
A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word spaceport, and even more so cosmodrome, has traditionally been used for sites capable of launching spacecraft into orbit around Earth or on interplanetary trajectories. However, rocket launch sites for purely sub-orbital flights are sometimes called spaceports, as in recent years new and proposed sites for suborbital human flights have been frequently referred to or named "spaceports". Space stations and proposed future bases on the Moon are sometimes called spaceports, in particular if intended as a base for further journeys.

A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 1,000 and 1,500 km, such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. For certain purposes Sounding Rockets may be flown to altitudes as high as 3,000 kilometers to allow observing times of around 40 minutes to provide geophysical observations of the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere and mesosphere. Sounding rockets have been used for the examination of atmospheric nuclear tests by revealing the passage of the shock wave through the atmosphere. In more recent times Sounding Rockets have been used for other nuclear weapons research. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion, lifting 270–450-kg (600–1,000-pound) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 97 and 201 km.
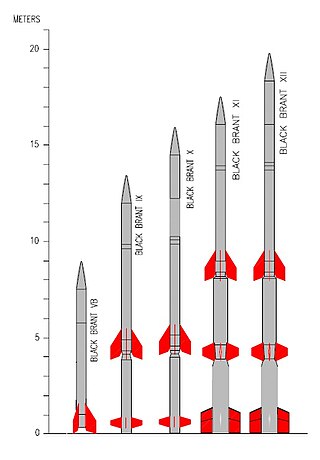
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.
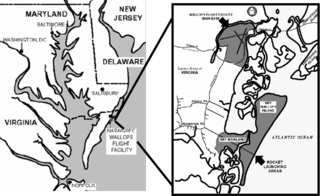
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.

The Rockair was first suggested by Hermann Oberth in his 1929 book Wege zur Raumschiffahrt. Rockair concepts were developed by both the United States Air Force and Navy, both generally finding marginal use in the concept. The Air Force began studying the concept of an air-launched sounding rocket in 1947, while the Navy managed to get the first launch on August 16, 1955, using an F2H2 off of Wallops Island. The folded-fin aerial rocket(FFAR) reached an altitude of 54,864 m (180,000 ft). The Air Force followed up with their first air-launched sounding rocket concept on December 13, 1956, under the name "Rockaire". A Deacon rocket was used, launched from a F-86 fighter aircraft.

A rockoon is a sounding rocket that, rather than being lit immediately while still on the ground, is first carried into the upper atmosphere by a gas-filled balloon, then separated from the balloon and ignited. This allows the rocket to achieve a higher altitude, as the rocket does not have to move under power through the lower and thicker layers of the atmosphere. A 2016 study by Acta Astronautica concluded that low-mass and high altitude launches give the best results.
Astrobee is the designation of series of American sounding rockets with one to three stages.

The Naval Aviation Ordnance Test Station (NAOTS) was a United States Navy base located at 37°55′N75°22′W, near Chincoteague, VA, that was used as a suborbital launch site. In 1955, research rockets of the Rockair type were launched from F2H-2 planes based there. An altitude of 54,864 m was reached with a 70mm (2.75-in.) folded-fin aerial rocket (FFAR) of Korean vintage. In spite of successful tests, the rockair concept never achieved the popularity of the rockoon. Apparently no important scientific rocket research was carried out with rockaires, in contrast to the hundreds of rockoons fired during the 1950s.
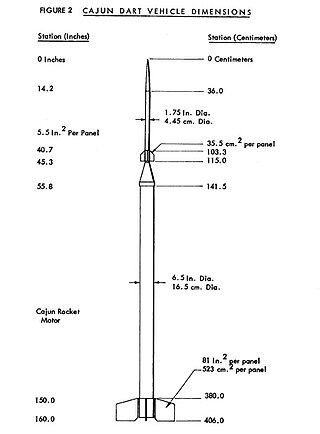
Cajun Dart is the designation of an American sounding rocket. The Cajun Dart was used 87 times between 1964 and 1970. The Cajun rocket motor was developed from Deacon.

Arcas was the designation of an American sounding rocket, developed by the Atlantic Research Corp., Alexandria, Va.

ASP, (Atmospheric Sounding Projectile is the designation of an American sounding rocket family. ASP-I was used to sample nuclear explosions and resultant clouds The ASP was the fastest single stage sounding rocket when developed. The Asp was manufactured by Cooper Development Corporation, California. The solid propellant motor was made by Grand Central Rocket company.
The Mesquito is an American sounding rocket vehicle developed for the NASA Sounding Rocket Program on Wallops Island, Virginia. The Mesquito was developed to provide rocket-borne measurements of the mesospheric region of the upper atmosphere. An area of great science interest is in the 82–95 km region, where the conventional understanding of atmospherics physics is being challenged.

In 1955, both the United States and the Soviet Union (USSR) announced plans for launching the world's first satellites during the International Geophysical Year (IGY) of 1957–58. Project Vanguard, proposed by the US Navy, won out over the US Army's Project Orbiter as the satellite and rocket design to be flown in the IGY. Development of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles, the Atlas by the US and the R-7 by the USSR, accelerated, entering the design and construction phase.

The year 1954 saw the conception of Project Orbiter, the first practicable satellite launching project, utilizing the Redstone, a newly developed Short Range Ballistic Missile.

The year 1953 saw the rockoon join the stable of sounding rockets capable of reaching beyond the 100 kilometres (62 mi) boundary of space. Employed by both the University of Iowa and the Naval Research Laboratory, 22 total were launched from the decks of the USS Staten Island and the USCGC Eastwind this year. All branches of the United States military continued their program of Aerobee sounding rocket launches, a total of 23 were launched throughout 1953. The Soviet Union launched no sounding rockets in 1953; however, the Soviet Union did conduct several series of missile test launches.

The Terrier Orion sounding rocket is a combination of the Terrier booster rocket with the Orion rocket used as a second stage. This spin stabilized configuration is most often used by the Goddard Space Flight Center, who operate out of the Wallops Flight Facility for sounding rocket operations. The system supports payloads ranging from 200 to 800 pounds, and is capable of achieving altitudes as high as 120 miles (200 km), but at least 50 miles (80 km), depending on payload size.

Launch Area 3 (LA-3) at the Wallops Flight Facility is a launch complex which was used, mostly by Scout rockets, between 1960 and 1985. Forty-one Scout launches occurred from the complex, making both orbital and suborbital. In addition, four Nike sounding rockets were launched from the complex in 1970.

Rohini is a series of sounding rockets developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for meteorological and atmospheric study. These sounding rockets are capable of carrying payloads of 2 to 200 kilograms between altitudes of 100 to 500 kilometres. The ISRO currently uses RH-200, RH-300,Mk-II, RH-560 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III rockets, which are launched from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Thumba and the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
The Star is a family of US solid-propellant rocket motors originally developed by Thiokol and used by many space propulsion and launch vehicle stages. They are used almost exclusively as an upper stage, often as an apogee kick motor. The number designations refer to the approximate diameter of the fuel casing in inches.
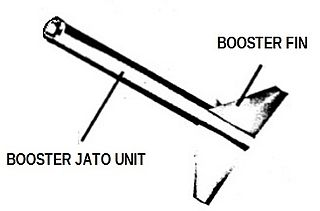
The Nike stage or Nike booster, a solid fuel rocket motor, was developed by Hercules Aerospace for use as the first stage of the Nike Ajax and Nike Hercules missiles as part of Project Nike.















