
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics which deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. For example, using interest rates, taxes, and government spending to regulate an economy's growth and stability. This includes regional, national, and global economies. According to a 2018 assessment by economists Emi Nakamura and Jón Steinsson, economic "evidence regarding the consequences of different macroeconomic policies is still highly imperfect and open to serious criticism."

In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. As prices faced by households do not all increase at the same rate, the consumer price index (CPI) is often used for this purpose. The employment cost index is also used for wages in the United States.

In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0%. Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from disinflation, a slow-down in the inflation rate, i.e. when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive.
Verify or verification may refer to:
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:

The causes of the Great Depression in the early 20th century in the United States have been extensively discussed by economists and remain a matter of active debate. They are part of the larger debate about economic crises and recessions. The specific economic events that took place during the Great Depression are well established.
In philosophy and logic, a deflationary theory of truth is one of a family of theories that all have in common the claim that assertions of predicate truth of a statement do not attribute a property called "truth" to such a statement.
A semantic theory of truth is a theory of truth in the philosophy of language which holds that truth is a property of sentences.

Disinflation is a decrease in the rate of inflation – a slowdown in the rate of increase of the general price level of goods and services in a nation's gross domestic product over time. It is the opposite of reflation.
According to the redundancy theory of truth, asserting that a statement is true is completely equivalent to asserting the statement itself. For example, asserting the sentence "'Snow is white' is true" is equivalent to asserting the sentence "Snow is white". The philosophical redundancy theory of truth is a deflationary theory of truth.
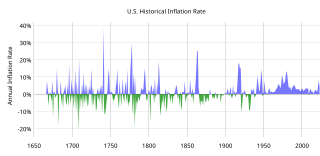
The Great Deflation or the Great Sag refers to the period from 1870 until 1890 in which the world prices of goods, materials and labor decreased, although at a low rate of less than 2% annually. This was one of the few sustained periods of deflationary growth in the history of the United States. This had a positive effect on the economy in general, as the purchasing power improved.
In macroeconomics, inflation targeting is a monetary policy where a central bank follows an explicit target for the inflation rate for the medium-term and announces this inflation target to the public. The assumption is that the best that monetary policy can do to support long-term growth of the economy is to maintain price stability, and price stability is achieved by controlling inflation. The central bank uses interest rates as its main short-term monetary instrument.
The Grand Supercycle is the longest period, or wave, in the growth of a financial market as described by the Elliott wave principle, originally conceived and formulated by Ralph Nelson Elliott. Elliott speculated that a Grand Supercycle advance had started in the United States stock market in 1857 and ran to the year 1928, but acknowledged another interpretation that it may have been the third or even the fifth Grand Supercycle wave. However, these assignments have been reevaluated and clarified using larger historical financial data sets in the works of A. J. Frost and R.R. Prechter, and the start is now considered to be 1789, when stock market data began to be recorded.
Biflation is a state of the economy, in which the processes of inflation and deflation occur simultaneously in different parts of the economy. The term was first coined in 2003 by Dr. F. Osborne Brown, a senior financial analyst at Phoenix Investment Group, and has later been widely used in the media. During the biflation, there is a simultaneous rise in prices (inflation) for commodities bought out of the basic income (earnings), and a parallel fall in prices (deflation) for goods bought mainly on credit. Biflation may be seen in the CPI composition: some CPI components are in the inflationary territory, while others are facing deflationary pressure. As such, biflation reflects the complexity of the modern financial system.
Inflation most commonly refers to a rise in the general price level over a period of time.
Debt deflation is a theory that recessions and depressions are due to the overall level of debt rising in real value because of deflation, causing people to default on their consumer loans and mortgages. Bank assets fall because of the defaults and because the value of their collateral falls, leading to a surge in bank insolvencies, a reduction in lending and by extension, a reduction in spending.
The Bernanke doctrine refers to measures, identified by Ben Bernanke while Chairman of the Board of Governors of the United States Federal Reserve, that the Federal Reserve can use in conducting monetary policy to combat deflation.
Inflationism is a heterodox economic, fiscal, or monetary policy, that predicts that a substantial level of inflation is harmless, desirable or even advantageous. Similarly, inflationist economists advocate for an inflationist policy.
Paper wealth means wealth as measured by monetary value, as reflected in price of assets – how much money one's assets could be sold for. Paper wealth is contrasted with real wealth, which refers to one's actual physical assets.



