
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA. The genome includes both the genes and the noncoding DNA, as well as mitochondrial DNA and chloroplast DNA. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of several organisms have been sequenced and genes analyzed. The Human Genome Project reported the sequencing of the entire genome for Homo sapiens in April 2003, although only 92% of the DNA was actually decoded. With advancements in technology that could handle sequencing of the many repetitive sequences found in human DNA that were not fully uncovered by the original Human Genome Project study, scientists reported the first end-to-end human genome sequence in March, 2022.
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing during maturation of the final RNA product. In other words, introns are non-coding regions of an RNA transcript, or the DNA encoding it, that are eliminated by splicing before translation. The word intron is derived from the term intragenic region, i.e. a region inside a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. Sequences that are joined in the final mature RNA after RNA splicing are exons.
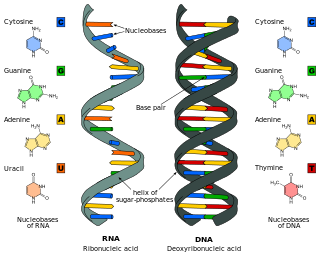
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA.

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.

RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns and splicing back together exons. For nuclear-encoded genes, splicing occurs in the nucleus either during or immediately after transcription. For those eukaryotic genes that contain introns, splicing is usually needed to create an mRNA molecule that can be translated into protein. For many eukaryotic introns, splicing occurs in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). There exist self-splicing introns, that is, ribozymes that can catalyze their own excision from their parent RNA molecule. The process of transcription, splicing and translation is called gene expression, the central dogma of molecular biology.

Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions. Notably, alternative splicing allows the human genome to direct the synthesis of many more proteins than would be expected from its 20,000 protein-coding genes.
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological databases, and others.

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.
Post-transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell. There are many types of post-transcriptional modifications achieved through a diverse class of molecular mechanisms.
Marlene Belfort is an American biochemist known for her research on the factors that interrupt genes and proteins. She is a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and has been admitted to the United States National Academy of Sciences.
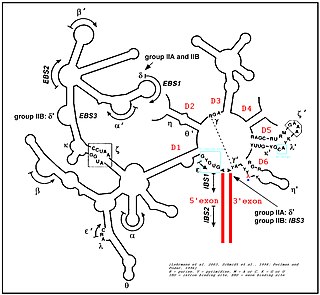
Group II introns are a large class of self-catalytic ribozymes and mobile genetic elements found within the genes of all three domains of life. Ribozyme activity can occur under high-salt conditions in vitro. However, assistance from proteins is required for in vivo splicing. In contrast to group I introns, intron excision occurs in the absence of GTP and involves the formation of a lariat, with an A-residue branchpoint strongly resembling that found in lariats formed during splicing of nuclear pre-mRNA. It is hypothesized that pre-mRNA splicing may have evolved from group II introns, due to the similar catalytic mechanism as well as the structural similarity of the Group II Domain V substructure to the U6/U2 extended snRNA. Finally, their ability to site-specifically insert into DNA sites has been exploited as a tool for biotechnology. For example, group II introns can be modified to make site-specific genome insertions and deliver cargo DNA such as reporter genes or lox sites

The homing endonucleases are a collection of endonucleases encoded either as freestanding genes within introns, as fusions with host proteins, or as self-splicing inteins. They catalyze the hydrolysis of genomic DNA within the cells that synthesize them, but do so at very few, or even singular, locations. Repair of the hydrolyzed DNA by the host cell frequently results in the gene encoding the homing endonuclease having been copied into the cleavage site, hence the term 'homing' to describe the movement of these genes. Homing endonucleases can thereby transmit their genes horizontally within a host population, increasing their allele frequency at greater than Mendelian rates.
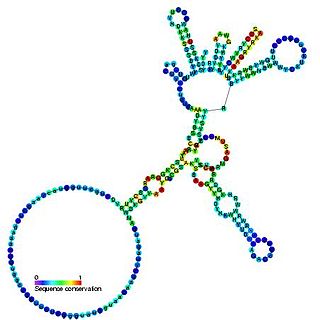
Group I introns are large self-splicing ribozymes. They catalyze their own excision from mRNA, tRNA and rRNA precursors in a wide range of organisms. The core secondary structure consists of nine paired regions (P1-P9). These fold to essentially two domains – the P4-P6 domain and the P3-P9 domain. The secondary structure mark-up for this family represents only this conserved core. Group I introns often have long open reading frames inserted in loop regions.

A retron is a distinct DNA sequence found in the genome of many bacteria species that codes for reverse transcriptase and a unique single-stranded DNA/RNA hybrid called multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA). Retron msr RNA is the non-coding RNA produced by retron elements and is the immediate precursor to the synthesis of msDNA. The retron msr RNA folds into a characteristic secondary structure that contains a conserved guanosine residue at the end of a stem loop. Synthesis of DNA by the retron-encoded reverse transcriptase (RT) results in a DNA/RNA chimera which is composed of small single-stranded DNA linked to small single-stranded RNA. The RNA strand is joined to the 5′ end of the DNA chain via a 2′–5′ phosphodiester linkage that occurs from the 2′ position of the conserved internal guanosine residue.

16S ribosomal RNA is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome. It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.

Nucleic acid tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a nucleic acid polymer. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structural motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.
Numerous key discoveries in biology have emerged from studies of RNA, including seminal work in the fields of biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, molecular biology, molecular evolution and structural biology. As of 2010, 30 scientists have been awarded Nobel Prizes for experimental work that includes studies of RNA. Specific discoveries of high biological significance are discussed in this article.
The split gene theory is a theory of the origin of introns, long non-coding sequences in eukaryotic genes between the exons. The theory holds that the randomness of primordial DNA sequences would only permit small (< 600bp) open reading frames (ORF), and that important intron structures and regulatory sequences are derived from stop codons. In this introns-first framework, the spliceosomal machinery and the nucleus evolved due to the necessity to join these ORFs into larger proteins, and that intronless bacterial genes are less ancestral than the split eukaryotic genes. The theory originated with Periannan Senapathy.











