Related Research Articles

A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house in the territory of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.

Fishbourne Roman Palace or Fishbourne Villa is in the village of Fishbourne, near Chichester in West Sussex. The palace is the largest known Roman residence north of the Alps, and has an unusually early date of 75 AD, around thirty years after the Roman conquest of Britain.

Camulodunum, the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest recorded town in Britain" has become popular with residents and is still used on heritage roadsigns on trunk road approaches. Originally the site of the Brythonic-Celtic oppidum of Camulodunon, capital of the Trinovantes and later the Catuvellauni tribes, it was first mentioned by name on coinage minted by the chieftain Tasciovanus some time between 20 and 10 BC. The Roman town began life as a Roman legionary base constructed in the AD 40s on the site of the Brythonic-Celtic fortress following its conquest by the Emperor Claudius. After the early town was destroyed during the Iceni rebellion in AD 60/61, it was rebuilt, reaching its zenith in the 2nd and 3rd centuries. During this time it was known by its official name Colonia Claudia Victricensis, often shortened to Colonia Victricensis, and as Camulodunum, a Latinised version of its original Brythonic name. The town was home to a large classical temple, two theatres, several Romano-British temples, Britain's only known chariot circus, Britain's first town walls, several large cemeteries and over 50 known mosaics and tessellated pavements. It may have reached a population of 30,000 at its height.
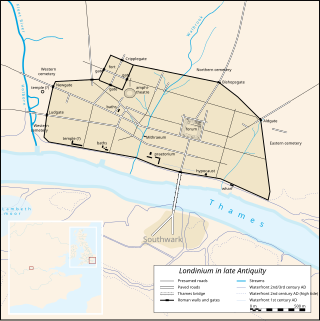
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. Most twenty-first century historians think that it was originally a settlement established shortly after the Claudian invasion of Britain, on the current site of the City of London around 47–50 AD, but some defend an older view that the city originated in a defensive enclosure constructed during the Claudian invasion in 43 AD. Its earliest securely-dated structure is a timber drain of 47 AD. It sat at a key ford at the River Thames which turned the city into a road nexus and major port, serving as a major commercial centre in Roman Britain until its abandonment during the 5th century.

Sir Henry Hamilton Johnston was a British explorer, botanist, artist, colonial administrator, and linguist who travelled widely across Africa to speak some of the languages spoken by people on that continent. He published 40 books on subjects related to the continent of Africa and was one of the key players in the Scramble for Africa that occurred at the end of the 19th century.

Dorchester is the county town of Dorset, England. It is situated between Poole and Bridport on the A35 trunk route. A historic market town, Dorchester is on the banks of the River Frome to the south of the Dorset Downs and north of the South Dorset Ridgeway that separates the area from Weymouth, 7 miles (11 km) to the south. The civil parish includes the experimental community of Poundbury and the suburb of Fordington.

Stroud is a market town and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is the main town in Stroud District. The town's population was 13,500 in 2021.

Butser Ancient Farm is an archaeological open-air museum and experimental archaeology site located near Petersfield in Hampshire, southern England. Butser features experimental reconstructions of prehistoric, Romano-British and Anglo-Saxon buildings. Examples of Neolithic dwellings, Iron Age roundhouses, a Romano-British villa and an early Saxon house are on display. The site is used as both a tourist attraction and a site for the undertaking of experimental archaeology. In this latter capacity, it was designed so that archaeologists could learn more about the agricultural and domestic economy in Britain during the millennium that lasted from circa 400 BCE to 400 CE, in what was the Late British Iron Age and Romano-British periods.

Walton-on-the-Hill is a village in the Reigate and Banstead district, in the county of Surrey, England. It is midway between the market towns of Reigate and Epsom. The village is a dispersed cluster on the North Downs centred less than one mile inside of the M25 motorway. The village hosts the Walton Heath Golf Club, whose former members include King Edward VIII, Winston Churchill and David Lloyd George.
The year 1965 in archaeology involved some significant events.

Brantingham is a village and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, about 2 miles (3 km) north of Brough, 12 miles (19 km) west of Hull and north of the A63 road. The 2011 UK Census gave the parish had a population of 370, marking a decrease from the 2001 UK census figure of 410. The 2019 estimate was 319.

Guy Martyn Thorold Huchet de la Bédoyère is a British historian who has published widely on Roman Britain and other subjects and appeared regularly on Time Team, an archaeological television series first broadcast on Channel 4.

Sparsholt (/ˈspɑːʃəʊlt/) is a village and civil parish in Hampshire, England, 2+1⁄2 miles (4 km) west of Winchester. In 1908 its area was 3,672 acres (1,486 ha). The 2011 Census recorded its population as 982.

Rockbourne Roman Villa is a Roman courtyard villa excavated and put on public display in the village of Rockbourne in the English county of Hampshire. The villa was discovered in 1942 by a local farmer and excavated by A. T. Morley Hewitt over the next thirty years.
Roman villas in northwestern Gaul functioned as colonial economic centers. Most villas did not resemble the luxurious, aristocratic country retreats of the Mediterranean region. Their owners were absentee investors, managed by local Gauls whose families were rewarded after the Gallo-Roman wars.

Sparsholt Roman Villa was a Roman villa near the village of Sparsholt, Hampshire, England. It was constructed in phases from the 2nd to the 5th century, and then abandoned. It was excavated in 1965–72. Nothing is visible at the site today, but finds from the excavations are on display in Winchester City Museum, and one wing of the villa has been reconstructed at Butser Ancient Farm.
George Nicolas "Nick" Georgano was a British author, specialising in motoring history. His most notable work is The Complete Encyclopedia of Motorcars, first published in 1968.

Keynsham Roman Villa refers to a cluster of villas built during the Roman occupation of Britain near Keynsham in Somerset, England. Two villas have been found, the larger of which is thought to be one of the grandest villas constructed in all of Britain. The sites have never been fully excavated, in part because portions of each are located underneath a cemetery, a major road, and the now shuttered Somerdale Chocolate Factory.
Frances Stackhouse Acton was a British botanist, archaeologist, writer and artist. Her father was noted botanist, Thomas Andrew Knight, who encouraged her education and included her in his experiments. She married an older land owner and, as they had no children, when he died she pursued her own interests, which included archaeology and architecture. She excavated a Roman villa, built a number of buildings and saved others in need of repair. She was keen on painting buildings and eventually went on to publish a charitable book, The Castles & Old Mansions of Shropshire.
The Hampshire Field Club & Archaeological Society is a local history and archaeological society for Hampshire, England. It was founded in 1885 by Thomas W. Shore. It publishes a newsletter, monographs and other longer publications, and a journal Hampshire Studies: Proceedings of the Hampshire Field Club and Archaeological Society. The society has published the second series of Hampshire Papers since 2015, following on from the first series which was published by the Hampshire Record Office between 1991 and 2010.
References
- ↑ "Shire – Author Profile – David E. Johnston". shirebooks.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ↑ "Show Person 2995". biab.ac.uk. Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ↑ Johnston, D.E. (2004). Roman Villas. Shire Publications, Limited. ISBN 9780747806004 . Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ↑ Johnston, D.E. (2002). Discovering Roman Britain. Shire. ISBN 9780747804529 . Retrieved 14 January 2014.
- ↑ Johnston, D.E. (1979). An illustrated history of Roman roads in Britain. Spurbooks. ISBN 978-0-904978-33-9 . Retrieved 14 January 2014.