Related Research Articles

The Purus River is a tributary of the Amazon River in South America. Its drainage basin is 371,042 km2 (143,260 sq mi), and the mean annual discharge is 11,207 m3/s (395,800 cu ft/s). The river shares its name with the Alto Purús National Park and the Purús Province, one of the four provinces of Peru in the Ucayali Region.

The federative units of Brazil are subnational entities with a certain degree of autonomy and endowed with their own government and constitution, which together form the Federative Republic of Brazil. There are 26 states and one federal district. The states are generally based on historical, conventional borders which have developed over time. The states are divided into municipalities, while the Federal District assumes the competences of both a state and a municipality.
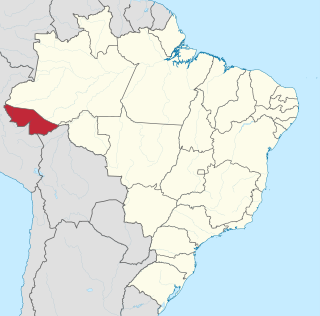
Acre is a state located in the west of the North Region of Brazil and the Amazonia Legal. Located in the westernmost part of the country, at a two-hour time difference from Brasília, Acre is bordered clockwise by the Brazilian states of Amazonas and Rondônia to the north and east, the Bolivian department of Pando to the southeast, and the Peruvian regions of Madre de Dios, Ucayali and Loreto to the south and west. The state, which has 0.42% of the Brazilian population, generates 0.2% of the Brazilian GDP.

Manaus is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian state of Amazonas. It is the seventh-largest city in Brazil, with an estimated 2020 population of 2,219,580 distributed over a land area of about 11,401 km2 (4,402 sq mi). Located at the east center of the state, the city is the center of the Manaus metropolitan area and the largest metropolitan area in the North Region of Brazil by urban landmass. It is situated near the confluence of the Negro and Solimões rivers. It is the only city in the Amazon Rainforest with a population over 1 million people.

The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small portion of westernmost Brazil in South America, along with certain Caribbean and Atlantic islands.

Rio Branco is a Brazilian municipality, capital of the state of Acre. Located in the valley of the Acre River in northern Brazil, it is the most populous municipality in the state, with 413,418 inhabitants, according to the 2018 census, almost half the state population. Rio Branco was one of the first settlements to develop in the region, being the westernmost major settlement in the country and the 4th-oldest state capital city in Northern Brazil, after Belém, Manaus and Macapá.

José Maria da Silva Paranhos Júnior, Baron of Rio Branco was a Brazilian noble, diplomat, geographer, historian, politician and professor, considered to be the "father of Brazilian diplomacy". He was the son of statesman José Paranhos, Viscount of Rio Branco. The Baron of Rio Branco was a member of the Brazilian Academy of Letters, occupying its 34th chair from 1898 until his death in 1912. As a representative of Brazil, he managed to peacefully resolve all Brazil's border disputes with its South American neighbours and incorporate 900 thousand square kilometers through his diplomacy alone.

The North Region of Brazil is the largest region of Brazil, corresponding to 45.27% of the national territory. It is the second least inhabited of the country, and contributes with a minor percentage in the national GDP and population. It comprises the states of Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Roraima and Tocantins.

Arawan is a family of languages spoken in western Brazil and Peru (Ucayali).

The Treaty of Petrópolis, signed on November 11, 1903, in the Brazilian city of Petrópolis, ended the Acre War between Bolivia and Brazil over the then-Bolivian territory of Acre, a desirable territory in the Bolivia-Brazil border during the contemporary rubber boom.
The Roosevelt River is a Brazilian river, a tributary of the Aripuanã River about 760 km (470 mi) in length.

The Acre River is a 680 kilometres (420 mi) long river in central South America.

Panoan is a family of languages spoken in Peru, western Brazil, and Bolivia. It is possibly a branch of a larger Pano–Tacanan family.

Lençóis Maranhenses National Park is a national park in Maranhão state in northeastern Brazil, just east of the Baía de São José. Protected on June 2, 1981, the 155,000 ha (380,000-acre) park includes 70 km (43 mi) of coastline, and an interior composed of rolling sand dunes. During the rainy season, the valleys among the dunes fill with freshwater lagoons, prevented from draining due to the impermeable rock beneath. The park is home to a range of species, including four listed as endangered, and has become a popular destination for ecotourists.

Time in Brazil is calculated using standard time, and the country is divided into four standard time zones: UTC−02:00, UTC−03:00, UTC−04:00 and UTC−05:00.

Santana de Parnaíba is a city and municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo. The population is 142,301 in an area of 179.95 km2 (69.48 sq mi). It was founded in 1625 near the Tietê River by Susana Dias, an important Bandeirante wife. It was the birthplace of prominent Bandeirante Domingos Jorge Velho.
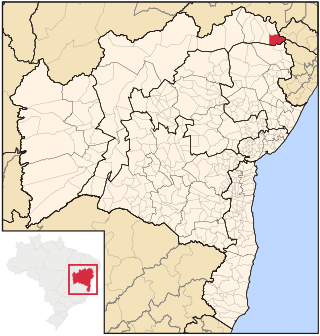
Paulo Afonso is a city in Bahia, Brazil. It was founded in 1958.

Xapuri is a municipality located in the southeast of the Brazilian state of Acre. It was the scene of an early bloodless victory during the war to make Acre independent of Bolivia. The town is known as the birthplace of the rubber tapper and environmentalist Chico Mendes and of the surgeon and professor Adib Jatene.

Alcobaça is a municipality of Bahia, Brazil.

The Acre War, known in Brazil as Acrean Revolution and in Spanish as La Guerra del Acre was a border conflict between Bolivia and the First Brazilian Republic over the Acre Region, which was rich in rubber and gold deposits. The conflict had two phases between 1899 and 1903 and ended with an Acrean victory and the subsequent Treaty of Petrópolis, which ceded Acre to Brazil. The outcome also affected territories disputed with Peru.