World Heritage Site Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin.

Charlottenhof Palace or Charlottenhof Manor is a former royal palace located southwest of Sanssouci Palace in Sanssouci Park at Potsdam, Germany. It is best known as the summer residence of Crown Prince Frederick William. Today it is maintained by the Prussian Palaces and Gardens Foundation Berlin-Brandenburg.

The Ruinenberg is a hill in the Bornstedt borough of Potsdam, located north of Sanssouci Park. In 1748, the Prussian king Frederick the Great had a water tank with a capacity of around 7,600 cubic metres (270,000 cu ft) built on top to supply the Sanssouci water features, and had it decorated with artificial ruins. From 1841 a surrounding landscape garden was laid out at the behest of King Frederick William IV of Prussia, according to plans designed by Peter Joseph Lenné.

The New Palace is a palace situated on the western side of the Sanssouci park in Potsdam, Germany. The building was begun in 1763, after the end of the Seven Years' War, under King Friedrich II and was completed in 1769. It is considered to be the last great Prussian Baroque palace.
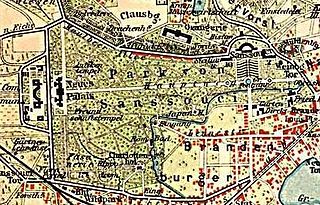
Sanssouci Park is a large park surrounding Sanssouci Palace in Potsdam, Germany, built under Frederick the Great in the mid-18th centurys. Following the terracing of the vineyard and the completion of the palace, the surroundings were included in the structure. A Baroque flower garden with lawns, flower beds, hedges and trees was created. In the hedge quarter 3,000 fruit trees were planted. The greenhouses of the numerous nurseries contained oranges, melons, peaches and bananas. The goddesses Flora and Pomona, who decorate the entrance obelisk at the eastern park exit, were placed there to highlight the connection of a flower, fruit and vegetable garden. Along with the Sanssouci Palace and other nearby palaces and parks, Sanssouci Park was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1990 for its unique architectural unity and testimony to 18th and 19th century landscaping in Europe.

Bornstedt is a borough of Potsdam, Germany. Located north of Sanssouci Park and the Orangery Palace, it is known for the Bornstedt Crown Estate, former residence of Princess Royal Victoria, and the Bornstedt Cemetery with numerous tombs of famous personages.

The Berlin Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum is a botanical garden in the Lichterfelde locality of the borough of Steglitz-Zehlendorf, Berlin, Germany. Constructed between 1897 and 1910 under the guidance of architect Adolf Engler, it has an area of 43 hectares [ha] and around 22,000 different plant species. The garden is part of the Free University of Berlin.

Sanssouci is a historical building in Potsdam, near Berlin. Built by Prussian King Frederick the Great as his summer palace, it is often counted among the German rivals of Versailles. While Sanssouci is in the more intimate Rococo style and is far smaller than its French Baroque counterpart, it, too, is notable for the numerous temples and follies in the surrounding park. The palace was designed and built by Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff between 1745 and 1747 to meet Frederick's need for a private residence where he could escape the pomp and ceremony of the royal court. The palace's name is a French phrase meaning "without worries" or "carefree", emphasising that the palace was meant as a place of relaxation rather than a seat of power.

The Marmorpalais is a former royal residence in Potsdam, near Berlin in Germany, built on the grounds of the extensive Neuer Garten on the shores of the Heiliger See. The palace was commissioned by King Frederick William II of Prussia and designed in the early Neoclassical style by the architects Carl von Gontard and Carl Gotthard Langhans. Despite the name, brick is the main material. The palace remained in use by the Hohenzollern family until the early 20th century. It served as a military museum under communist rule, but has since been restored and is once again open to the public.

The Schloss Britz is the former manor-house of the historical Rittergut and village Britz, now a district of Berlin-Neukölln. Today it is the headquarters of the cultural organization Kulturstiftung Schloss Britz and includes authentic reconstructed rooms from around 1880. The house is a museum demonstrating interiors of the Gründerzeit era. The manorial park is also well preserved with its mature trees and its 1890s system of trails. In 1997 the park was honored with the German Gustav Meyer Prize for the accuracy and historic authenticity of the reconstruction.
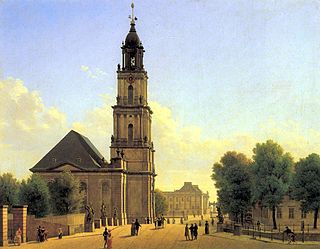
The Garrison Church was a Protestant church in the historic centre of Potsdam. Built by order of King Frederick William I of Prussia according to plans by Philipp Gerlach from 1730 to 1735, it was considered as a major work of Prussian Baroque architecture. With a height of almost 90 metres, it was Potsdam's tallest building and shaped its cityscape. In addition, the Garrison Church was part of the city's famous "Three Churches View" together with the St. Nicholas Church and the Holy Spirit Church. After it was damaged during the British bombing in World War II, the East German authorities demolished the church in 1968. After the German reunification, the Garrison Church is currently being rebuilt as a centre for remembrance and reconciliation.

The New Garden in Potsdam is a park of 102.5 hectares located southwest of Berlin, Germany, in northern Potsdam and bordering on the lakes Heiliger See and Jungfernsee. Starting in 1787, Frederick William II of Prussia (1744-1797) arranged to have a new garden laid out on this site, and the design and landscaping was carried out by Johann August Eyserbeck, who had previously worked on the Dessau-Wörlitz Garden Realm.

Przyrzecze street is a street located in the old town district of Bydgoszcz, Poland. Many of its buildings are part of Bydgoszcz local history. Due to the proximity of the river, its townhouses represent a picturesque urban complex.

The Stern Hunting Lodge in Potsdam was built between 1730 and 1732 under the reign of the Soldier King Frederick William I in the style of a simple Dutch town house. The contract for the construction was probably awarded to Cornelius van den Bosch, a grenadier and master carpenter from Holland, and the building was supervised by Pierre de Gayette, Captain of the Corps of Engineers and Court Architect.