
Howland Island is an uninhabited coral island located just north of the equator in the central Pacific Ocean, about 1,700 nautical miles (3,100 km) southwest of Honolulu. The island lies almost halfway between Hawaii and Australia and is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States. Together with Baker Island it forms part of the Phoenix Islands. For statistical purposes, Howland is grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands. The island has an elongated cucumber-shape on a north–south axis, 1.40 by 0.55 miles, and covers 1 square mile.

Amelia Mary Earhart was an American aviation pioneer and writer. Earhart was the first female aviator to fly solo across the Atlantic Ocean. She set many other records, was one of the first aviators to promote commercial air travel, wrote best-selling books about her flying experiences, and was instrumental in the formation of The Ninety-Nines, an organization for female pilots.

Nikumaroro, previously known as Kemins Island or Gardner Island, is a part of the Phoenix Islands, Kiribati, in the western Pacific Ocean. It is a remote, elongated, triangular coral atoll with profuse vegetation and a large central marine lagoon. Nikumaroro is about 7.5 km (4.7 mi) long by 2.5 km (1.6 mi) wide. The rim has two narrow entrances, both of which are blocked by a wide reef, which is dry at low tide. The ocean beyond the reef is very deep, and the only anchorage is at the island's west end, across the reef from the ruins of a mid-20th-century British colonial village, but this is safe only with the southeast trade winds. Landing has always been difficult and is most often done south of the anchorage. Although occupied at various times during the past, the island is uninhabited today.

Frederick Joseph "Fred" Noonan was an American flight navigator, sea captain and aviation pioneer, who first charted many commercial airline routes across the Pacific Ocean during the 1930s. As the flight navigator for famed aviator Amelia Earhart in their pioneering attempt at circumnavigating the globe, they disappeared somewhere over the central Pacific Ocean on July 2, 1937.
The Lockheed Model 10 Electra is an American twin-engined, all-metal monoplane airliner developed by the Lockheed Aircraft Corporation, which was produced primarily in the 1930s to compete with the Boeing 247 and Douglas DC-2. The type gained considerable fame as one was flown by Amelia Earhart and Fred Noonan on their ill-fated around-the-world expedition in 1937.
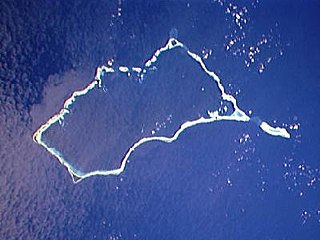
Mili Atoll is a coral atoll of 92 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. It is located approximately 78 kilometers (48 mi) southeast of Arno. Its total land area is 14.9 square kilometers (5.8 sq mi) making it the second largest of the Marshall Islands after Kwajalein.

Johan Adolf Pengel International Airport, also known as Paramaribo-Zanderij International Airport, and locally referred to simply as JAP, is an airport located in the town of Zanderij and hub for airline carrier Surinam Airways, 45 kilometres (28 mi) south of Paramaribo. It is the larger of Suriname's two international airports, the other being Zorg en Hoop with scheduled flights to Guyana, and is operated by Airport Management, Ltd./ NV Luchthavenbeheer.

USCGC Itasca was a Lake-class cutter of the United States Coast Guard launched on 16 November 1929 and commissioned 12 July 1930. It acted as "picket ship" supporting Amelia Earhart's 1937 world flight attempt, and was the last vessel in radio contact with her as she and Fred Noonan were supposed to be reaching Howland island in the Pacific. In 1941, it was transferred to the United Kingdom and served as a convoy escort in World War II as HMS Gorleston.

Mir was a class of two self-propelled deep-submergence vehicles. The project was initially developed by the USSR Academy of Sciences along with Lazurit Central Design Bureau, and two vehicles were ordered from Finland. The Mir-1 and Mir-2, delivered in 1987, were designed and built by the Finnish company Rauma-Repola's Oceanics subsidiary. The project was carried out under the supervision of constructors and engineers of the Shirshov Institute of Oceanology.

INS Dakar was a diesel–electric submarine in the Israeli Navy. The vessel, a modified World War II British T-class submarine, had previously been HMS Totem of the Royal Navy. She was purchased by Israel from the Government of the United Kingdom in 1965 as part of a three T-class submarine deal.
The International Group for Historic Aircraft Recovery (TIGHAR) is an American nonprofit organization based in Pennsylvania. It was founded by Richard Gillespie in 1985. According to TIGHAR's Federal Tax Exemption Form 990 for Non Profits, the organization's mission is to "promote responsible aviation archaeological and historic preservation".

Elgen Marion Long was an American aviator and author who set fifteen aviation records and firsts, including his 1971 flight around the world over both poles. He received the FAI Gold Air Medal for his accomplishment. He developed the "Crash and Sink" theory explaining the disappearance of Amelia Earhart and Fred Noonan. For over 35 years, Long researched the last leg of Earhart and Noonan's flight in an attempt to determine where their Lockheed Electra may have crashed. He and his wife, Marie K. Long documented the people and data involved in the disappearance, a collection that is held by the SeaWord Foundation.

The first USS Swan (AM-34/AVP-7) was a Lapwing-class minesweeper acquired by the United States Navy.

Amelia is a 2009 biographical film about aviatrix Amelia Earhart. The film stars Hilary Swank as Earhart, and co-stars Richard Gere, Ewan McGregor, Christopher Eccleston and Joe Anderson. The film was directed by Mira Nair and based on The Sound of Wings by Mary S. Lovell. The film received predominantly negative reviews, with critics polarized over the performances and criticizing the film's story.

Ann Dearing Holtgren Pellegreno is a professional musician, teacher, author, lecturer, and farmer. In 1967, Pellegreno and a crew of three successfully flew a similar aircraft to complete a world flight that closely mirrored Amelia Earhart's flight plan in 1937. On the 30th anniversary of Earhart's disappearance, Pellegreno dropped a wreath in her honor over tiny Howland Island and returned to Oakland, California, completing the 28,000-mile (45,000 km) commemorative flight on July 7, 1967.

NOAAS Davidson was a survey ship in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) from 1970 to 1989. Prior to her NOAA service, she was in commission in the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey from 1967 to 1970 as USC&GS Davidson, the second Coast and Geodetic Survey ship of the name. She was the only sister ship of NOAAS McArthur (S 330).
Phoenix International Holdings, Inc. (Phoenix) is a marine services company that performs manned and unmanned underwater operations worldwide.

Joan Merriam Smith was an American aviator, famous for her 1964 solo flight around the world, in which she became the second woman to complete the trip, by following the equatorial route attempted in 1937 by Amelia Earhart. In doing so she also became the first woman to fly a twin-engine aircraft around the world, and the first woman to fly the Pacific Ocean from west to east in a twin-engine plane. She died the following year when the plane she was piloting suffered structural failure and crashed in California.

Amelia Earhart: The Lost Evidence is a 2017 documentary broadcast by the US television network History that purported to have new evidence supporting the Japanese capture hypothesis of the disappearance of Amelia Earhart and Fred Noonan. Its main piece of evidence, a photograph purportedly showing the two still alive after their 1937 disappearance, was soon proven to have been published in 1935, and subsequent showings of the documentary were cancelled.

Linda (Dueler) Finch, also known as Linda Finch Doctor, is an American businesswoman, aviator, and aviation historian from San Antonio, Texas. Finch had 30 years of experience in the construction industry, making prefabricated buildings, and operating healthcare facilities. She began her career managing nursing homes in her twenties and owned several nursing homes in her thirties. Finch became a pilot and purchased an airplane that she used in her nursing-home business. She later added construction firms to her portfolio.
















