Related Research Articles

Welsh is a Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales, by some in England, and in Y Wladfa.

The history of what is now Wales begins with evidence of a Neanderthal presence from at least 230,000 years ago, while Homo sapiens arrived by about 31,000 BC. However, continuous habitation by modern humans dates from the period after the end of the last ice age around 9000 BC, and Wales has many remains from the Mesolithic, Neolithic, and Bronze Age. During the Iron Age the region, like all of Britain south of the Firth of Forth, the culture had become Celtic, with a common Brittonic language. The Romans, who began their conquest of Britain in AD 43, first campaigned in what is now northeast Wales in 48 against the Deceangli, and gained total control of the region with their defeat of the Ordovices in 79. The Romans departed from Britain in the 5th century, opening the door for the Anglo-Saxon settlement. Thereafter, the culture began to splinter into a number of kingdoms. The Welsh people formed with English encroachment that effectively separated them from the other surviving Brittonic-speaking peoples in the early middle ages.

Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the southwest and the Bristol Channel to the south. As of the 2021 census, it had a population of 3,107,494. It has a total area of 21,218 km2 (8,192 sq mi) and over 1,680 miles (2,700 km) of coastline. It is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon, its highest summit. The country lies within the north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff.

Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell, was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubarth, and proceeded to gain control over the entire country from Prestatyn to Pembroke. As a descendant of Rhodri Mawr through his father Cadell, Hywel was a member of the Dinefwr branch of the dynasty. He was recorded as King of the Britons in the Annales Cambriæ and the Annals of Ulster.

In Welsh culture, an eisteddfod is an institution and festival with several ranked competitions, including in poetry and music. The term eisteddfod, which is formed from the Welsh morphemes: eistedd, meaning 'sit', and fod, meaning 'be', means, according to Hywel Teifi Edwards, "sitting-together." Edwards further defines the earliest form of the eisteddfod as a competitive meeting between bards and minstrels, in which the winner was chosen by a noble or royal patron.

The Kingdom of Gwynedd was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain.
Davies is a patronymic surname of Welsh origin. There are two main theories concerning its beginnings, neither of which has been definitively proved. The first theory states that it may be a corruption of "Dyfed", the name of a medieval Welsh kingdom located in what is now Carmarthenshire; however, the origin of the kingdom's name is itself disputed, with the traditional belief being that it was founded by the powerful Irish Déisi dynasty in the third century, or otherwise that it derives from the name of the Demetae people. "Dyfed" as a surname and the related first name "Dafydd" appear from the 12th century, with the latter generally translated into English as "David". The second theory contends that the surname may derive directly from the Hebrew name "David", which is also the name of Wales' patron saint.

The Principality of Wales was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the conquest of Wales by Edward I of England of 1277 to 1283, those parts of Wales retained under the direct control of the English crown, principally in the north and west of the country, were re-constituted as a new Principality of Wales and ruled either by the monarch or the monarch's heir though not formally incorporated into the Kingdom of England. This was ultimately accomplished with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542 when the Principality ceased to exist as a separate entity.

Smith is an occupational surname originating in England. It is the most prevalent surname in the United Kingdom, the United States, Australia, Canada, and New Zealand, and the fifth most common surname in the Republic of Ireland. In the United States, the surname Smith is particularly prevalent among those of English, Scottish, and Irish descent, but is also a common surname among African-Americans, which can be attributed either to African slaves having been given the surname of their masters, or to being an occupational name, as some southern African-Americans took this surname to reflect their or their father's trade. 2,442,977 Americans shared the surname Smith at the time of the 2010 census, and more than 500,000 people shared it in the United Kingdom as of 2006. At the turn of the 20th century, the surname was sufficiently prevalent in England to have prompted the statement: "Common to every village in England, north, south, east, and west"; and sufficiently common on the (European) continent to be "common in most countries of Europe".

Llanybydder is a market town and community straddling the River Teifi in Carmarthenshire, West Wales. At the 2011 Census, the population of the community was 1638, an increase from 1423 at the 2001 Census.

The Welsh are an ethnic group native to Wales. "Welsh people" applies to those who were born in Wales and to those who have Welsh ancestry, perceiving themselves or being perceived as sharing a cultural heritage and shared ancestral origins.

Fixed surnames were adopted in Wales from the 15th century onwards. Until then, the Welsh had a patronymic naming system.
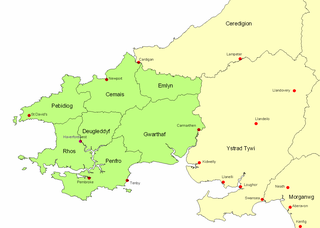
The Kingdom of Dyfed, one of several Welsh petty kingdoms that emerged in 5th-century sub-Roman Britain in southwest Wales, was based on the former territory of the Demetae. The medieval Irish narrative, The Expulsion of the Déisi, attributing the kingdom's founding to Eochaid, son of Artchorp, being forced across the Irish sea, in the 5th century; his descendants founding the line of the kings of Dyfed, down to "Tualodor mac Rígin". The Normans invaded Wales, and by 1138 incorporated Dyfed into a new shire called Pembrokeshire after the Norman castle built in the Cantref of Penfro and under the rule of the Marcher Earl of Pembroke.

David is a common masculine given name. It is of Hebrew origin, and its popularity derives from King David, a figure of central importance in the Hebrew Bible and in the religious traditions of Judaism, Christianity and Islam.

Wales in the early Middle Ages covers the time between the Roman departure from Wales c. 383 until the middle of the 11th century. In that time there was a gradual consolidation of power into increasingly hierarchical kingdoms. The end of the early Middle Ages was the time that the Welsh language transitioned from the Primitive Welsh spoken throughout the era into Old Welsh, and the time when the modern England–Wales border would take its near-final form, a line broadly followed by Offa's Dyke, a late eighth-century earthwork. Successful unification into something recognisable as a Welsh state would come in the next era under the descendants of Merfyn Frych.
Jones is a surname of Welsh and English origin meaning "son of John". The surname is common in Wales. It evolved from variations of traditionally Welsh names: Ieuan, Iowan, Ioan, Iwan, or even Siôn. The sound generated from ‘Si-’ in Siôn is a Welsh approximation of the English ‘J’ sound that does not exist natively to the language, equivalent to the English ‘Sh’ such as in “shed.”

Wales in the High Middle Ages covers the 11th to 13th centuries in Welsh history. Beginning shortly before the Norman invasion of the 1060s and ending with the Conquest of Wales by Edward I between 1278 and 1283, it was a period of significant political, cultural and social change for the country.

Wales in the Middle Ages covers the history of the country that is now called Wales, from the departure of the Romans in the early fifth century to the annexation of Wales into the Kingdom of England in the early sixteenth century. This period of about 1,000 years saw the development of regional Welsh kingdoms, Celtic conflict with the Anglo-Saxons, reducing Celtic territories, and conflict between the Welsh and the Anglo-Normans from the 11th century.

The conquest of Wales by Edward I took place between 1277 and 1283. It is sometimes referred to as the Edwardian Conquest of Wales, to distinguish it from the earlier Norman conquest of Wales. In two campaigns, in 1277 and 1282–83, respectively, Edward I of England first greatly reduced the territory of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, and then completely overran it, as well as the other remaining Welsh principalities.
References
- 1 2 3 "Davis Surname Meaning and Distribution". forebears.co.uk. Retrieved 23 January 2014
- ↑ A dictionary of Irish surnames: with special American instances; Bardsley, Charles Wareing Endell, London. H. Frowde. 1901
- ↑ "Diffusion of surname DAVIS". Surname Map United Kingdom. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ↑ United States Census Bureau (2000). Retrieved 2008-07-04
- ↑ "Last name:Davies". SurnameDB. Retrieved 28 April 2021.