Related Research Articles

Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft.
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis.
Allotransplant is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, or homograft. Most human tissue and organ transplants are allografts.
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Professor Marshall Urist and Professor Hari Reddi discovered their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now considered to constitute a group of pivotal morphogenetic signals, orchestrating tissue architecture throughout the body. The important functioning of BMP signals in physiology is emphasized by the multitude of roles for dysregulated BMP signalling in pathological processes. Cancerous disease often involves misregulation of the BMP signalling system. Absence of BMP signalling is, for instance, an important factor in the progression of colon cancer, and conversely, overactivation of BMP signalling following reflux-induced esophagitis provokes Barrett's esophagus and is thus instrumental in the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma.

Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee, or preserved before reconstruction through an arthroscopic procedure. ACL repair is also a surgical option. This involves repairing the ACL by re-attaching it, instead of performing a reconstruction. Theoretical advantages of repair include faster recovery and a lack of donor site morbidity, but randomised controlled trials and long-term data regarding re-rupture rates using contemporary surgical techniques are lacking.
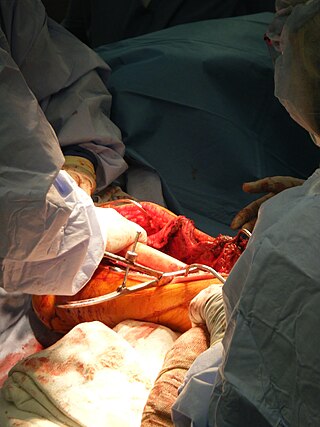
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured without bone grafting, but the risk is greater for large fractures like compound fractures.

Arthrodesis, also known as artificial ankylosis or syndesis, is the artificial induction of joint ossification between two bones by surgery. This is done to relieve intractable pain in a joint which cannot be managed by pain medication, splints, or other normally indicated treatments. The typical causes of such pain are fractures which disrupt the joint, severe sprains, and arthritis. It is most commonly performed on joints in the spine, hand, ankle, and foot. Historically, knee and hip arthrodeses were also performed as pain-relieving procedures, but with the great successes achieved in hip and knee arthroplasty, arthrodesis of these large joints has fallen out of favour as a primary procedure, and now is only used as a procedure of last resort in some failed arthroplasties.

Nonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false joint" or pseudoarthrosis. The diagnosis is generally made when there is no healing between two sets of medical imaging, such as X-ray or CT scan. This is generally after 6–8 months.
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person.

Nanofibers are fibers with diameters in the nanometer range. Nanofibers can be generated from different polymers and hence have different physical properties and application potentials. Examples of natural polymers include collagen, cellulose, silk fibroin, keratin, gelatin and polysaccharides such as chitosan and alginate. Examples of synthetic polymers include poly(lactic acid) (PLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), polyurethane (PU), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV), and poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate) (PEVA). Polymer chains are connected via covalent bonds. The diameters of nanofibers depend on the type of polymer used and the method of production. All polymer nanofibers are unique for their large surface area-to-volume ratio, high porosity, appreciable mechanical strength, and flexibility in functionalization compared to their microfiber counterparts.
Guided bone regeneration (GBR) and guided tissue regeneration (GTR) are dental surgical procedures that use barrier membranes to direct the growth of new bone and gingival tissue at sites with insufficient volumes or dimensions of bone or gingiva for proper function, esthetics or prosthetic restoration. Guided bone regeneration typically refers to ridge augmentation or bone regenerative procedures; guided tissue regeneration typically refers to regeneration of periodontal attachment.
Articular cartilage repair treatment involves the repair of the surface of the articular joint's hyaline cartilage, though these solutions do not perfectly restore the articular cartilage. These treatments have been shown to have positive results for patients who have articular cartilage damage. They can provide some measure of pain relief, while slowing down the accumulation of damage, or delaying the need for joint replacement surgery.
Nano-scaffolding or nanoscaffolding is a medical process used to regrow tissue and bone, including limbs and organs. The nano-scaffold is a three-dimensional structure composed of polymer fibers very small that are scaled from a Nanometer scale. Developed by the American military, the medical technology uses a microscopic apparatus made of fine polymer fibers called a scaffold. Damaged cells grip to the scaffold and begin to rebuild missing bone and tissue through tiny holes in the scaffold. As tissue grows, the scaffold is absorbed into the body and disappears completely.
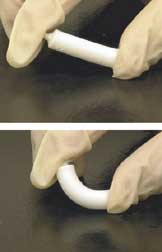
Artificial bone refers to bone-like material created in a laboratory that can be used in bone grafts, to replace human bone that was lost due to severe fractures, disease, etc.
Acellular dermis is a type of biomaterial derived from processing human or animal tissues to remove cells and retain portions of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These materials are typically cell-free, distinguishing them from classical allografts and xenografts, can be integrated or incorporated into the body, and have been FDA approved for human use for more than 10 years in a wide range of clinical indications.
Osteopromotive describes a material that promotes the de novo formation of bone.
Nerve allotransplantation is the transplantation of a nerve to a receiver from a donor of the same species. For example, nerve tissue is transplanted from one person to another. Allotransplantation is a commonly used type of transplantation of which nerve repair is one specific aspect.
Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) or leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) is a derivative of PRP where autologous platelets and leukocytes are present in a complex fibrin matrix to accelerate the healing of soft and hard tissue and is used as a tissue-engineering scaffold in oral and maxillofacial surgeries. PRF falls under FDA Product Code KST, labeling it as a blood draw/Hematology product classifying it as 510(k) exempt.

Gingival grafting, also called gum grafting or periodontal plastic surgery, is a generic term for the performance of any of a number of periodontal surgical procedures in which the gum tissue is grafted. The aim may be to cover exposed root surfaces or merely to augment the band of keratinized tissue.
Tissue transplantation is a surgical procedure involving the removal of tissue from a donor site or the creation of new tissue, followed by tissue transfer to the recipient site. The aim of tissue transplantation is to repair or replace tissues that are missing, damaged, or diseased, thereby improving patients' survival, functionality and quality of life.
References
- ↑ Urist, Marshall R. (1965). "Bone: formation by autoinduction". Science 12:150 (698): 893–899. doi : 10.1126/science.150.3698.893. PMID 5319761.
- ↑ Graham, S.M., et al., Biological therapy of bone defects: the immunology of bone allo-transplantation. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 2010. 10(6): p. 885-901.
- ↑ Glowacki, J., S. Zhou, and S. Mizuno, Mechanisms of osteoinduction/chondroinduction by demineralized bone. J Craniofac Surg, 2009. 20 Suppl 1: p. 634-8.