| Look up demand in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Demand is the desire to own something and the ability to pay for it.
Contents
Demand may also refer to:
| Look up demand in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Demand is the desire to own something and the ability to pay for it.
Demand may also refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Demand. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Economics is the social science that studies how people interact with scarce resources, in particular the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.

Keynesian economics are various macroeconomic theories about how, in the short run – and especially during recessions – economic output is strongly influenced by aggregate demand. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy; instead, it is influenced by a host of factors and sometimes behaves erratically, affecting production, employment, and inflation.

Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms.
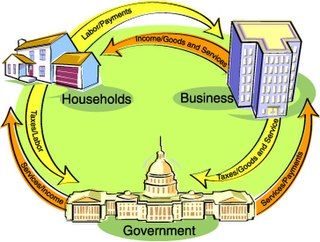
Macroeconomics means using interest rates, taxes and government spending to regulate an economy’s growth and stability. It is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as GDP, unemployment rates, national income, price indices, output, consumption, unemployment, inflation, saving, investment, energy, international trade, and international finance.
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics focusing on the determination of goods, outputs, and income distributions in markets through supply and demand. This determination is often mediated through a hypothesized maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production, in accordance with rational choice theory, a theory that has come under considerable question in recent years.

In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded will equal the quantity supplied, resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.

Alfred Marshall was a British economist, who was one of the most influential economists of his time. His book, Principles of Economics (1890), was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years. It brings the ideas of supply and demand, marginal utility, and costs of production into a coherent whole. He is known as one of the founders of neoclassical economics. Although Marshall took economics to a more mathematically rigorous level, he did not want mathematics to overshadow economics and thus make economics irrelevant to the layman.

Post-Keynesian economics is a school of economic thought with its origins in The General Theory of John Maynard Keynes, with subsequent development influenced to a large degree by Michał Kalecki, Joan Robinson, Nicholas Kaldor, Sidney Weintraub, Paul Davidson, Piero Sraffa and Jan Kregel. Historian Robert Skidelsky argues that the post-Keynesian school has remained closest to the spirit of Keynes' original work. It is a heterodox approach to economics.
This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:

Sir John Hicks was a British economist. He is considered one of the most important and influential economists of the twentieth century. The most familiar of his many contributions in the field of economics were his statement of consumer demand theory in microeconomics, and the IS–LM model (1937), which summarised a Keynesian view of macroeconomics. His book Value and Capital (1939) significantly extended general-equilibrium and value theory. The compensated demand function is named the Hicksian demand function in memory of him.
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. The reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of water, for example, owes to the greater additional satisfaction of the diamonds over the water. Thus, while the water has greater total utility, the diamond has greater marginal utility.

An academic discipline or field of study is a branch of knowledge, taught and researched as part of higher education. A scholar's discipline is commonly defined by the university faculties and learned societies to which they belong and the academic journals in which they publish research.

The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money of 1936 is the last and most important book by the English economist John Maynard Keynes. It created a profound shift in economic thought, giving macroeconomics a central place in economic theory and contributing much of its terminology – the "Keynesian Revolution". It had equally powerful consequences in economic policy, being interpreted as providing theoretical support for government spending in general, and for budgetary deficits, monetary intervention and counter-cyclical policies in particular. It is pervaded with an air of mistrust for the rationality of free-market decision making.
Managerial Economics deals with the application of the economic concepts, theories, tools, and methodologies to solve practical problems in a business. In other words, managerial economics is the combination of economics theory and managerial theory. It helps the manager in decision-making and acts as a link between practice and theory. It is sometimes referred to as business economics and is a branch of economics that applies microeconomic analysis to decision methods of businesses or other management units.

Consumption, defined as spending for acquisition of utility, is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of future income.

In economics, goods are items that satisfy human wants and provide utility, for example, to a consumer making a purchase of a satisfying product. A common distinction is made between goods which are transferable, and services, which are not transferable.

In macroeconomic theory, liquidity preference is the demand for money, considered as liquidity. The concept was first developed by John Maynard Keynes in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936) to explain determination of the interest rate by the supply and demand for money. The demand for money as an asset was theorized to depend on the interest foregone by not holding bonds. Interest rates, he argues, cannot be a reward for saving as such because, if a person hoards his savings in cash, keeping it under his mattress say, he will receive no interest, although he has nevertheless refrained from consuming all his current income. Instead of a reward for saving, interest, in the Keynesian analysis, is a reward for parting with liquidity. According to Keynes, money is the most liquid asset. Liquidity is an attribute to an asset. The more quickly an asset is converted into money the more liquid it is said to be.
The Technische Universität Ilmenau is a German public research university located in Ilmenau, Thuringia, Germany. Founded in 1894, it has five academic departments (faculties) with about 7,200 students.
The neoclassical synthesis, or the neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis, was a post-World War II academic movement in economics that worked towards absorbing the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard Keynes into neoclassical economics. The resultant macroeconomic theories and models are termed neo-Keynesian economics. Mainstream economics was largely dominated by the synthesis until the 1970s, being largely Keynesian in macroeconomics and neoclassical in microeconomics.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to economics: