
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, formerly the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1969, consisting of 57 member states, with 48 being Muslim-majority countries. The organisation states that it is "the collective voice of the Muslim world" and works to "safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony".

Jeddah, alternatively transliterated language as Jidda or Jodda, is a port city in Makkah Province, Saudi Arabia, located along the Red Sea coast in the Hejaz region. Jeddah is the commercial center of the country. It is not known when Jeddah was founded, but Jeddah's prominence grew in 647 when the Caliph Uthman made it a travel hub serving Muslim travelers going to the holy city of Mecca for Islamic pilgrimage. Since those times, Jeddah has served as the gateway for millions of pilgrims who have arrived in Saudi Arabia, traditionally by sea and recently by air.
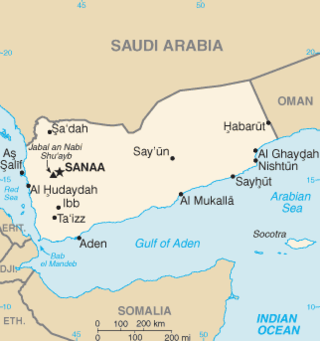
The Saudi–Yemen barrier is a physical barrier constructed by Saudi Arabia along part of its 1,800-kilometer (1,100 mi) border with Yemen. It is a structure made of pipeline three metres (10 ft) high filled with concrete, acting as a "security barrier along sections of the now fully demarcated border with Yemen" and fitted with electronic detection equipment.

Human rights in Saudi Arabia are a topic of concern and controversy. The Saudi government, which mandates both Muslim and non-Muslim observance of Islamic law under the absolute rule of the House of Saud, has been accused of and denounced by various international organizations and governments for violating human rights within the country. The authoritarian regime ruling the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is consistently ranked among the "worst of the worst" in Freedom House's annual survey of political and civil rights.

Elections in Saudi Arabia are rare. Municipal elections were last held in 2015, the first time women had the right to vote and stand as candidates.
Capital punishment exists in Saudi Arabia, with most executions in the country being carried out by decapitation (beheading) – Saudi Arabia being the only country in the world to still use the method. In 2022, recorded executions in Saudi Arabia reached 196, the highest number recorded in the country in 30 years.

Women's rights in Saudi Arabia are a topic of concern and controversy internationally. Saudi women have experienced major legal rights reforms since 2017, after facing Wahhabism religious fundamentalist dominance for decades.

Russia–Saudi Arabia relations are the bilateral relations between Russian Federation and Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The two countries are referred to as the two petroleum superpowers and account for about a quarter of the world's crude oil production between them.

The protests in Saudi Arabia were part of the Arab Spring that started with the 2011 Tunisian revolution. Protests started with a self-immolation in Samtah and Jeddah street protests in late January 2011. Protests against anti-Shia discrimination followed in February and early March in Qatif, Hofuf, al-Awamiyah, and Riyadh. A Facebook organiser of a planned 11 March "Day of Rage", Faisal Ahmed Abdul-Ahad, was allegedly killed by Saudi security forces on 2 March, with several hundred people protesting in Qatif, Hofuf and al-Amawiyah on the day itself. Khaled al-Johani demonstrated alone in Riyadh, was interviewed by BBC Arabic Television, was detained in ʽUlaysha Prison, and became known online as "the only brave man in Saudi Arabia". Many protests over human rights took place in April 2011 in front of government ministry buildings in Riyadh, Ta'if and Tabuk and in January 2012 in Riyadh. In 2011, Nimr al-Nimr encouraged his supporters in nonviolent resistance.

The following is a timeline of the 2011–2012 Saudi Arabian protests from January to April 2011. The 2011–2012 Saudi Arabian protests are a series of ongoing protests taking place in Saudi Arabia, which began in January 2011, influenced by concurrent protests in the region.

Samar bint Muhammad Badawi is a Saudi Arabian human rights activist. She and her father filed court cases against each other. Badawi's father accused her of disobedience under the Saudi Arabian male guardianship system and she charged her father with adhl—"making it hard or impossible for a person, especially a woman, to have what she wants, or what's rightfully hers; e.g, her right to marry" according to Islamic jurisprudence—for refusing to allow her to marry. After Badawi missed several trial dates relating to the charge, an arrest warrant was issued for her, and Badawi was imprisoned on 4 April 2010. In July 2010, Jeddah General Court ruled in Samar Badawi's favor, and she was released on 25 October 2010, and her guardianship was transferred to an uncle. There had been a local and international support campaign for her release. The Saudi NGO Human Rights First Society described Badawi's imprisonment as "outrageous illegal detention".

Saud Mukhtar al-Hashimi is a Saudi Arabian doctor.

Raif bin Muhammad Badawi is a Saudi writer, dissident and activist, as well as the creator of the website Free Saudi Liberals.

Waleed Sami Abulkhair is a Saudi Arabian lawyer and human rights activist, and the head of the Monitor of Human Rights in Saudi Arabia (MHRSA) organization. He is the first activist to be prosecuted by the Terrorism Law. He was arrested on 15 April 2014, and was sent to al-Ha'ir Prison while awaiting prosecution. On 6 July 2014, Abulkhair was sentenced to 15 years in prison by the Specialized Criminal Court, and a travel ban for another 15 years, in addition to a fine of 200,000 riyals (US$53,333). On 12 January 2015, the case returned to the Court of Appeals, after which the judge requested increasing the previous sentence, because Abulkhair refused to apologize. Thus, the judgment was tightened to 15-year executed. In response, Abulkhair prayed for God's victory and refused to recognize the legitimacy of the Specialized Criminal Court. Abulkhair is incarcerated in the Dhahban Central Prison in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, a facility used to hold high-profile political prisoners, as well as members of Al Qaeda and the Islamic State.

On 26 March 2015, Saudi Arabia, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, launched an intervention in Yemen following a new joint request from Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after his forces were ousted from Sanaʽa by Houthi insurgents during the Yemeni Civil War. Government forces, Houthi rebels, and other armed groups fought after the draft constitution and power-sharing arrangements collapsed, despite progress made by the UN during the political transition at that time. Violence escalated in mid-2014. Houthis and allied insurgents seized control of Sana'a in September 2014 and thereafter. In response, President Hadi asked Saudi Arabia to intervene against the Iranian-backed Houthis.

War crimes and human rights violations, committed by all warring parties, have been widespread throughout the Yemeni civil war. This includes the two main groups involved in the ongoing conflict: forces loyal to the current Yemeni president, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and Houthis and other forces supporting Ali Abdullah Saleh, the former Yemeni president. Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant have also carried out attacks in Yemen. The Saudi-led coalition, backed by the United States and other nations, has also been accused of violating human rights and breaking international law, especially in regards to airstrikes that repeatedly hit civilian targets.

Saudi Vision 2030 is a government program launched by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia that aims to achieve the goal of increased diversification economically, socially and culturally, in line with the vision of Saudi Crown Prince and Prime Minister Mohammed bin Salman. It was first announced on 25 April 2016 by the Saudi government.
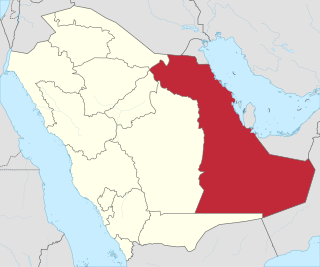
The Qatif conflict is a modern phase of sectarian tensions and violence in Eastern Arabia between Arab Shia Muslims and Arab Sunni majority, which has ruled Saudi Arabia since early 20th century. The conflict encompasses civil unrest which has been sporadically happened since the 1979 uprising, pro-democracy and pro-human rights protests and occasional armed incidents, which increased in 2017 as part of the 2017–20 Qatif unrest.
Dhahban Central Prison, also known as Dhahban Prison, is a maximum security prison facility located near Dahaban, Jeddah, in Saudi Arabia. It was built in 2015 as part of a renovation of the Jeddah Prisons infrastructure, at a cost of SR400 million. It has capacity for 7,500 inmates. When it opened, 3,000 inmates were transferred in from Braiman Prison. In 2015, the regional director for prisons Mani Al-Otaibi said it was the most advanced prison in Saudi Arabia, with state of the art surveillance technologies.

The Saudi Arabian Grand Prix is a Formula One motor racing event which took place for the first time in 2021. The inaugural edition of the race was held in Jeddah, in Saudi Arabia. It was the fifth full-night race title on the Formula One calendar, following the Singapore, Bahrain, Sakhir and Qatar Grands Prix.















