
Fortaleza is the state capital of Ceará, located in Northeastern Brazil. It is Brazil's 4th largest city, having surpassed Salvador in 2022 census with a population of slightly over 2.4 million, and the 12th largest city by gross domestic product. It forms the core of the Fortaleza metropolitan area, which is home to almost 4 million people.

The Juruá River is a southern affluent river of the Amazon River west of the Purus River, sharing with this the bottom of the immense inland Amazon depression, and having all the characteristics of the Purus as regards curvature, sluggishness and general features of the low, half-flooded forest country it traverses.

Bahia is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population and the 5th-largest by area. Bahia's capital is the city of Salvador, on a spit of land separating the Bay of All Saints from the Atlantic. Once a stronghold of supporters of direct rule of Brazil by the Portuguese monarchy, and dominated by agricultural, slaving, and ranching interests, Bahia is now a predominantly working-class industrial and agricultural state. The state is home to 7% of the Brazilian population and produces 4.2% of the country's GDP.

Conceição da Barra is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Espírito Santo. The city is the northernmost coastal city of the state. Its population was 31,273 (2020) and its area is 1,188.044 km².
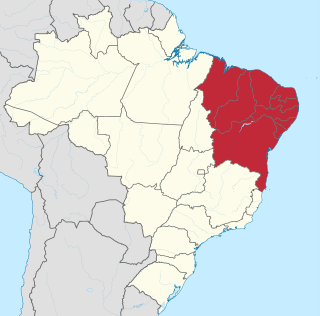
The Northeast Region of Brazil is one of the five official and political regions of the country according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Of Brazil's twenty-six states, it comprises nine: Maranhão, Piauí, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe and Bahia, along with the Fernando de Noronha archipelago.

Empresa Brasileira de Infraestrutura Aeroportuária is a Brazilian government corporation founded in 1973, authorized by Law 5,862, that is responsible for operating the main Brazilian commercial airports. In 2011 Infraero's airports carried 179,482,228 passengers, 1,464,484 tons of cargo, and operated 2,893,631 take-offs and landings. Presently it manages 45 airports.

Salvador–Deputado Luís Eduardo Magalhães International Airport, formerly called Dois de Julho International Airport and known by the trade name Salvador Bahia Airport, is the airport serving Salvador, Brazil. Since 16 June 1998, by Federal Law, the airport is named after Luís Eduardo Maron Magalhães (1955–1998), an influential politician of the state of Bahia.
Nordeste Linhas Aéreas Regionais S/A was a regional airline based in Brotas, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil which operated scheduled passenger services in northeast and southeast Brazil. Its main base was Deputado Luís Eduardo Magalhães International Airport.

The Vaza-Barris River is a river in northeastern Brazil. The Vaza-Barris originates in northeastern Bahia state, and flows east through Bahia and Sergipe states to empty into the Atlantic Ocean near São Cristóvão.

Brumado is a Brazilian municipality in the interior of Bahia, in the Northeast region of the country, precisely in the Center-South mesoregion of the State, in the homonymous microregion to the do municipality name, to the do 555 kilometers from Salvador, state capital. Its territorial area is 2 207,612 square kilometers, the headquarters's area occupying 2 174 square kilometers, have altitude of 454 meters. According to data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), in 2023 its population was estimated at 70 268 inhabitants. The Human Development Index (HDI) is 0.656 (average).

The Jutaí River is a river in Amazonas state in north-western Brazil.

The Tapauá River is a river of Amazonas state in north-western Brazil. It is a left tributary of the Purus River.
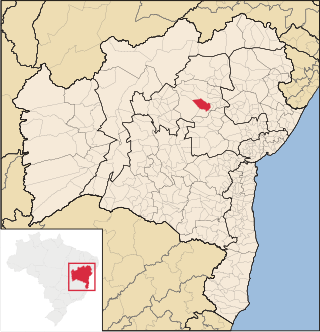
Miguel Calmon is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil.

Jeremoabo is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil.
In Brazilian football, G-12 refers to a group of 12 clubs: Atlético Mineiro, Botafogo, Corinthians, Cruzeiro, Flamengo, Fluminense, Grêmio, Internacional, Palmeiras, Santos, São Paulo, and Vasco da Gama. They are considered the most popular and successful sides in Brazilian football, having won all but six editions of the Brasileirão between them since the tournament's inception.

The Tocantins basin, or Araguaia-Tocantins basin, is a Brazilian river basin, almost entirely located between the 2ºS and 18ºS parallels and the 46ºW and 56ºW meridians. The main rivers in the basin are Tocantins and Araguaia.
Álvaro Coutinho Aguirre was a Brazilian agronomist, zoologist and naturalist. Aguirre created the first reserve park for wild animals in Brazil, the Sooretama Biological Reserve at the state of Espírito Santo (the first protected area created in Brazil was in 1937. He dedicated his life to the preservation of the Brazilian flora and fauna, especially the Atlantic Forest and the biggest primate of the Americas, the Muriqui. During the 1960s, he undertook many expeditions to study the life and habits of the Muriqui and its conditions at the time. The results showed a considerable reduction of the groups of the animals, due to deforestation and lack of preservation of their habitat.

The Jaguaripe River is a river located in Bahia, Brazil. It is administered by the state of Bahia under Region of Planning and Water Management IX, the Recôncavo Sul. The river derives its name from the Tupi language term îagûarype, meaning "in the river of jaguars". The river extends 107 kilometres (66 mi) from the municipality Castro Alves and empties into the Bay of All Saints. It is one of three large rivers that flow into the bay, the others being the Paraguaçu and the Subaé. The Rio da Dona flows parallel to the Jaguaripe, and joins its near the mouth of the bay.

The Doce River Basin is located in the southeastern region of Brazil. According to the Doce River Basin Committee (CBH-Doce), it belongs to the Southeast Atlantic hydrographic region, has a drainage area of 86,175 square kilometers and covers all or part of 229 municipalities. 86% of the basin's area belongs to the state of Minas Gerais, in the Doce River Valley, and 14% to Espírito Santo.

















