Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety, suspicion, or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself. Paranoia is distinct from phobias, which also involve irrational fear, but usually no blame.
A delusion is a false fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some other misleading effects of perception, as individuals with those beliefs are able to change or readjust their beliefs upon reviewing the evidence. However:

Delusional disorder, traditionally synonymous with paranoia, is a mental illness in which a person has delusions, but with no accompanying prominent hallucinations, thought disorder, mood disorder, or significant flattening of affect. Delusions are a specific symptom of psychosis. Delusions can be bizarre or non-bizarre in content; non-bizarre delusions are fixed false beliefs that involve situations that could occur in real life, such as being harmed or poisoned. Apart from their delusion or delusions, people with delusional disorder may continue to socialize and function in a normal manner and their behavior does not necessarily seem odd. However, the preoccupation with delusional ideas can be disruptive to their overall lives.
Richard Bentall is a Professor of Clinical Psychology at the University of Sheffield in the UK.
Thought broadcasting is a type of delusional condition in which the affected person believes that others can hear their inner thoughts, despite a clear lack of evidence. The person may believe that either those nearby can perceive their thoughts or that they are being transmitted via mediums such as television, radio or the internet. Different people can experience thought broadcasting in different ways. Thought broadcasting is most commonly found among people who have a psychotic disorder, specifically schizophrenia.
Virtual reality therapy (VRT), also known as virtual reality immersion therapy (VRIT), simulation for therapy (SFT), virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET), and computerized CBT (CCBT), is the use of virtual reality technology for psychological or occupational therapy and in affecting virtual rehabilitation. Patients receiving virtual reality therapy navigate through digitally created environments and complete specially designed tasks often tailored to treat a specific ailment; and is designed to isolate the user from their surrounding sensory inputs and give the illusion of immersion inside a computer-generated, interactive virtual environment. This technology has a demonstrated clinical benefit as an adjunctive analgesic during burn wound dressing and other painful medical procedures. Technology can range from a simple PC and keyboard setup, to a modern virtual reality headset. It is widely used as an alternative form of exposure therapy, in which patients interact with harmless virtual representations of traumatic stimuli in order to reduce fear responses. It has proven to be especially effective at treating PTSD, and shows considerable promise in treating a variety of neurological and physical conditions. Virtual reality therapy has also been used to help stroke patients regain muscle control, to treat other disorders such as body dysmorphia, and to improve social skills in those diagnosed with autism.

Dame Uta Frith is a German-British developmental psychologist and emeritus professor in cognitive development at the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London (UCL). She pioneered much of the current research into autism and dyslexia. Her book Autism: Explaining the Enigma introduced the cognitive neuroscience of autism. She is credited with creating the Sally–Anne test along with fellow scientists Alan Leslie and Simon Baron-Cohen. Among students she has mentored are Tony Attwood, Maggie Snowling, Simon Baron-Cohen and Francesca Happé.
Susan Fiona Dorinthea Michie is a British academic, clinical psychologist, and professor of health psychology, director of The Centre for Behaviour Change and head of The Health Psychology Research Group, all at University College London. She is also an advisor to the British Government via the SAGE advisory group on matters concerning behavioural compliance with government regulations during the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2022, she was appointed Chair of the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) Technical Advisory Group on Behavioural Insights and Sciences for Health.
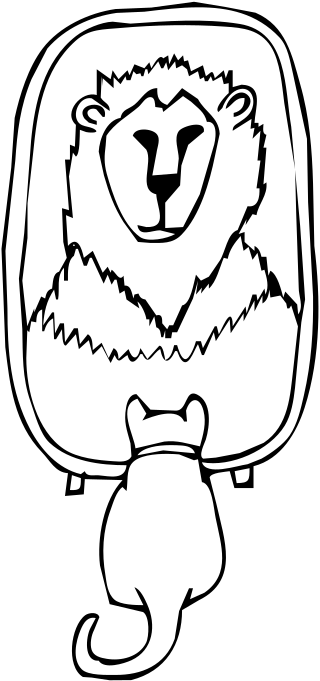
Grandiose delusions (GDs), also known as delusions of grandeur or expansive delusions, are a subtype of delusion characterized by extraordinary belief that one is famous, omnipotent, wealthy, or otherwise very powerful. Grandiose delusions often have a religious, science fictional, or supernatural theme. Examples include the extraordinary belief that one is a deity or celebrity, or that one possesses extraordinary talents, accomplishments, or superpowers.

A persecutory delusion is a type of delusional condition in which the affected person believes that harm is going to occur to oneself by a persecutor, despite a clear lack of evidence. The person may believe that they are being targeted by an individual or a group of people. Persecution delusions are very diverse in terms of content and vary from the possible, although improbable, to the completely bizarre. The delusion can be found in various disorders, being more usual in psychotic disorders.
A religious delusion is defined as a delusion, or fixed belief not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence, involving religious themes or subject matter. Religious faith, meanwhile, is defined as a belief in a religious doctrine or higher power in the absence of evidence. Psychologists, scientists, and philosophers have debated the distinction between the two, which is subjective and cultural.

Doctoring the Mind: Why psychiatric treatments fail is a 2009 book by Richard Bentall, his thesis is critical of contemporary Western psychiatry. Bentall, a professor of clinical psychology, argues that recent scientific research shows that the medical approach to mental illness is fatally flawed. According to Bentall, it seems there is no "evidence that psychiatry has made a positive impact on human welfare" and "patients are doing no better today than they did a hundred years ago".
Anke Ehlers is a German psychologist and expert in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). She is a Fellow of the major science academies of the UK and Germany.
Jane Wardle FBA FMedSci was a professor of clinical psychology and director of the Cancer Research UK Health Behaviour Research Centre at University College London. She was one of the pioneers of health psychology in the UK and internationally, known for her seminal work on the contribution of psychology to public health, particularly the role of psychological research in cancer prevention and work on the behavioural and genetic determinants of eating behaviour and obesity.

Francesca Gabrielle Elizabeth Happé is Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience and Director of the MRC Social, Genetic and Developmental Psychiatry Centre at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King's College London. Her research concerns autism spectrum conditions, specifically the understanding social cognitive processes in these conditions.

Philippa Garety is Professor of Clinical Psychology and Clinical Director of the Psychosis Clinical Academic Group (CAG), South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust. Garety specializes in the psychological understanding and treatment of psychosis and, in particular, delusions.

Elizabeth Alice Kuipers is a professor of psychology at the Institute of Psychiatry, King's College London, and was head of the Psychology Department from 2006- 2012. Kuipers is a consultant clinical psychologist and until 2012, had an honorary appointment at the South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust, working as part of the psychosis community mental health team in Southwark. She is a founding director of the PICuP clinic and was the chair of the NICE Schizophrenia Guideline update 2007-9 and the Psychosis and Schizophrenia update 2011-2014
Metacognitive training (MCT) is an approach for treating the symptoms of psychosis in schizophrenia, especially delusions, which has been adapted for other disorders such as depression, obsessive–compulsive disorder and borderline over the years. It was developed by Steffen Moritz and Todd Woodward. The intervention is based on the theoretical principles of cognitive behavioral therapy, but focuses in particular on problematic thinking styles that are associated with the development and maintenance of positive symptoms, e.g. overconfidence in errors and jumping to conclusions. Metacognitive training exists as a group training (MCT) and as an individualized intervention (MCT+).
Nicholas Tarrier, FBA, FBPsS is a psychologist and academic. He was Professor of Clinical Psychology at the University of Manchester from 1991 to 2011, and Professor of Clinical Psychology and eHealth Studies at King's College London from 2011 to 2014.
Willem Kuyken is a British/Dutch scientist, teacher and author. He is the Ritblat Professor of Mindfulness and Psychological Science at the University of Oxford, United Kingdom, and Director of the University of Oxford Mindfulness Centre.








