
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a product or service. Advertising aims to put a product or service in the spotlight in hopes of drawing it attention from consumers. It is typically used to promote a specific good or service, but there are wide range of uses, the most common being the commercial advertisement.

A television advertisement is a span of television programming produced and paid for by an organization. It conveys a message promoting, and aiming to market, a product, service or idea. Advertisers and marketers may refer to television commercials as TVCs.

Sex appeal is often used in advertising to help sell a particular product or service. According to research, sexually appealing content, such as imagery, used for marketing does not need to pertain to the product or service in question. Rather, such content is utilized as an attempt to shape or shift brand image held by the consumer. As more companies have adopted the ad strategy of "sex sells", the prevalence of sexual campaigns has led to controversy. Consumers in society have voiced concern over the techniques and content used for titillating audiences, often stemming from the fact that such ads challenge conventional morals and cultural standards.
Digital display advertising is online graphic advertising through banners, text, images, video, and audio. The main purpose of digital display advertising is to post company ads on third-party websites. A display ad is usually interactive, which allows brands and advertisers to engage deeper with the users. A display ad can also be a companion ad for a non-clickable video ad.

Google Ads is an online advertising platform developed by Google, where advertisers bid to display brief advertisements, service offerings, product listings, or videos to web users. It can place ads both in the results of search engines like Google Search and on non-search websites, mobile apps, and videos. Services are offered under a pay-per-click (PPC) pricing model.
In politics, campaign advertising is the use of an advertising campaign through the media to influence a political debate, and ultimately, voters. These ads are designed by political consultants and political campaign staff. Many countries restrict the use of broadcast media to broadcast political messaging. In the European Union, many countries do not permit paid-for TV or radio advertising for fear that wealthy groups will gain control of airtime, making fair play impossible and distorting the political debate in the process.
Music in advertising refers to music integrated into mass electronic media advertisements to enhance its success. Music in advertising affects the way viewers perceive the brand by different means and on different levels, and "can significantly affect the emotional response to television commercials." It also affects the musicians whose music is featured in advertisements.
Interactive advertising uses online or offline interactive media to communicate with consumers and to promote products, brands, services, and public service announcements, corporate or political groups.

Digital marketing is the component of marketing that uses the Internet and online based digital technologies such as desktop computers, mobile phones and other digital media and platforms to promote products and services. Its development during the 1990s and 2000s changed the way brands and businesses use technology for marketing. As digital platforms became increasingly incorporated into marketing plans and everyday life, and as people increasingly use digital devices instead of visiting physical shops, digital marketing campaigns have become prevalent, employing combinations of search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, influencer marketing, content automation, campaign marketing, data-driven marketing, e-commerce marketing, social media marketing, social media optimization, e-mail direct marketing, display advertising, e–books, and optical disks and games have become commonplace. Digital marketing extends to non-Internet channels that provide digital media, such as television, mobile phones, callback, and on-hold mobile ring tones. The extension to non-Internet channels differentiates digital marketing from online advertising.
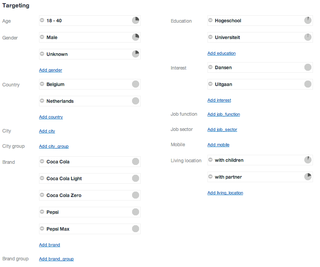
Targeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic with a focus on race, economic status, sex, age, generation, level of education, income level, and employment, or psychographic focused on the consumer values, personality, attitude, opinion, lifestyle and interest. This focus can also entail behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent online activities. The process of algorithm targeting eliminates waste.
Social network advertising, also social media targeting, is a group of terms that are used to describe forms of online advertising/digital marketing that focus on social networking services. One of the major benefits of this type of advertising is that advertisers can take advantage of the users' demographic information and target their ads appropriately.

Social media marketing is the use of social media platforms and websites to promote a product or service. Although the terms e-marketing and digital marketing are still dominant in academia, social media marketing is becoming more popular for both practitioners and researchers. Most social media platforms have built-in data analytics tools, enabling companies to track the progress, success, and engagement of ad campaigns. Companies address a range of stakeholders through social media marketing, including current and potential customers, current and potential employees, journalists, bloggers, and the general public. On a strategic level, social media marketing includes the management of a marketing campaign, governance, setting the scope and the establishment of a firm's desired social media "culture" and "tone."

Adriel O. Hampton is an American entrepreneur, strategist, and political figure from California. Hampton runs The Adriel Hampton Group, a digital advertising agency dedicated to supporting progressive causes. In 2020, he co-founded New Noise Works, a video game studio that distributes 60 percent of revenue to activist and mutual aid organizations. Additionally, Hampton is the founder of The Really Online Lefty League political action committee (PAC).
140 Proof is an advertising company that uses social data from many sources in targeting relevant ads based on consumers' interests as indicated by their social activity across networks.

Brandalism is an anti-advertising movement. It is a form of creative activism that uses subvertising to alter and critique corporate advertising by creating parodies or spoofs to replace ads in public areas. The art is typically intended to draw attention to political and social issues such as consumerism and the environment. Advertisements produced by the Brandalism movement are silk screen printed artworks, and may take the form of a new image, or a satirical alteration to an existing image, icon or logo. The advertisements are often pasted over billboards, or propped under the glass of roadside advertising spaces.

Propaganda is a form of persuasion that is often used in media to further some sort of agenda, such as a personal, political, or business agenda, by evoking an emotional or obligable response from the audience. It includes the deliberate sharing of realities, views, and philosophies intended to alter behavior and stimulate people to act.

The Honest Ads Act was a bill in the United States Senate intended to regulate online campaign advertisements by companies. The bill was proposed on October 19, 2017, as a response to Facebook's disclosure of Russia purchasing political ads during the 2016 United States presidential election. The Honest Ads Act was eventually incorporated into the For the People Act, which has passed the House but stalled in the Senate during the 116th and 117th Congresses.
"Project Alamo" was a database of voter information created for Donald Trump's 2016 presidential campaign and an associated fundraising and political advertising operation on social media platforms. It was organized by the Giles-Parscale firm in San Antonio, Texas. The campaign paid Giles-Parscale as much as $94 million for fundraising, political advertising, and digital media services, including the creation of Trump's web site. A new database of voter information named "Project Alamo" was at the heart of Giles-Parscale's efforts, allowing highly targeted advertising on social media platforms. The advertising campaigns added to the database over time, driving more effective targeting. The scale of the fundraising and political advertising campaigns on social media was massive, with hundreds of thousands of targeted ads being delivered daily. Project Alamo has been credited as an important factor in Trump's 2016 victory.
In the 2010s, personal data belonging to millions of Facebook users was collected without their consent by British consulting firm Cambridge Analytica, predominantly to be used for political advertising.
Social media was used extensively in the 2020 United States presidential election. Both incumbent president Donald Trump and Democratic Party nominee Joe Biden's campaigns employed digital-first advertising strategies, prioritizing digital advertising over print advertising in the wake of the pandemic. Trump had previously utilized his Twitter account in the past to reach his voters and make announcements, both during and after the 2016 election. The Democratic Party nominee Joe Biden also made use of social media networks to express his views and opinions on important events such as the Trump administration's response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the protests following the murder of George Floyd, and the controversial appointment of Amy Coney Barrett to the Supreme Court.











